VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) and Video Conferencing are integral tools reshaping how we connect and collaborate. With an increasing demand for streamlined and cost-effective communication solutions, understanding the difference between these two technologies becomes essential.
This blog post explores 8 unique differences between VoIP and Video Conferencing, emphasizing their influence on the way we connect and collaborate.
Understanding VoIP
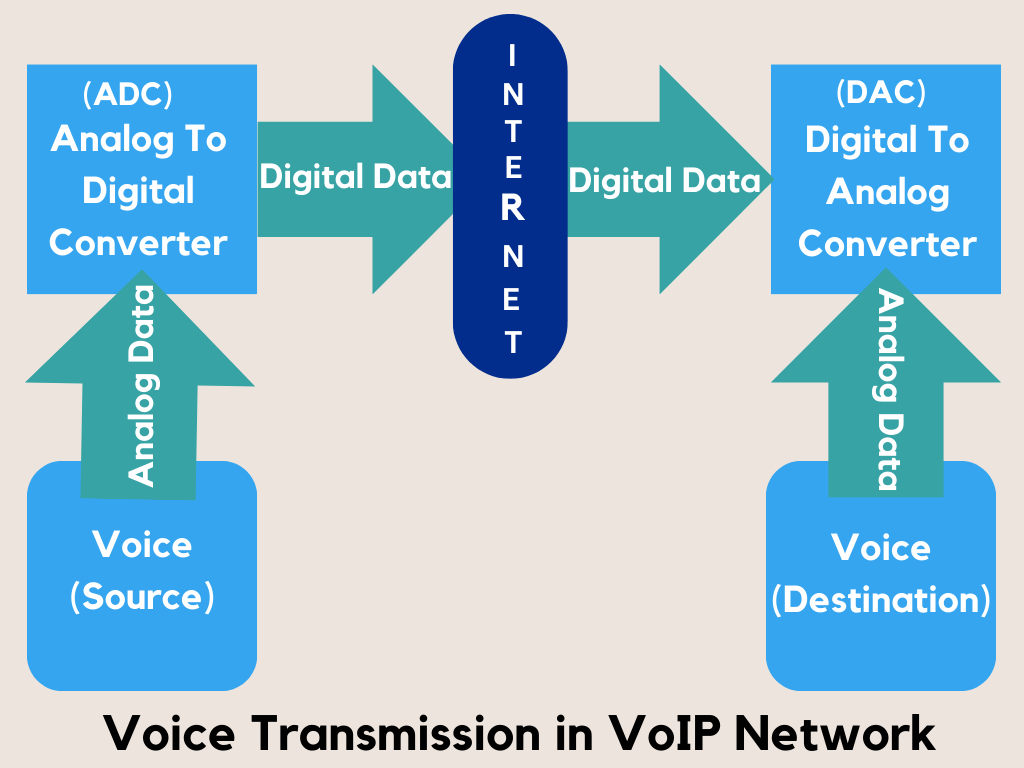
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) is a technology that enables voice calls to be transmitted over the Internet, instead of relying on traditional phone lines. By converting voice signals into digital data, it offers a cost-effective solution for long-distance and international calls.
VoIP can turn your computer, mobile phone, or another device into a full-featured telephone. However, it’s important to note that for using VoIP a stable internet connection is crucial to ensure uninterrupted and clear communication.
Key Features of VoIP
The core functionality of VoIP is not only to make and receive phone calls but to do so with a range of features that streamline communication and collaboration within your business:
- Call Forwarding and Routing: Calls can be routed to any device—desk phone, cell phone, softphone, or any combination.
- Voicemail-to-Email: Voicemail messages can be transcribed into text and sent to your email, providing easily accessible records of communications.
- Conference Calling and Collaboration Tools: VoIP phone systems often include conference calling features and collaboration tools to help your team stay connected and work more efficiently.
- Call Analytics: Advanced analytics allows you to track call volumes, duration, and more, providing insights that can inform business decisions.
What is Video Conferencing

Video conferencing is an advanced form of online communication that allows for both audio and video interaction between two or more participants in real time. It facilitates face-to-face meetings without the need for physical presence, making it the perfect solution for remote teams and businesses with international partners. Video conferencing often includes additional features like text chat, file sharing, and more.
Pros and Cons of Video conferencing
Pros
- Increased Productivity: Fast and efficient decision-making is possible with real-time sharing and collaboration during video conferences.
- Enhanced Communication: Video conferencing allows for face-to-face interaction, providing the opportunity to observe non-verbal signals like facial expressions and body language.
- Geographical Flexibility: No matter where you are, as long as you have internet access, you can participate in a video conference. It eliminates the need for physical presence, which is a benefit for remote workers and global teams.
Cons
- Security Concerns: Confidential data shared during video conferences can be at risk if the platform isn’t secure.
- Technical Issues: Unstable internet connections, poor audio or video quality, and software glitches can disrupt the smooth flow of the meeting and impact productivity.
- User Adaptation: Not everyone is comfortable with technology. Some team members may struggle with using video conferencing tools, which can affect meeting efficiency.
The main differences between VoIP and Video Conferencing
Voice over Internet Protocol and Video Conferencing are both technologies that facilitate real-time communication over the Internet, but they differ significantly in their primary purposes, functionalities, and user experiences. Here’s an in-depth explanation of the differences between VoIP and Video Conferencing:
1/ Communication Medium:
The first major difference between VoIP and Video Conferencing is the primary communication medium they enable. With VoIP, communication is limited to voice calls. It can be as simple as using a phone with VoIP capability or a computer with VoIP software installed. Voice calls can occur between any two devices connected to the internet.
Video Conferencing, in contrast, offers a much richer interactive experience by adding video to the mix. It involves the transmission of audio and video signals with chat functionalities, making it possible for participants to see each other as they communicate.
2/ Equipment and Setup:
For VoIP, the setup can be incredibly simple. In its most basic form, all that’s needed is a computer, a headset or a microphone and speakers (or even a smartphone), and the VoIP application or software. If you are an advanced user you may opt for phones specifically designed for VoIP technologies that look and feel like traditional desk phones but have native IP capabilities.
Video Conferencing requires slightly more complex equipment. You need a camera to broadcast your video and a display monitor to view other participants. Quality audio is also crucial, which often means the inclusion of a dedicated microphone and speakers or a headset. These can be integrated into your device or added as separate external devices. The combination of these components makes Video Conferencing optimal for diverse business communication scenarios.
3/ Communication Modes:
With VoIP, communication is generally in the form of one-to-one voice calls. While some different types of VoIP services offer the capability to place video calls, this typically isn’t its main function. Where VoIP stands out is in its ability to handle business phone calls more cost-effectively through IP networks, with added features like voicemail, call forwarding and conference calling.
Video Conferencing is tailored to multi-party video calls. This includes the ability to share a screen, collaborate on documents, and conduct meetings virtually. Video Conferencing solutions often include chat functionality and the sharing of multimedia content, making them powerful tools for remote collaboration.
4/ Visual Interaction:
The clearest difference between VoIP and Video Conferencing can be seen in their visual capabilities. VoIP is purely voice-based and lacks any video component. This can either be a drawback or a matter of preference, depending on the context. Some individuals might prefer the simplicity and convenience of a voice call without the need for visual interaction.
Video Conferencing not only adds the visual element but also tries to replicate a face-to-face conversation. It creates a more personal and engaging environment for participants, especially when discussing complex topics or when nonverbal cues are important. Video Conferencing’s visual interaction can develop better relationships and understanding among remote team members or with clients.
5/ Use Cases:
The use cases for VoIP are broad, but it is primarily used for voice calls, serving as a cost-effective telephone service for individuals, businesses, and call centers. It is especially popular for remote work setups, as it allows employees to handle business calls from anywhere with an internet connection.
Video Conferencing is ideal for more synchronous, collaborative activities. It’s often used for team meetings, client presentations, and remote training sessions where participants can benefit from in-person communication without needing to be in the same physical space.
6/ Bandwidth Requirements:
Because VoIP is voice-only, it requires significantly less bandwidth than video conferencing. This can be a benefit in situations where high-speed internet is not available or when many calls need to be made in quick succession.
VoIP Usage | Bandwidth Requirement |
Minimum bandwidth per VoIP line | 100 Kbps |
VoIP telephone calls (optimal performance) | 5-25 Mbps download speed |
Email and web browsing | 1 Mbps download speed |
File downloading | 10 Mbps download speed |
HD video teleconferencing | 6 Mbps download speed |
Video Conferencing, however, needs much higher levels of bandwidth, especially for high-definition video and audio streams. This is why a stable and fast internet connection is often listed as a top requirement for ensuring a smooth Video Conferencing experience. High bandwidth also makes Video Conferencing less accessible in areas with poor internet infrastructure.
7/ Cost Considerations:
One of the most significant advantages of VoIP is its cost-effectiveness. Lower infrastructure requirements, the use of existing IT setups, and the ability to make long-distance calls at no extra cost (beyond an internet connection) can lead to significant savings, particularly for businesses with high-frequency phone usage.
Video Conferencing, while it can also offer cost savings compared to in-person meetings, often requires more investment. High-quality cameras, microphones, and a reliable internet connection can be costly, and there may be subscription fees for the Video Conferencing platform itself, especially for more feature-rich solutions.
8/ Integration with Other Platforms:
Both VoIP and Video Conferencing can integrate with other collaboration and productivity tools. VoIP services often have integrations with customer relationship management (CRM) systems and productivity applications to enhance users’ experiences.
Video Conferencing solutions frequently integrate with project management platforms, document-sharing services, and other communication tools to streamline the collaborative process. This level of integration makes it easier for Video Conferencing to fit seamlessly into existing business workflows, whereas VoIP, is often seen as an addition to other services.
Difference between Voice and Video Conferencing
When it comes to remote communication, both voice and video conferencing play a vital role. However, they offer distinct features and are best suited to different scenarios:
1/ Visual Engagement: Video conferencing provides the opportunity to see visual cues such as facial expressions and body language. This can greatly enhance understanding in a conversation. On the other hand, voice conferencing lacks this visual element, focusing purely on audio communication.
2/ Bandwidth Requirements: Video conferencing demands higher bandwidth due to the transmission of visual data. Voice conferencing, being audio only, requires less bandwidth, making it a more viable option in areas with limited internet connectivity.
3/ Formality Levels: Video conferencing tends to be more formal and is often used for business meetings, presentations, or interviews, where visual interaction is crucial. Voice conferencing, being less formal, is typically utilized for quick check-ins or updates.
4/ Multitasking Capabilities: During a voice conference, participants often have the option to multitask, as they are not visually present. Video conferencing, however, requires participants to be visually engaged, limiting the ability to multitask.
5/ User Experience: The user experience can also differ significantly between the two. Video conferencing can sometimes lead to ‘virtual meeting exhaustion‘ due to the constant focus required on the screen. Voice conferencing, being audio-centric, may be less exhausting and allows for a more natural conversation flow as participants do not have to worry about their on-screen appearance.
It is important to note that choosing between voice and video conferencing depends on your specific needs, the nature of the conversation, and the resources available to you.
Why voice calls are better than video calls
There are several reasons why voice calls are often a more effective form of communication compared to video calls. Here’s why you should consider using voice calls in certain situations:
1/ Efficiency: Voice calls are often more efficient than video calls. They allow you to engage in discussion while performing other tasks, making them ideal for multitasking.
2/ Convenience: Unlike video calls, voice calls require less preparation. You don’t have to worry about your appearance or surrounding environment, which can be a major relief for many individuals.
3/ Connectivity Issues: Voice calls generally require less bandwidth than video calls, making them less vulnerable to connection issues. In places with unstable internet connections, voice calls are often a more reliable option.
4/ Focus on Conversation: With video calls, non-verbal cues can sometimes distract from the conversation. On a voice call, the focus remains purely on verbal communication, which can lead to more focused and productive conversations.
What is the difference between VoIP video calls and video calls?
Video calling and VoIP video calling are both communication technologies, however, they operate differently and have unique characteristics. Video calling is a communication method that allows two or more individuals to interact through both audio and video transmissions in real time.
This method uses various platforms such as mobile devices, web browsers, and even dedicated video conferencing systems. It relies on both the Internet and cellular networks, with quality depending on the strength of your Internet connection or cellular network.
VoIP video calling, on the other hand, explicitly uses the Internet to transmit audio and video signals. This means that instead of relying on a specific network, VoIP video calls operate on IP networks, which can range from your local area network (LAN) to the entirety of the internet.
This technology converts analog audio signals, like those typically experienced during phone discussions, into digital data that can be transmitted over the Internet.
VoIP video calls are typically higher quality due to the use of codecs that compress data for faster transmission, and they are often more cost-effective as they avoid the traditional telephony service charges.
While both video calling and VoIP video calling allow for audio-visual communication, they differ in the transmission process and network utilized.
Traditional video calling can use either Internet or cellular networks and might incur network-specific charges, while VoIP video calling exclusively employs the Internet for signal transmission, often leading to cost savings and enhanced call quality.
VoIP also allows for both video and voice calls and often includes features like chat and file sharing. These calls are typically conducted through a VoIP service provider, requiring an application or software on your device.
Role of VoIP and Video conferencing on the Internet
VoIP and video conferencing play a significant role in shaping the internet as a global communication tool. These technologies utilize the internet to facilitate real-time communication, transforming how businesses and individuals interact.
With VoIP’s ability to transmit voice signals over the internet, it offers the flexibility to make calls from any location and can also significantly reduce communication costs.
According to a study switching to VoIP can result in a reduction of more than 50% in monthly telecom expenses for companies.. This significant boost in efficiency can help organizations achieve their goals more effectively and efficiently.
Similarly, video conferencing enables you to have face-to-face interaction among your team members, regardless of their physical location. This not only streamlines workflow by facilitating instant decision-making but also develops a sense of community within geographically spread teams.
By implementing VoIP and video conferencing, your business can enhance its communication systems while keeping costs low. The integration of these technologies can lead to improved collaboration, resulting in successful projects and better overall performance for the company.
So, if you’re looking to enhance your communication and collaboration tools, consider incorporating VoIP and video conferencing into your operations for a more efficient and productive workplace.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1) Can VoIP be used for video calls?
Ans: Yes, VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) can be used for video calls. This technology allows for voice and video communication over an internet connection rather than traditional phone lines.
Q2) What is the difference between tele and video conferencing?
Ans: Teleconferencing is a broad term that includes any electronic communication between two or more people. On the other hand, video conferencing is a form of teleconferencing that employs video technology to enable participants to have real-time visual interaction.
Q3) Is Zoom the same as video conferencing?
Ans: Zoom is a platform that provides video conferencing services. While Zoom is a specific brand, video conferencing is a general term for technology that allows video communication between remote participants.
Q4) What is the difference between video conferencing and Internet calling?
Ans: Video conferencing typically allows for multiple participants and includes features such as screen sharing and virtual meeting rooms. Internet calling, also known as VoIP, is often a one-to-one communication method, primarily used for voice communication, but can also support video calls.
Q5) What is the difference between audio and video conferencing?
Ans: Audio conferencing allows participants to communicate through voice only, either via phone lines or internet connections. Video conferencing, in contrast, includes both audio and visual components, allowing participants to both hear and see each other in real time.

