Advancements in telecommunication technology have transformed the way we connect and collaborate. Two popular technologies that have transformed business communication are VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) and SIP (Session Initiation Protocol).
In this article, we will explore the differences between VoIP and SIP, their functionalities, and how they can benefit your business.
What is VoIP
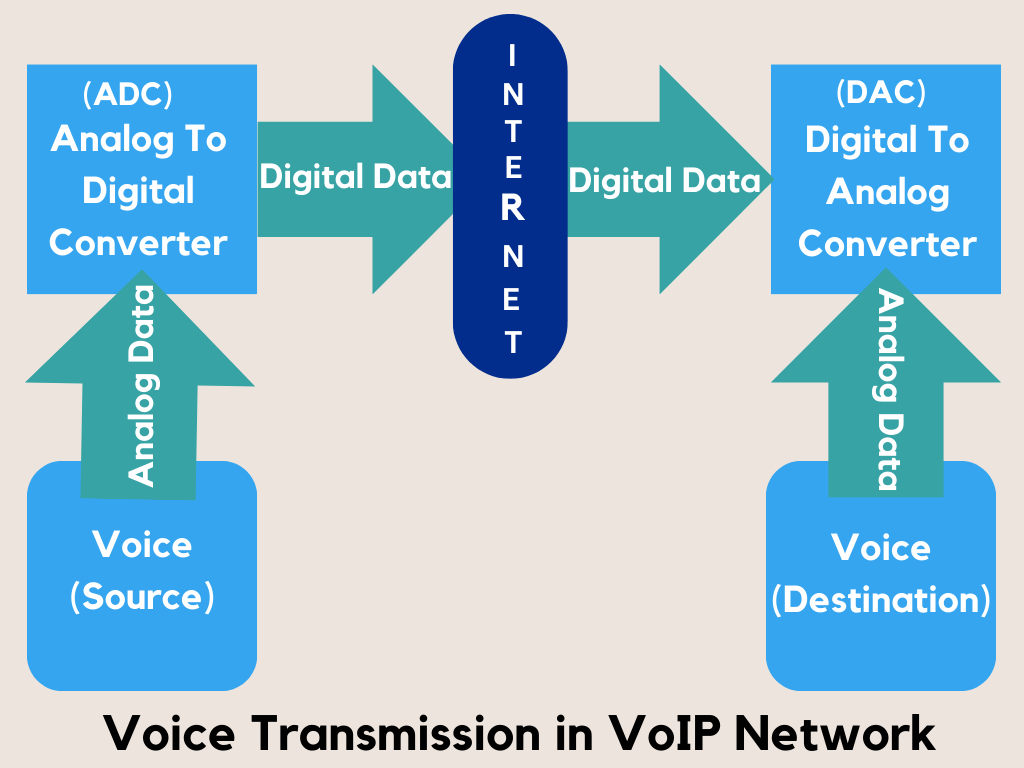
VoIP, short for Voice over Internet Protocol, is a technological advancement that allows voice calls to be made over an Internet connection, eliminating the need for traditional telephone lines.
Whether you’re communicating with a colleague or connecting with someone on the other side of the world, VoIP makes it possible through its internet-based system.
VoIP converts your voice into a digital signal that travels over the internet to its destination. This technology provides the flexibility to make calls from computers, VoIP phones, and other data-driven devices.
Benefits and Challenges of VoIP
VoIP offers several advantages, such as:
- Cost Effectiveness: VoIP services often come at a lower cost compared to traditional phone systems, especially for long-distance and international calls.
- Scalability: VoIP systems can easily accommodate growing businesses and evolving communication needs without significant infrastructure changes.
- Flexibility: VoIP excels in integrating telephony services across multiple platforms. Calls can be made and received on various devices like smartphones and desktop computers, making your communication more flexible and accessible.
- Advanced Features: VoIP systems provide a diverse set of features, such as voicemail, call forwarding, video conferencing, and virtual extensions, enhancing overall communication capabilities.
Challenges that may arise with VoIP implementation:
- Dependence on a stable Internet connection: VoIP calls rely on a consistent and reliable Internet connection. Disruptions or network congestion can impact call quality and lead to dropped calls or poor audio.
- Security concerns: VoIP systems may require additional security measures to protect against potential threats such as hacking or unauthorized access. Without proper security measures, your sensitive information transmitted over VoIP can be at risk.
- Limitations with emergency services: Emergency services like 911 may function differently with VoIP compared to traditional landline services. It is crucial to understand the limitations and ensure proper setup for emergencies to ensure timely and accurate assistance.
Related Reading: What are the benefits and challenges of VoIP
What protocol is needed for VoIP
For Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) to function effectively, it relies on a crucial protocol known as the Real-Time Transport Protocol (RTP).
RTP plays a vital role in the delivery of audio and video data across IP networks, ensuring a reliable and efficient transmission of voice packets
By employing advanced techniques such as packetization, timestamping, and sequence numbering, RTP ensures accurate synchronization and optimal quality of the transmitted media.
With its reliable functionality, RTP serves as the backbone of VoIP communications, facilitating clear and reliable voice conversations over IP networks.
What is SIP & how does it work
SIP, or Session Initiation Protocol, is a signaling protocol that facilitates multimedia communication sessions over the Internet. While VoIP refers to the technology used to transmit voice signals, SIP is responsible for initiating, modifying, and terminating these sessions. SIP sets up and manages communication sessions, including voice and video calls, multimedia conferences, and quick messaging.
SIP operates by initiating multimedia communication sessions. When a SIP user intends to begin a communication session, whether it be a voice or video call, the SIP client sends a SIP INVITE message to the intended recipient.
This message includes details about the session type, the codecs supported by the initiator, and the preferred IP address for media reception.
Upon receiving the INVITE, the recipient responds with a SIP message that either confirms acceptance (200 OK response) or rejects the session. If accepted, the session begins. To conclude the session, the SIP client sends a BYE message to terminate the active session.
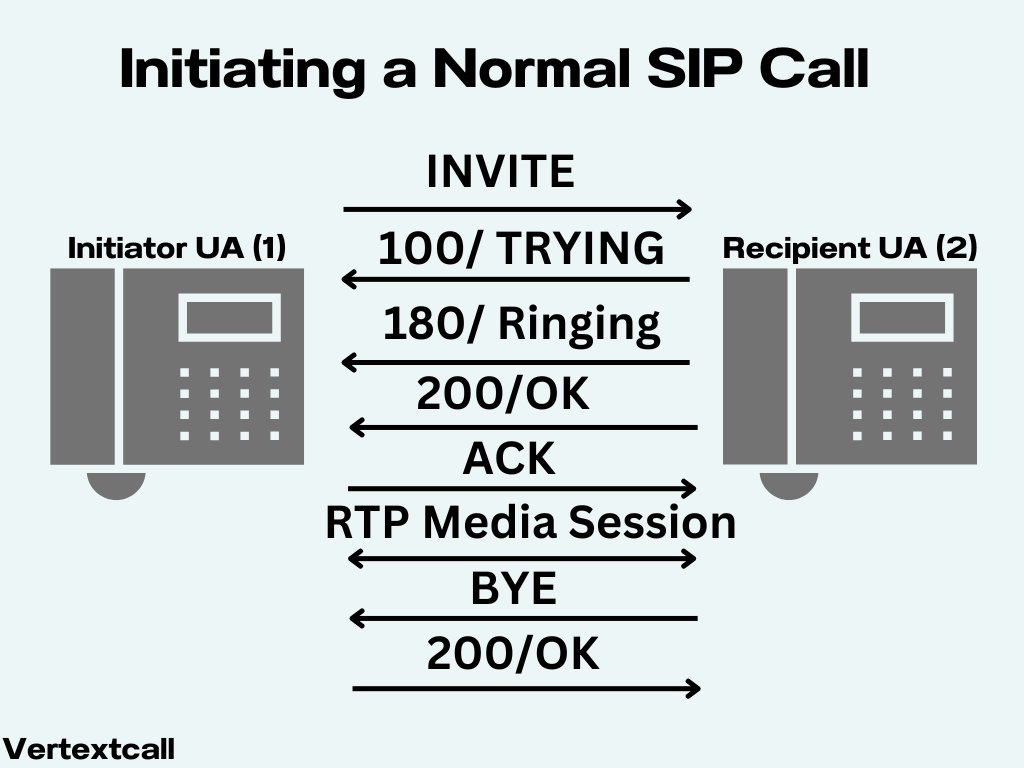
It is important to note that SIP itself does not transfer data; it solely initiates, modifies, and concludes sessions. The actual transfer of data within the session is managed by other protocols, such as RTP for voice and video.
Benefits and Challenges of SIP
Some advantages of SIP over traditional telephony systems include:
- Scalability and Flexibility: SIP allows your business to scale its communication systems easily and integrate with other services, such as email or instant messaging.
- Cost Efficiency: By using existing IP networks, SIP eliminates the need for separate voice networks, reducing infrastructure and operational costs.
- Unified Communications: SIP enables the integration of various communication channels, such as voice, video, and messaging, into a single unified platform, streamlining communication and enhancing productivity.
Challenges that may come with implementing SIP:
- Need for Consistent Bandwidth: Similar to VoIP, the quality of SIP calls is highly dependent on the consistency of your internet connection. Bandwidth fluctuations can lead to poor call quality, including dropped calls and jitter.
- Interoperability Issues: SIP is a protocol that expects interoperability amongst different devices and applications. However, not all devices and applications comply strictly with SIP standards, which may result in compatibility issues.
- Emergency Services: Like VoIP, emergency services may function differently or have limitations when using SIP, making it essential to understand these differences and ensure the appropriate setup.
- Security Vulnerabilities: When SIP sessions travel through the internet, they become open to numerous security risks, such as eavesdropping, session hijacking, and denial of service attacks. Hence, it is critical to implement strong security measures to safeguard SIP-based communication.
Example of SIP calling
An example of SIP calling can be seen in making a VoIP call. When initiating a call, SIP is responsible for sending an invite request to the recipient’s device, which establishes the session between the two parties. Once the call is established, SIP continues to manage the session until either party terminates the call.
What protocol does SIP use?
SIP operates primarily over the protocol known as User Datagram Protocol (UDP), but it is not limited to this alone. It can also function over Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and Transport Layer Security (TLS).
This multi-functionality is one of the key aspects of SIP, enabling it to adapt according to network requirements and conditions, which highlights its extensive use in internet telephony. UDP offers speed and efficiency as it doesn’t require extensive error-checking mechanisms.
However, TCP provides reliability because it uses acknowledgment segments to ensure the delivery of packets. TLS adds a layer of security by encrypting the data being transmitted, thus making SIP a secure protocol for communication.
This ability to operate over multiple protocols according to specific needs ensures SIP’s durability and adaptability in the digital communications space.
To know more about UDP and TCP check out this guide.
Key Differences Between VoIP and SIP
While VoIP and SIP often go hand in hand, it’s important to understand their distinctions. Here are the key differences between the two:
Protocol and Technology
- VoIP enables voice communication to take place using the Internet.
- SIP is a protocol used for initiating, modifying, and terminating multimedia communication sessions.
Call Setup and Management
- VoIP focuses on transmitting voice signals over the internet, using various protocols such as SIP, H.323, or others.
- SIP specifically handles call setup, termination, and signaling, allowing for advanced features like call forwarding, call transfer, and multi-party conferencing.
Scalability and Flexibility
- VoIP provides the foundation for transmitting voice signals over IP networks, offering scalability and flexibility regarding hardware and software choices.
- As a signaling protocol, SIP enables the integration of additional multimedia services and applications, enhancing the scalability and flexibility of communication sessions.
Integration with Other Services
- VoIP can be combined with various protocols and technologies to enable voice communication.
- SIP allows integration with other services beyond voice calls, such as video conferencing, instant messaging, and collaboration tools.
How does VoIP work with SIP?
The VoIP-SIP architecture consists of various components, including VoIP phones or devices, VoIP service providers, and SIP servers or proxies. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of the process:
1/ User Initiation: A VoIP call is initiated by the user by dialing a phone number or selecting a contact.
2/ Call Setup: The VoIP device sends a SIP INVITE message to the SIP server or proxy, indicating the intent to establish a call.
3/ Authentication and Address Resolution: The SIP server authenticates the user and resolves the recipient’s IP address or phone number.
4/ Session Establishment: Once the recipient’s address is obtained, a SIP session is established between the two parties.
5/ Media Transfer: The voice data is packaged into packets, transmitted over the IP network, and reassembled at the recipient’s end.
6/ Call Termination: When the call ends, a SIP BYE message is sent to terminate the session.
Additionally, to facilitate VoIP-SIP integration, several components work seamlessly together. These include VoIP phones or devices, which can be hardware-based or software-based applications that enable voice communication; VoIP service providers, who offer the infrastructure and connectivity to make calls possible; and SIP servers or proxies, responsible for call routing, authentication, and handling SIP signaling.
What is the purpose of SIP in VoIP?
The Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) performs various essential functions that enhance the overall effectiveness of VoIP services.
As discussed above the primary purpose of SIP is to establish, modify, and terminate multimedia sessions, including VoIP calls, video conferencing, and even instant messaging. By handling the signaling process, SIP ensures the successful initiation and termination of these communication sessions.
Moreover, SIP plays a pivotal role in user location and identification. It resolves the IP address or phone number of the intended recipient, guaranteeing the accurate routing of VoIP calls. This address resolution function is integral in the proper delivery of VoIP services.
Authentication and access control are also integral aspects of SIP’s purpose in VoIP. By verifying users and granting access permissions, SIP adds a layer of security to VoIP communications, ensuring that only authorized parties can establish a session.
Lastly, SIP enhances the functionalities of VoIP services. Its ability to manage multiple sessions simultaneously enables features like call hold, call transfer, and multi-party conferencing, which are integral to modern communication needs.
In a nutshell, SIP is a critical component of VoIP, improving its capabilities and ensuring the delivery of efficient, secure, and high-quality voice communication over internet networks.
Difference between a SIP server and a VoIP server
SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) and VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) often work together, but they have distinct roles in Internet-based communication.
1/ SIP Server: A SIP server is a type of VoIP server that uses the SIP protocol to initiate and manage communication sessions. Its primary function is to handle SIP signaling for call setup and tear down, user registration, and SIP packet routing within a network. The SIP server enables advanced communication features like call hold, transfer, and multi-party conferencing.
2/ VoIP Server: On the other hand, a VoIP server refers to the hardware or software that allows voice data to be transmitted over an internet connection. It provides the infrastructure for sending voice data in packets, using various protocols including SIP. The VoIP server ensures that voice packets are correctly delivered and reassembled, facilitating voice communication over the Internet.
Essentially, a SIP server is a subset of VoIP servers, focused on handling SIP protocol operations within the broader VoIP communication framework. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for implementing or using VoIP services effectively.
Difference between SIP trunking and VoIP
Whilst SIP Trunking and VoIP are both crucial in digital communication, their roles are fundamentally distinct. Here are five primary differences between the two:
Aspect | SIP Trunking | VoIP |
Definition | SIP trunking is a service that enables the connection of a Private Branch Exchange (PBX) to the Internet using the SIP protocol. | VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) is a general term for the transmission of voice communication over the Internet or other IP-based networks. SIP is one of the protocols used in VoIP. |
Scope | Focuses specifically on the connection between a PBX and the service provider's network. | Includes a wider range of communication services, including voice, video, and messaging, and can be implemented in various scenarios beyond traditional PBX connections. |
Physical Infrastructure | Involves the use of SIP trunks, which are virtual connections over the Internet, eliminating the need for traditional phone lines. | Can be implemented with or without physical infrastructure changes. VoIP can be used over existing data networks, and physical phone lines may not be required. |
Scalability | Scalability is often based on the capacity of the SIP trunks, and additional channels can be added as needed. | Scalability is determined by the network's capacity and the capabilities of the VoIP system, allowing for flexible expansion. |
Typical Users | Commonly used by businesses with on-premises PBX systems looking to leverage VoIP for external communications. | Widely used by businesses and individuals for various communication needs, including phone calls, video conferencing, and messaging. |
Which is better SIP or VoIP?
When considering VoIP or SIP for your communication needs, several factors come into play. Consider the following:
1/ Business Size and Requirements
Evaluate your organization’s size, communication volume, and specific requirements. Larger organizations may benefit from the advanced features and scalability offered by SIP, while smaller businesses may find VoIP solutions to be more cost-effective.
2/ Cost and Implementation Considerations
Assess the costs associated with hardware, software, maintenance, and ongoing support. Consider the complexity of implementation and whether your existing infrastructure can support VoIP or SIP solutions effectively.
3/ Integration with Existing Infrastructure:
Determine the compatibility of the solution with your current network infrastructure, devices, and software systems.
In conclusion, understanding the differences between VoIP and SIP is crucial for making informed decisions about your communication needs. While VoIP focuses on transmitting voice signals over the Internet, SIP adds advanced call management and multimedia capabilities to enhance communication sessions. By evaluating your organization’s needs and requirements, you can choose the solution that best suits your business goals.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1) Is SIP considered VoIP?
Ans: No, SIP is not considered VoIP but rather a fundamental component of it. VoIP is a broad term that includes any voice call transmitted over an internet connection. It involves a range of protocols and technologies that collectively enable this form of communication.
Q2) Is SIP a protocol for VoIP?
Ans: Yes, SIP is a key protocol used in VoIP technology. It is used to establish, modify, and terminate multimedia sessions including VoIP calls.
Q3) Can you have VoIP without SIP?
Ans: Yes, while SIP is a common protocol used in VoIP technology, it’s not the only one. Other protocols such as H.323, Media Gateway Control Protocol (MGCP), and Inter-Asterisk eXchange (IAX) can also be used in VoIP implementations. Thus, VoIP can function without SIP, but SIP is often preferred due to its robustness and versatility.
Q4) What ports does SIP use?
Ans: The Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) primarily uses two ports: UDP Port 5060 and TCP Port 5060. These ports are usually used for non-encrypted SIP communication. If SIP over TLS (Transport Layer Security) is used for encryption, then the default port is TCP 5061.
Q5) What is PBX vs VoIP vs SIP?
Ans: PBX (Private Branch Exchange), VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol), and SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) are all integral components of modern telephony, but they serve different functions. PBX is an internal phone system used within a company to manage and route calls. VoIP is a technology that converts voice signals into digital data, allowing calls to be made over the internet. SIP, on the other hand, is a protocol used in VoIP technology to initiate, maintain, modify, and terminate multimedia sessions, including voice calls, video calls, and instant messaging.
Q6) What is the difference between VoIP, SIP, and IP telephony?
Ans: VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol), IP telephony, and SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) are all technologies related to communication over the Internet, but they serve different functions. VoIP is a broad term that applies to any phone call that’s made over the Internet, instead of traditional telephone lines.
IP telephony, or Internet Protocol telephony, refers to the technology that enables voice communication and multimedia sessions over the Internet Protocol (IP). It converts voice and multimedia signals into data packets that are transmitted over other IP-based networks. On the other hand, SIP is a specific protocol used to enable VoIP and other forms of digital communication.
Q7) What is the difference between hosted VoIP and SIP?
Ans: Hosted VoIP is a service where the VoIP equipment, servers, and services are hosted by a third-party service provider. This means businesses don’t need to invest in their infrastructure, which can be especially beneficial for small to medium-sized businesses. SIP, on the other hand, is a protocol used to facilitate VoIP and other forms of digital communication. While hosted VoIP is a service, SIP is a technology that helps to enable that service.

