When it comes to modern communication, two terms often come up: VoIP and IP Telephony. While they are related, their key differences are important to understand.
In this comparison, we’ll explore the difference between VoIP and IP Telephony to help you make informed decisions for your organization.
What is VoIP
Voice over Internet Protocol is a technology that allows voice communication and multimedia sessions to occur via the Internet. By converting analog voice signals into digital packets, VoIP allows for the transmission of voice calls, video calls, and other forms of communication using data networks. This technology has gained popularity due to its numerous benefits for businesses.
- Cost Savings: VoIP streamlines communication by integrating voice and data networks, saving your costs on both infrastructure and maintenance.
- Mobility: With VoIP, you can make and receive calls from any location with internet connectivity, promoting flexibility and remote work capabilities.
- Scalability: VoIP systems provide higher scalability, making it simple for your business to add or remove users without the need for substantial hardware upgrades.
- Voice Quality: Modern VoIP services deliver high-definition voice quality that excels beyond traditional telephony, especially in stable internet conditions.
Examples of VoIP
Here are some examples of VoIP applications and services:
1/ RingCentral:
A cloud-based communications platform that offers VoIP services along with features such as video conferencing, team messaging, and online fax.
3/ Nextiva:
Nextiva is a business VoIP provider that enables businesses to manage phone calls, video conferencing, and messaging services through an internet connection, as opposed to traditional telephone lines.
4/ Skype:

Skype utilizes VoIP technology to facilitate real-time communication, allowing your business to connect seamlessly through audio and video channels.
2/ CallHippo:
CallHippo is a cloud-based VoIP service that provides virtual phone numbers, allowing businesses to make and receive calls over the Internet. It offers features such as call forwarding, IVR, call recording, and analytics.
Related Reading: Best CallHippo Alternatives for Businesses
These examples showcase the diverse range of VoIP applications and services available for personal, business, and collaborative communication.
What is IP Telephony
IP Telephony, also known as Internet Protocol Telephony or IP telephoning, refers to the transmission of voice, fax, and other forms of communication over Internet protocols. It utilizes data communications to exchange phone calls, making it an alternative to traditional telephone systems. By using the Internet, IP Telephony enables voice data to be transported in packets via a Local Area Network (LAN) or the Internet itself.
Features of IP telephony
IP Telephony systems offer a range of features that enhance communication capabilities. Some notable features include:
- Superior Voice Quality: High-quality voice transmission, providing clear and precise communication.
- Unified Number for Multiple Devices: A single phone number can be used across multiple devices, ensuring accessibility and convenience.
- Least Call Routing: Automatically selects the most cost-effective route for outgoing calls, reducing expenses.
- Effortless Call Transfer: Seamless transfer of ongoing calls between different devices or networks, providing uninterrupted communication.
- Fixed-Mobile Convergence: Integrates fixed and mobile telephony, allowing users to seamlessly switch between devices and locations.
- Key Protocols in IP Telephony: IP Telephony relies on several protocols such as Session Initiation Protocol (SIP), H.323, Real-Time Transport Protocol (RTP), Real-Time Control Protocol (RTCP), Secure Real-Time Transport Protocol (SRTP), and Session Description Protocol (SDP).
Related Reading: Difference between VoIP and SIP Explained in Detail
Examples of IP telephony
Here are some examples of IP telephony applications and services:
1/ Cisco Unified Communications Manager (CUCM): This is an enterprise-level IP telephony solution by Cisco, offering features like call routing, voice messaging, and video conferencing.
2/ 3CX: 3CX is a software-based PBX (Private Branch Exchange) that supports VoIP calling, video conferencing, and other unified communications features for businesses.
3/ Google Voice: Google Voice offers VoIP calling, voicemail transcription, and other communication features. It allows you to make calls to mobile and landline numbers as well.
Unique Benefits of IP Telephony
IP Telephony brings several benefits to your business. Some of the key advantages include:
- Efficient Cost Management: By consolidating voice and data networks, IP Telephony significantly reduces infrastructure and operational costs. Additionally, it offers more cost-effective solutions for long-distance and global communication, leading to substantial overall savings.
- Mobile Connectivity: IP Telephony facilitates seamless connectivity by allowing users to initiate and accept voice communications from any global location with internet access. This mobility enables remote work capabilities, improving productivity and flexibility.
- Scalable Solutions: IP Telephony systems are highly scalable, allowing your business to easily add or remove users as needed. This scalability is especially advantageous for expanding businesses or those experiencing variations in communication requirements.
- Integrated Collaboration Platform: IP Telephony integrates voice, video, instant messaging, and other communication channels into a unified platform. This integration streamlines collaboration, improves efficiency, and enhances the user experience.
Disadvantages of IP telephony
- Reliability and Call Quality: One of the primary concerns with IP telephony is call quality and reliability. Unlike traditional telephone systems, IP telephony is at risk of network congestion, latency issues, and packet loss, which can result in poor call quality or dropped calls. This can be particularly challenging if your business relies heavily on voice communications.
- Security Risks: IP telephony is not protected from security threats. Just like any other internet-based system, IP telephony can be vulnerable to hacking and unauthorized access. To protect your communication channels, you should enforce strong security measures, including encryption and firewalls.
- Complexity of Implementation: Integrating IP telephony systems may pose challenges, particularly for businesses lacking extensive technical expertise. It requires proper network infrastructure, configuration, and maintenance to ensure optimal performance. The initial setup and ongoing management may require additional resources and technical support.
- Power Dependency: Unlike traditional telephone systems that can operate during power outages, IP telephony is dependent on electricity and network infrastructure. In the event of a power failure, communication services may be disrupted.
- Emergency Services Limitations: IP telephony may present challenges in providing accurate location information to emergency services. Your business needs to have proper protocols and solutions in place to address emergencies effectively.
How does IP telephony work
The key steps in how IP telephony works are as follows:
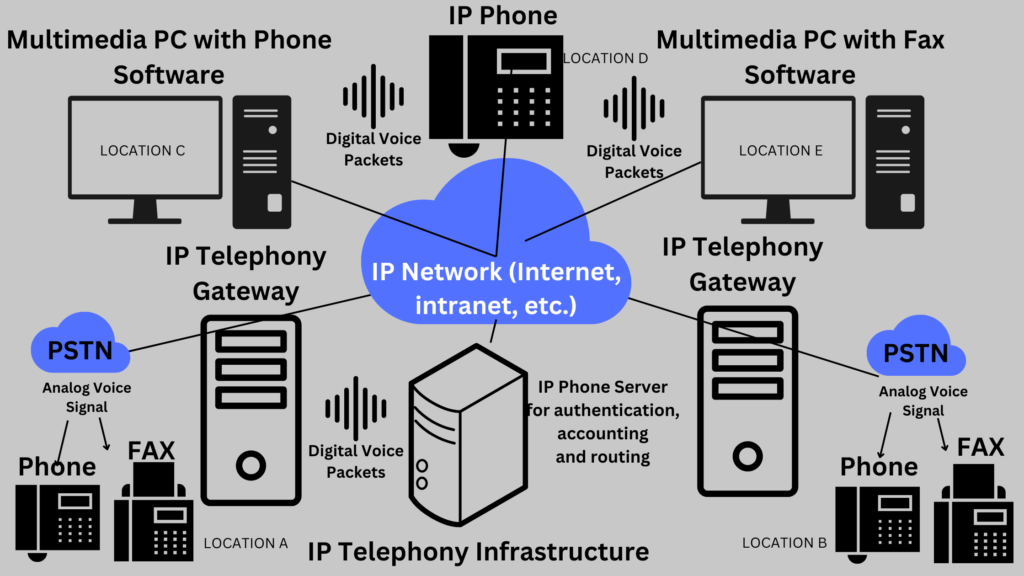
1/ Analog-to-Digital Conversion: When you speak into a VoIP-enabled device, such as an IP phone or a softphone application, your voice is captured and converted into digital data using an analog-to-digital converter.
2/ Packetization: The digital voice data is then broken down into small packets, each containing a portion of the voice signal along with additional information such as source and destination addresses.
3/ Routing: The voice packets are transmitted over the IP network, using the existing internet infrastructure. Routers analyze the destination IP address and forward the packets to their intended recipients.
4/ Packet Delivery: At the receiving end, the voice packets are reconstructed and transformed back into analog signals through a digital-to-analog converter. This process allows the recipient to hear the voice message.
What is VoIP in IP telephony?
To put it simply, Voice over Internet Protocol is a subset of IP telephony that specifically focuses on voice calls delivered via the Internet or a private IP-based network. It is a technology that enables you to make and receive phone calls using IP networks, eliminating the need for traditional telephone lines.
As previously mentioned in relation to VoIP, the conversion of voice traffic into digital data packets enables efficient and cost-effective communication over IP networks.
While IP telephony includes a broader range of services, VoIP stands out as the go-to solution for voice communication over IP networks.
The main difference between VoIP and IP telephony
While both VoIP and IP Telephony involve the transmission of voice and other forms of communication over IP networks, there are several key differences to consider:
1/ Infrastructure Requirements:
VoIP requires an internet connection and a VoIP service provider, whereas IP telephony typically requires an on-premises private branch exchange (PBX) system or a cloud-based PBX.
2/ Quality of Service:
Elements like internet bandwidth and network congestion may influence the quality of VoIP service. On the other hand, IP telephony offers greater control over call quality as it uses dedicated networks.
3/ Scalability and Flexibility:
Both VoIP and IP telephony offer scalability, but VoIP has an advantage in terms of flexibility as calls can be made from any location with an internet connection.
4/ Cost Considerations:
VoIP often offers cost savings on long-distance and international calls, while IP telephony may have higher initial setup costs due to infrastructure requirements.
Decision Factors for Choosing between VoIP and IP Telephony
When selecting between VoIP and IP telephony, consider the following factors:
1/ Business Needs: Evaluate your organization’s communication requirements, considering call volume, collaboration needs, and integration with existing systems.
2/ Cost Analysis: Compare the upfront costs, ongoing expenses, and potential savings associated with each solution. Consider factors such as hardware, maintenance, and call rates.
3/ Implementation Considerations: Assess the feasibility of implementing each solution within your organization. Consider factors such as network infrastructure, bandwidth requirements, and compatibility with existing systems.
What is the difference between VoIP and conventional telephony
VoIP and conventional telephony differ significantly in technology, cost, flexibility, and features. Here are the key differences between them:
1/ Technology: Traditional telephony, often referred to as Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN), operates on copper wires or fiber-optic cables, while VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) uses the Internet to transmit voice data in packets.
2/ Cost: VoIP is generally more cost-effective compared to conventional telephony, especially for long-distance and international calls. This is due to the use of the Internet for call transmission, reducing the need for physical infrastructure and associated costs.
3/ Flexibility and Scalability: VoIP provides greater flexibility and scalability than traditional telephony. It allows you to make and receive calls from any location with an Internet connection, making it ideal for remote work and international operations.
4/ Features: VoIP comes with a variety of advanced features not typically available in traditional telephony, including call forwarding to multiple devices, automatic call rerouting, video conferencing, and integration with other business software.
Use Cases and Examples
Both VoIP and IP Telephony have found extensive adoption across various industries and businesses.
1/ VoIP Use Cases: Many organizations, including call centers, distributed teams, and remote workers, leverage VoIP for its cost savings, mobility, and unified communication capabilities. For example, customer support teams can benefit from features like call routing, call recording, and integration with CRM systems.
2/ IP Telephony Use Cases: Industries that require advanced communication features, such as healthcare, education, and finance, often adopt IP Telephony. For instance, hospitals can utilize IP Telephony for telemedicine services, video conferencing, and secure communication.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1) Is an IP Phone a VoIP Phone?
Ans: Yes, an IP Phone is a VoIP Phone. Both terms refer to phones that use the internet for voice transmission instead of traditional phone lines.
Q2) Is VoIP a landline or cellular?
Ans: VoIP is neither a landline nor a cellular service. It is a technology that allows you to make phone calls using a broadband internet connection instead of a traditional or cellular telephone system.
Q3) What is IP telephony also known as?
Ans: IP telephony is also commonly referred to as Internet telephony, broadband telephony, and broadband phone service.
Q4) Is VoIP a TCP or UDP?
Ans: VoIP can use both Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and User Datagram Protocol (UDP). TCP is connection-oriented, ensuring that all data packets reach their destination in the correct order, but it can be slower. On the other hand, UDP is connectionless and faster, but it doesn’t guarantee packet order or delivery. The decision between TCP and UDP relies on the specific needs and demands of the VoIP service.
Q5) Will VoIP replace traditional telephony?
Ans: The adoption rate of (VoIP) is certainly increasing, as it offers a range of benefits over traditional telephony systems. These benefits include cost-effectiveness, scalability, and advanced features like automatic transcription, video conferencing, voicemail-to-email, and virtual numbers. However, it’s important to note that while VoIP is growing in popularity, it is not likely to completely replace traditional telephony in the future. This is primarily due to certain areas worldwide still needing more stable and high-speed internet connectivity required for VoIP. Additionally, some businesses may prefer the reliability that comes with traditional landlines, especially for critical communications.
Q6) What is the difference between VoIP and Cloud telephony?
Ans: The main difference between VoIP and Cloud telephony is that VoIP is a technology that allows voice calls to be made over an Internet connection rather than a traditional phone line. On the other hand, Cloud telephony, also known as hosted telephony or cloud PBX, is a broader term encompassing all telephony services that are hosted in the cloud, including VoIP. While VoIP focuses primarily on making voice calls over the internet, Cloud Telephony provides a range of services such as call routing, recording, analytics, and integration with other cloud-based applications.

