VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) technology allows small businesses and individual consumers to optimize communication systems and reduce costs by enabling Internet-based calls. In the background, VoIP cables are crucial in smoothly connecting your voice across the digital environment, ensuring global connectivity.
Understanding these cables that make VoIP possible is crucial for maximizing the system’s benefits. This guide will simplify the types of VoIP cabling, enabling you to make informed decisions for both business and personal requirements.
Definition of VoIP Cables
VoIP cables serve as the physical mediums for transmitting digital signals in Voice over Internet Protocol communications. They play a crucial role in the VoIP system by facilitating the transmission of voice data over the Internet. Various cable types, including Ethernet, coaxial, and fiber-optic cables, have distinct functions within a VoIP setup. The choice of cable not only impacts voice communication clarity and reliability but also influences network performance and scalability.
Types of VoIP Cables
Understanding the various cables used in VoIP is the first step in creating a reliable communication network. Here we will explore the most popular types and their applications.
1/ Ethernet Cables:
Ethernet cables, particularly Cat5e, Cat6, and Cat7 types, serve as the foundation of most VoIP communications. These cables establish connections between VoIP devices, like phones and adapters, and the wider network infrastructure, facilitating effective transmission of voice data packets.
In VoIP configurations, the selection of Ethernet cable significantly impacts system performance. Opting for higher category cables, such as Cat6 or Cat7, is crucial as they are engineered to support faster data transmission rates and broader bandwidths, resulting in improved voice quality and reduced communication delays.
Moreover, these cables feature advanced protection to reduce interference from external sources, ensuring the clean and uninterrupted transmission of voice data. Choosing the right Ethernet cable for your VoIP system is a pivotal measure in ensuring optimal communication clarity and reliability.
Common categories: Cat5, Cat5e, Cat6, Cat6a, Cat7.
I. Cat5: Cat5 cables have played a foundational role in early VoIP setups.

These cables are intended to facilitate network speeds of up to 100 Mbps across a bandwidth of 100MHz, making them suitable for smaller-scale or older VoIP setups where high-speed internet isn’t a critical requirement. However, for environments demanding higher data transmission rates and better clarity in voice communications, upgrading to more advanced categories like Cat6 or Cat7 is recommended.
II. Cat5e: Building on the base provided by Cat5, Cat5e cables represent a significant advancement in terms of network performance and reliability for VoIP systems. These cables are designed to handle speeds up to 1 Gbps at distances of up to 100 meters, making them a superior choice for most modern VoIP communications. The “e” in Cat5e stands for “enhanced,” reflecting improvements in reducing cross-talk and interference, which are critical for maintaining clear and reliable voice transmissions.
III. Cat6: Cat6 cables mark a significant advancement in Ethernet technology, customized to meet the requirements of high-speed voice and data communication in VoIP systems.

These cables are designed to handle data transmission speeds of up to 10 Gbps at distances of up to 55 meters in a network setup, and up to 1 Gbps at lengths of up to 100 meters. This substantial Improve in capacity and performance compared to earlier versions like Cat5 and Cat5e is vital for extensive, high-demand VoIP communication, ensuring top voice quality with minimal delays. Moreover, Cat6 cables come with precise standards for crosstalk and system noise, significantly improving signal consistency and the accuracy of voice data transfer.
IV. Cat6a: The “a” in Cat6a stands for “augmented“, These cables support data speeds up to 10 Gbps, like Cat6 cables, but with an extended range of up to 100 meters. This increased length without compromising speed or quality is crucial for vast networks requiring long-distance cabling. Cat6a cables offer better shielding than Cat6, providing superior resistance to crosstalk and external noise. This leads to clearer voice communication, essential for professional environments and busy call centers.
Is CAT5 or CAT6 better for VoIP?
When deciding between CAT5 and CAT6 cables for VoIP applications, it is crucial to consider the specific requirements of your VoIP system. While CAT5e (enhanced Category 5) cables can sufficiently support VoIP communication by providing speeds up to 1 Gbps and a frequency of up to 100 MHz, CAT6 cables offer superior performance characteristics that make them the better choice for VoIP in many scenarios.
-Performance and Bandwidth: CAT6 cables support bandwidths of up to 250 MHz, double that of CAT5e, and can deliver speeds of up to 10 Gbps in short distances (up to 55 meters). This higher bandwidth and speed capability ensures that CAT6 cables can handle the data volumes of modern VoIP systems more effectively, minimizing latency and maximizing call quality.
-Crosstalk Reduction: CAT6 cables are designed with advanced twists and thicker protection, significantly reducing crosstalk and electromagnetic interference. This ensures that voice transmissions are clearer and more reliable, with less risk of distortion or data loss — a critical factor in maintaining high-quality VoIP communications.
-Future Readiness: Upgrading to or starting with CAT6 cabling for VoIP systems is a strategic, future-proofing decision. As VoIP technology and high-definition codecs evolve, requiring more bandwidth, CAT6 cables are better aligned to handle these advancements without the need for immediate cable upgrades.
V. Cat7: Cat7 Ethernet cabling technology is designed to accommodate ultra-high-speed data transmission rates of up to 10 Gbps across distances reaching 100 meters.

While matching Cat6a in performance, Cat7 excels with enhanced bandwidth capabilities of up to 600 MHz. This significant capacity enables consistent handling of extensive data loads, making Cat7 the preferred choice for demanding VoIP and multimedia applications.
Additionally, Cat7 cables feature extensive shielding for each pair of wires (and additional shielding for the cable as a whole), drastically minimizing crosstalk and interference from external sources.
2/ Coaxial Cables:
Coaxial cables are also commonly used in VoIP systems. They are especially useful when existing coaxial wiring supports VoIP communication. Coaxial cables have a unique design with a central conductor, an insulating layer, and a metallic shield.
This design provides strong protection against electromagnetic interference, which is crucial for maintaining voice transmission quality. While Ethernet cables are the preferred choice for VoIP due to their efficiency, coaxial cables offer a reliable and cost-effective alternative, particularly in buildings with existing coaxial infrastructure.
Pros of Coaxial Cables in VoIP Systems
- Durability: Coaxial cables are recognized for their durability and ability to endure tough conditions, making them ideal for long-term utilization in diverse environments.
- Resistance to Interference: The shielded design of coaxial cables offers superior protection against electromagnetic interference, ensuring clearer voice transmissions.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Utilizing existing coaxial cable infrastructure for VoIP can be more cost-effective than installing new Ethernet lines, especially in buildings already equipped with coaxial wiring.
- Flexibility in Installation: Due to their flexibility, coaxial cables can effortlessly navigate obstacles and tight spaces, streamlining the installation process.
Cons of Coaxial Cables in VoIP Systems
- Limited Bandwidth: Compared to the latest Ethernet cables (e.g., Cat6a, Cat7), coaxial cables offer limited bandwidth, which may affect data transmission speed and quality.
- Signal Loss Over Distance: Coaxial cables can experience signal loss over long distances, which might require the use of repeaters or amplifiers to maintain voice quality in larger installations.
- Less Future-Proof: With technological advancements, coaxial cables may become less ideal for upcoming high-speed, high-bandwidth uses when compared to Ethernet alternatives.
- Potential for Obsolescence: As Ethernet cables are increasingly favored in new VoIP setups, coaxial cables might face obsolescence, posing challenges for future upgrades or expansions.
3/ Fiber Optic Cables:

Fiber Optic Cables are a modern technology in the domain of VoIP and digital communications. They consist of one or more thin strands of glass or plastic fibers, which act as channels for data transmission via pulses of light.
Unlike traditional copper wires, where data is transmitted via electrical signals, fiber optic technology relies on light to carry information, allowing for significantly higher speeds and greater bandwidth. This method of data transmission not only ensures rapid delivery of voice communications but also reduces the risk of signal loss or degradation over long distances.
Additionally, fiber optic cables demonstrate strong resilience against electromagnetic interference, contributing to clearer, more reliable voice quality in VoIP systems.
The core advantages of fiber optic cables in VoIP networks include:
- High-Speed Data Transfer: Fiber optic cables can handle data speeds reaching several terabits per second, surpassing what copper cables can offer.
- Greater Bandwidth: Fiber cables have a much wider bandwidth than copper cables, enabling them to carry a huge volume of data. This is crucial for organizations that require the simultaneous handling of thousands of VoIP calls, along with other data-intensive services.
- Immunity to Electromagnetic Interference: Another notable benefit of fiber optic cables is their data transmission method—utilizing light instead of electricity. This unique characteristic renders them unaffected by electromagnetic interference. This results in fewer dropped calls and data transmission errors, ensuring reliable and clear VoIP communications.
- Reduced Signal Loss: Unlike copper cables, which can suffer significant signal loss over long distances, fiber optic cables maintain high-quality signal consistency over much greater distances. This makes them ideal for extensive campus networks or connections between distant office locations.
- Durability and Safety: Fiber optic cables are more resilient to temperature fluctuations, moisture, and chemical exposure. They also do not carry electric current, reducing the risk of fire hazards, and making them safer for use in diverse environments.
Types and Usage:
1/ Straight-Through Cables: Employed to establish connections between dissimilar devices, such as linking a computer to a network switch, these cables play a crucial role in ensuring seamless data transmission and network functionality within various technological setups.
2/ Crossover Cables: Typically used for connecting similar devices within a local network, such as linking one switch to another switch, or directly connecting a computer to another computer without the need for an intermediary network switch. This type of direct connection, known as a peer-to-peer connection, allows for data transfer between devices without routing through a central networking device.
Key features and benefits of using patch cables in VoIP systems include:
- Flexibility and Adaptability: Patch cables come in various lengths (including Ethernet Cat5e, Cat6, Cat6a, and fiber optic), offering flexibility to meet the specific configuration and space requirements of any VoIP network.
- High-Speed Data Transmission: With the capability to support high-speed data transfer rates, patch cables ensure that voice data is transmitted efficiently and without lag, contributing to clear and reliable voice communications.
- Ease of Installation and Maintenance: Due to their standardized connectors, patch cables can be easily connected, removed, or replaced, making the installation and maintenance of VoIP networks less time-consuming.
- Cost-Effectiveness: By using patch cables to connect devices within close range, your organizations can reduce the need for extensive cabling infrastructure, making this a cost-effective solution for smaller VoIP setups or temporary networking needs.
- Reduced Signal Interference: High-quality patch cables feature shielding that reduces electromagnetic interference, protecting voice data transmission integrity from external noise for uninterrupted voice calls.
Comparison between single-mode and multi-mode fiber optic cables based on various aspects.
Aspect | Single-mode Fiber Optic Cables | Multi-mode Fiber Optic Cables |
Core Diameter | Smaller core diameter (typically 8.3 to 10 microns) | Larger core diameter (50 to 62.5 microns) |
Data Transmission and Distance | Ideal for long-distance transmission without significant signal loss | Optimized for shorter distances, suitable for data communication within buildings or across campuses |
Bandwidth and Speed | Higher bandwidth supporting higher data rates and faster speeds for high-speed networks and ISPs | Limited bandwidth and speed due to modal dispersion, suitable for high data rates but restricted by distance limitations |
Cost Considerations | More expensive equipment like laser diode-based transmitters for precise long-distance data transmission | Cost-effective with LED or VCSEL sources, suited for short-range applications like data centers or inter-office communications |
4/ USB Cables:

![]()
![]()
![]()
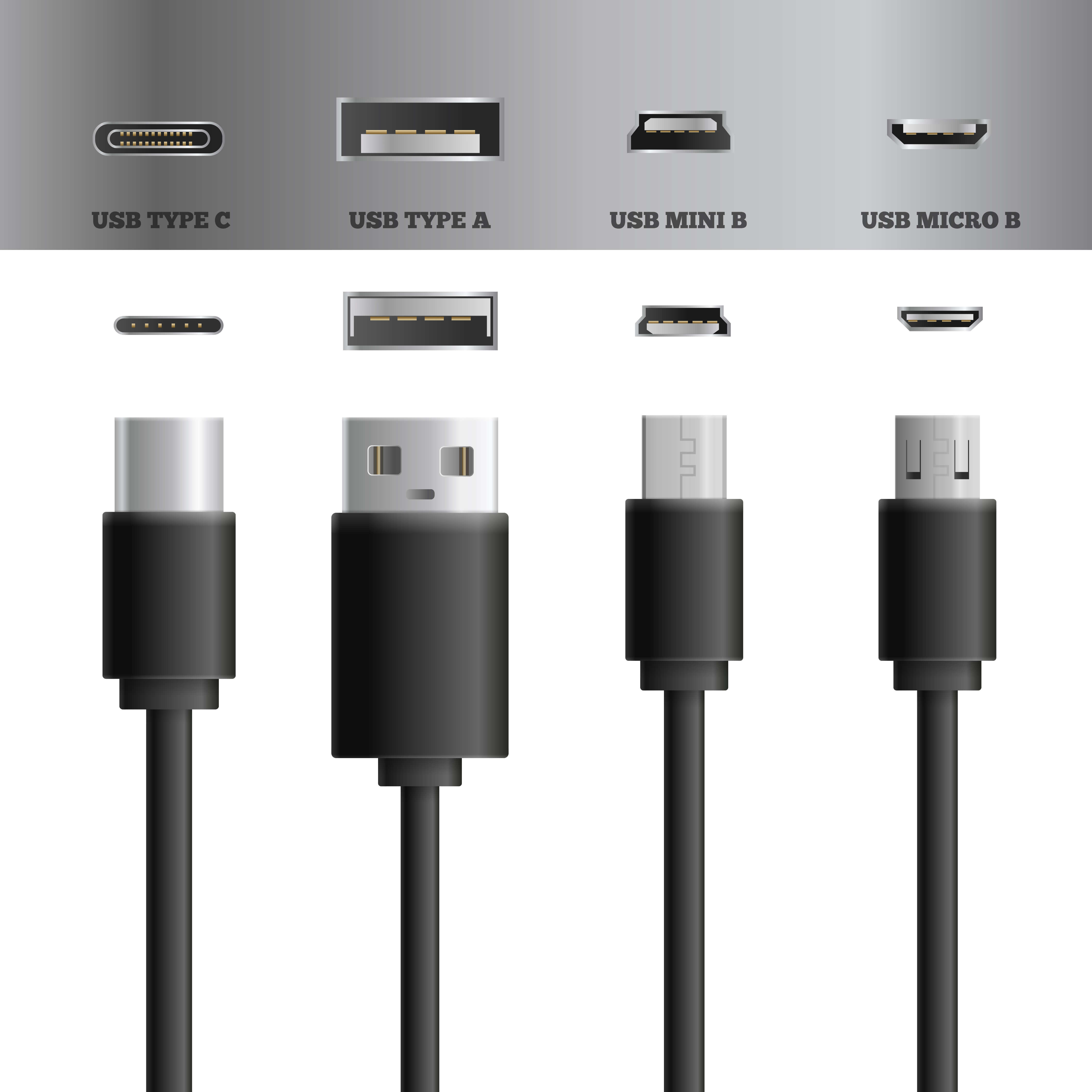
![]() USB cables play a pivotal role in VoIP applications, providing a universal solution for connecting various devices. These cables assist the connection of VoIP hardware, such as headsets, cameras, and phones, to computers and other network devices, ensuring easy integration and functionality.
USB cables play a pivotal role in VoIP applications, providing a universal solution for connecting various devices. These cables assist the connection of VoIP hardware, such as headsets, cameras, and phones, to computers and other network devices, ensuring easy integration and functionality.
The universal nature of USB standards means that these cables support a wide range of devices across different manufacturers, making them essential for a plug-and-play experience in VoIP systems.
Additionally, with advancements in USB technology, such as USB-C, the capabilities for faster data transfer rates and power delivery have significantly enhanced the performance and reliability of VoIP communications.
VoIP wiring diagram
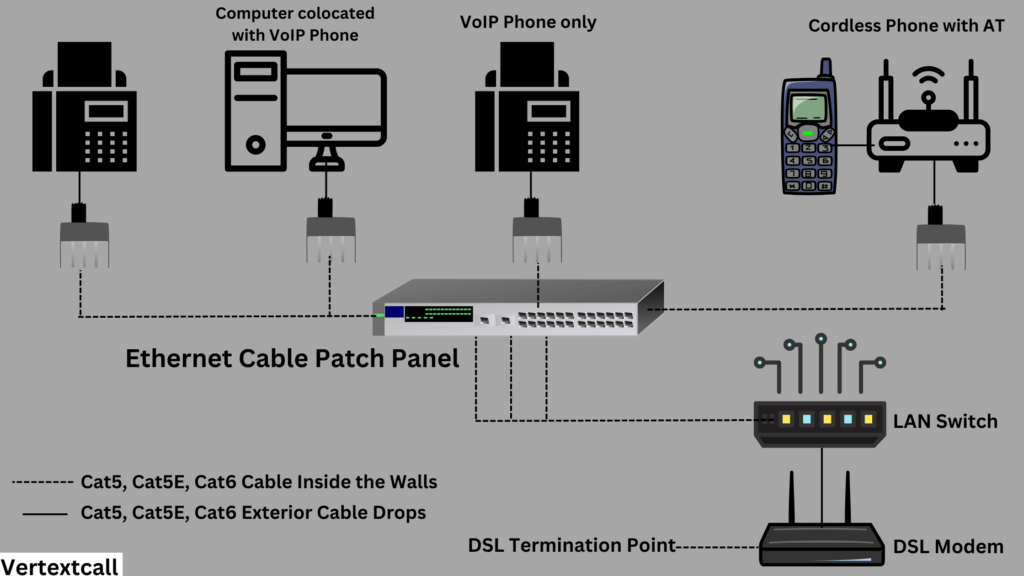
The LAN Switch shown the the above diagram is optional If you have 4 or fewer lines, you can plug them directly into the DSL Modem
Which cabling standard is better suited for VoIP and why?
Choosing the right cabling standard for VoIP applications requires careful consideration of the unique demands of voice-over IP technology. Effective voice data transmission relies on high-speed, low-latency, and dependable network connections to maintain clear and uninterrupted communication. In this context, Cat6a cabling stands out as the optimal solution for VoIP installations, offering superior performance for various reasons.
1/ High-Speed Data Transfer: Cat6a cables are engineered to facilitate data transmission speeds reaching up to 10 Gbps across lengths of up to 100 meters. This capability is particularly beneficial for VoIP applications, which require high bandwidth to manage voice data packets efficiently and with minimal delay.
2/ Enhanced Bandwidth: As discussed above Cat6a provides an increased bandwidth of up to 500 MHz, double that of Cat6 cables. This higher bandwidth allows for the more efficient handling of voice data, ensuring clearer and more reliable voice transmissions over VoIP systems.
3/ Reduced Crosstalk and Interference: Cat6a cables are equipped with improved shielding measures that significantly reduce crosstalk and environmental interference. This is crucial for VoIP systems, where even minor disruptions can degrade call quality. The enhanced shielding ensures that voice transmissions remain uninterrupted and clear across the network.
4/ Future-Proofing: With VoIP and other telecommunications technologies continually evolving, deploying Cat6a cabling provides an element of future-proofing. Its capacity to handle faster data rates and higher bandwidth requirements makes it a sensible investment for supporting not only current but also forthcoming VoIP technologies.
Considering these aspects, Cat6a cabling stands out as the more appropriate and effective choice for VoIP applications.
What are the factors to consider when choosing a cable for VoIP?
Selecting the correct cable for your VoIP system is a critical decision that can impact performance, cost, and future scalability. There are several factors to consider when making this choice:
- Bandwidth Requirements: Depending on the number of simultaneous calls and the nature of your business, you will need to ensure the selected cables can meet the bandwidth requirements for clear voice transmission and other data needs.
- Distance: The length of the cable run will determine the type of cable you should use. Longer distances might necessitate the use of cables with superior shielding and signal integrity.
- Environment: Cables operate in a variety of environments, from temperature-controlled server rooms to conduit spaces and outdoor installations. The right cable type should be chosen to suit the environmental factors at play.
How to connect a VoIP phone to the router
Connecting a VoIP phone to a router is critical in setting up a VoIP system, ensuring that voice data is efficiently transmitted across the network. Follow these instructional steps to ensure a secure and optimal connection:
1/ Prepare the Equipment: Ensure that you have your VoIP phone, a compatible router, and a high-quality Ethernet cable (preferably Cat6a, as discussed previously for its superior speed and bandwidth capabilities).
2/ Connect the Ethernet Cable: Plug one end of the Ethernet cable into the designated network slot on your VoIP phone. This port is typically labeled “Internet,” “Network,” or “LAN.”
3/ Connect to the Router: Insert the opposite end of the Ethernet cable into an open LAN port on your router. Make sure that the connection is stable and secure to prevent any disruptions.
4/ Power Up: Connect your VoIP phone to its power source and turn it on. If your VoIP phone supports Power over Ethernet (PoE), it may power on automatically upon connecting to the router, as PoE allows the transmission of power along with data over the same cable.
5/ Configure the Phone (if necessary): Some VoIP phones may require additional configuration to communicate with the router and VoIP service provider. This could involve entering specific network settings into the phone manually or through a web interface. Refer to your VoIP phone’s manual for detailed instructions.
6/ Test the Connection: Once connected and configured, make a test call to ensure the VoIP phone is successfully communicating with the VoIP service through the router. If the call quality is clear and there are no connection issues, your VoIP phone is correctly set up.
By Closely following these guidelines, you can effortlessly link your VoIP phone to your router.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1) Does VoIP use Rj11?
Ans: No, VoIP does not typically use RJ11 connectors. RJ11 connectors are commonly associated with traditional telephone lines and connections. VoIP systems use Internet-based networks for communication, thus they primarily rely on Ethernet connections. Devices in a VoIP setup, such as VoIP phones or adapters, usually connect to the network using RJ45 connectors, which are standard for Ethernet cables.
Q2) What are the most commonly used VoIP protocols?
Ans: Commonly used VoIP protocols include Session Initiation Protocol (SIP), Real-Time Protocol (RTP), and H.323. SIP plays a key role in multimedia session setup, modification, and termination. RTP delivers audio/video over IP networks efficiently. H.323, an ITU standard, offers a framework for real-time multimedia communications.
Q3) Can CAT5 be used for telephone?
Ans: Yes, CAT5 cable can indeed be used for traditional telephone connections. While CAT5 is mainly for network and internet use with higher data speeds, its wiring and physical characteristics are compatible with analog signals in traditional telephone systems. To use CAT5 for telephones, connect RJ11 connectors to the cable. This setup can handle multiple telephone lines due to CAT5’s several wire pairs compared to standard telephone cables.
Q4) Can I connect VoIP to home wiring?
Ans: Yes, connecting a VoIP system to your home’s existing telephone wiring is possible and can be an efficient way to extend VoIP functionality throughout your home. To accomplish this, you would first need to disconnect your home wiring from the traditional external telephone service to prevent any potential conflicts. Once disconnected, you can connect the VoIP adapter to your home’s phone jack using a standard telephone cable. This setup allows the VoIP service to be distributed across all telephone jacks in the home, enabling you to plug in traditional telephones anywhere in the house and use them with your VoIP service.
Q5) Do I need a special router for VoIP?
Ans: No, you don’t necessarily need a special router for VoIP communications. Most routers can support VoIP functionality. However, for optimal performance, it is advisable to use a router that is VoIP-compatible and supports Quality of Service (QoS) settings. QoS allows you to prioritize VoIP traffic over other types of internet traffic on your network, ensuring clearer call quality and better overall VoIP service reliability.
Q6) Which is the most common type of cable in phone systems for Voice use?
Ans: The most common type of cable used in phone systems for voice use, especially in modern VoIP systems, is the Category 5e (Cat5e) or Category 6 (Cat6) Ethernet cable. These cables connect VoIP phones and systems to the internet or local networks, providing high-speed data transmission that supports the bandwidth demands of voice communication.
Q7) What cable is best for VoIP?
Ans: For most modern VoIP setups, Cat6 cables are often the ideal choice. They offer high-speed data transfer, superior bandwidths, and excellent shielding against interference. This results in clear, reliable voice transmissions.

