In an era dominated by digital advancements, Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) emerges as an adaptable, economically viable, and featured communication alternative. But let’s explore the core questions: What exactly is VoIP, how does it work, and what benefits does it offer?
This comprehensive overview aims to clarify the essence of VoIP, explain its fundamental principles, and outline its pivotal role in transforming corporate communication strategies.
VoIP Definition
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) characterizes Interconnected VoIP as a service facilitating live, two-way voice communication. It necessitates a broadband connection from the user’s location, utilizes Internet protocol-compatible customer premises equipment (CPE), and generally allows users to both receive calls from and make calls to the public switched telephone network. (Source).
What is VoIP in simple terms?
At its core, VoIP enables you to place phone calls, while using your Internet connection rather than conventional phone lines. Think of it as converting your voice into digital information packets that are sent over the web to the receiver’s end, where these packets are then transformed back into voice sounds.
This shift from analog to digital communication enables you to avoid the restrictions and costs associated with traditional telephony. If you’ve got an internet connection, you can make calls, anywhere and at any time, without the need for a dedicated phone line.
This technology not only simplifies your communication infrastructure but also significantly reduces your business communication cost by 50%.
What is VoIP signaling?
VoIP signaling is the fundamental process of starting and overseeing communication transfers. It includes call initiation, routing, disconnecting voice or video connections, and ensuring that every service, whether it’s your regular team meeting or a brief customer call, is appropriately suited for the internet stage.
The core elements of VoIP Signaling are Session Initiation Protocol (SIP), Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP), Session Description Protocol (SDP), and H.323 Protocol Suite. Every component is crucial for a reliable VoIP service.
Note: The following protocol is discussed in detail later in the blog below.
What does a VoIP phone look like
VoIP phones come in various forms. Here is an example of the Polycom VVX 600 model:

Related Reading: Different types of VoIP Phones
How does VoIP work step by step?
VoIP technology operates on a relatively straightforward principle, consisting of a series of steps to transform analog voice signals into digital signals, which are then transported over the internet. Here, we break down the process into key steps, providing a clearer understanding of each stage involved in VoIP communication.
1/ Voice Signal Conversion: The initial step in the VoIP process involves the use of an Analog Telephone Adapter (ATA) or IP phone to convert your analog voice signal into digital format. This digitalization makes it possible for the data to be transmitted over the internet.
2/ Data Packetization: Once the voice is converted into a digital format, it’s segmented into data packets. These packets are small, manageable units that carry the digital voice data. Each packet includes both the sender’s and the recipient’s IP addresses, ensuring they’re routed to the correct destination.
3/ Compression and Encoding: To efficiently use bandwidth, the digital voice data is compressed and encoded. This process minimizes the size of the data packets and prepares them for transmission across the internet, ensuring quality communication even at lower bandwidths.
4/ Transmission Over the Internet: Following compression, the data packets are transmitted to the recipient. This step is where the ‘Internet Protocol’ aspect of VoIP comes into play. The packets travel through various networks and routers until they reach their destination.
5/ Decompression and Decoding: Upon reaching the recipient, the data packets are decoded from their compressed format back into digital voice data. This step reverses the compression process, ensuring the voice data can be understood.
6/ Digital-to-Analog Conversion: In the final step, the digital voice data is transformed back into analog signals by the recipient’s ATA or IP phone. This conversion enables the recipient to listen to the sender’s voice as an uninterrupted stream, completing the communication loop.
Each step in the VoIP process is crucial for ensuring efficient, clear, and uninterrupted communication.
VoIP work diagram
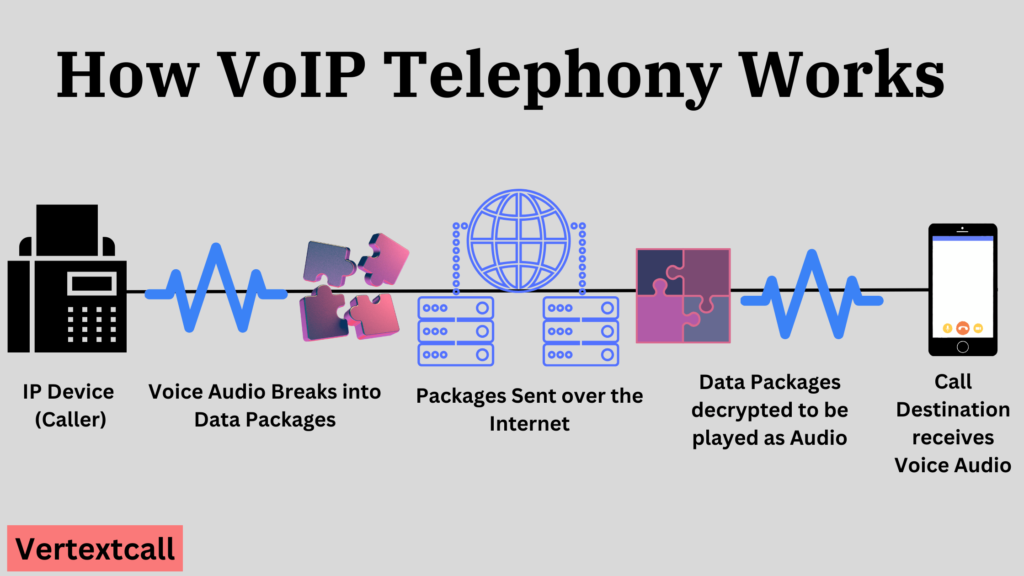
Components of VoIP
For VoIP technology to function perfectly, it relies on a set of essential components that work in synchronization. Here are the fundamental components that make up a VoIP system, supporting its function and ensuring its efficiency.
1/ IP Phones or VoIP Adapters (ATAs): IP phones are specialized hardware designed for VoIP communication, capable of converting analog voice signals directly into digital format. Alternatively, Analog Telephone Adapters (ATAs) allow conventional phones to be used for VoIP by performing the same conversion process.
2/ VoIP Servers: Central to VoIP communication, VoIP servers play a vital role in managing and routing calls over the internet. They serve as the core of a VoIP system, connecting all components and ensuring seamless operation, much like traditional PBX systems for standard phone lines.
3/ Gateways: Gateways are crucial for connecting VoIP systems with traditional phone networks, enabling uninterrupted communication between different communication methods. They convert voice and data formats as necessary to ensure compatibility and communication consistency.
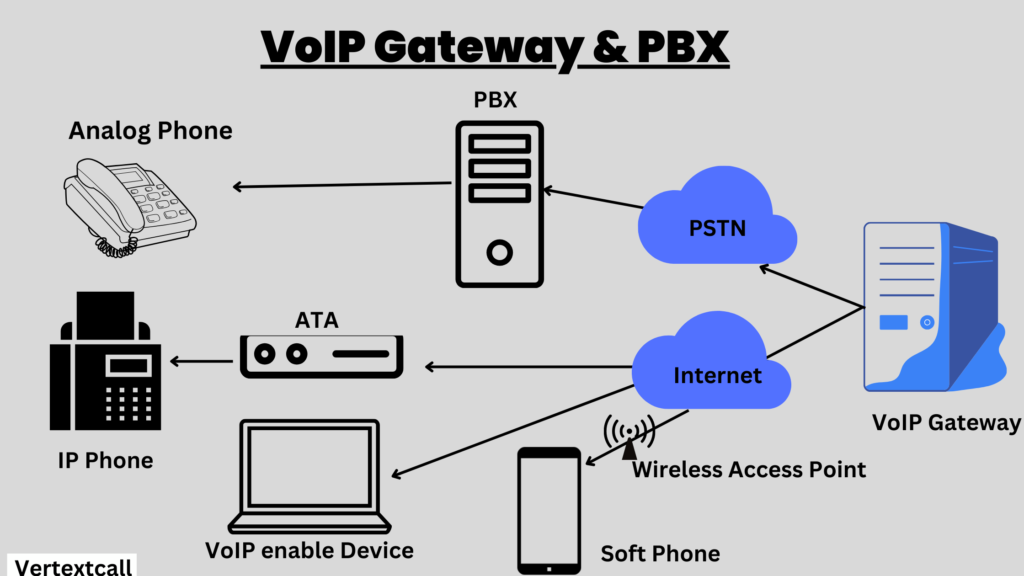
4/ Routers and Switches: Routers and switches are foundational to the network architecture that supports VoIP communication. They direct traffic on the network, guiding data packets to their destinations via the most efficient routes. VoIP-enabled routers connect multiple networks – a critical function that allows VoIP packets to travel across the internet, reaching beyond the local network to any destination worldwide.
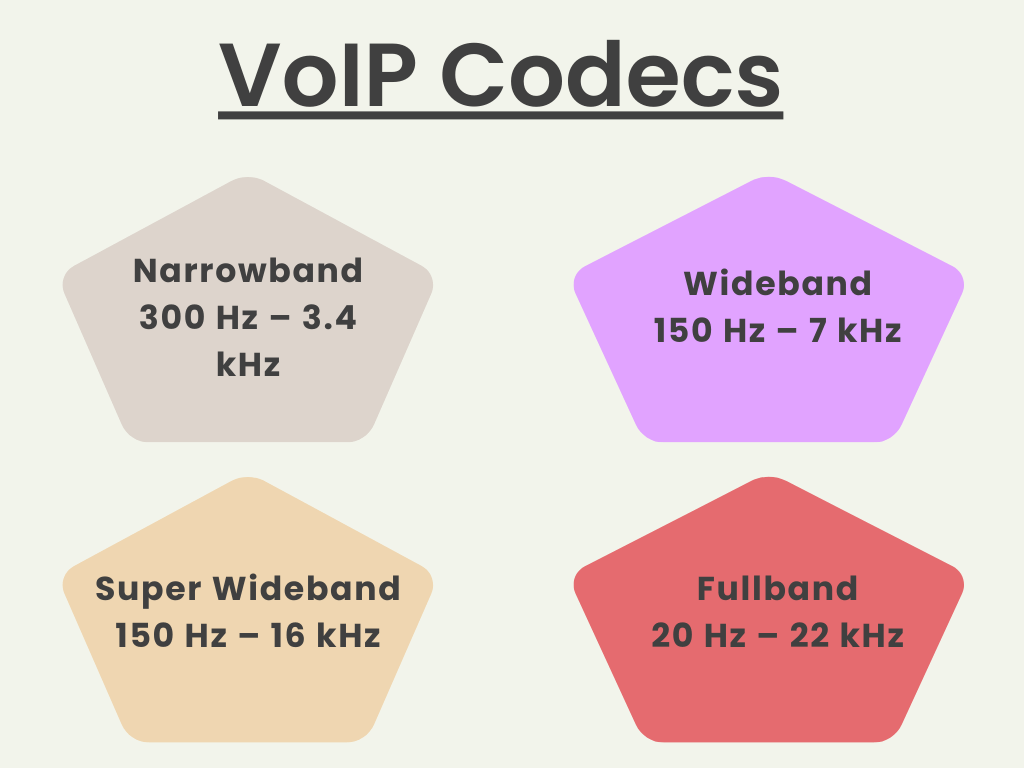
5/ Codec: Codec stands for “coder-decoder,” It’s a key technology that compresses voice data into smaller packets for efficient online transmission and then decompresses them upon receipt. This process is crucial for maintaining high-quality voice communication over the Internet, allowing for clear conversations without requiring large amounts of bandwidth.
6/ Softphones: Softphones are software-based phone systems, a crucial innovation that significantly enhances the way we communicate via VoIP. Unlike traditional or IP phones, Softphones eliminate the need for physical hardware for making calls. Installed on a computer or mobile device, they interact with the VoIP server via the internet, transforming these devices into a communication hub.
Types of VoIP
Understanding the various types of VoIP services is crucial if your business is aiming to make an informed decision on which system best fits its needs.
1/ Hosted VoIP Systems: Hosted VoIP solutions are managed by external providers, delivering all the benefits of VoIP technology without the need for in-house maintenance or hardware.
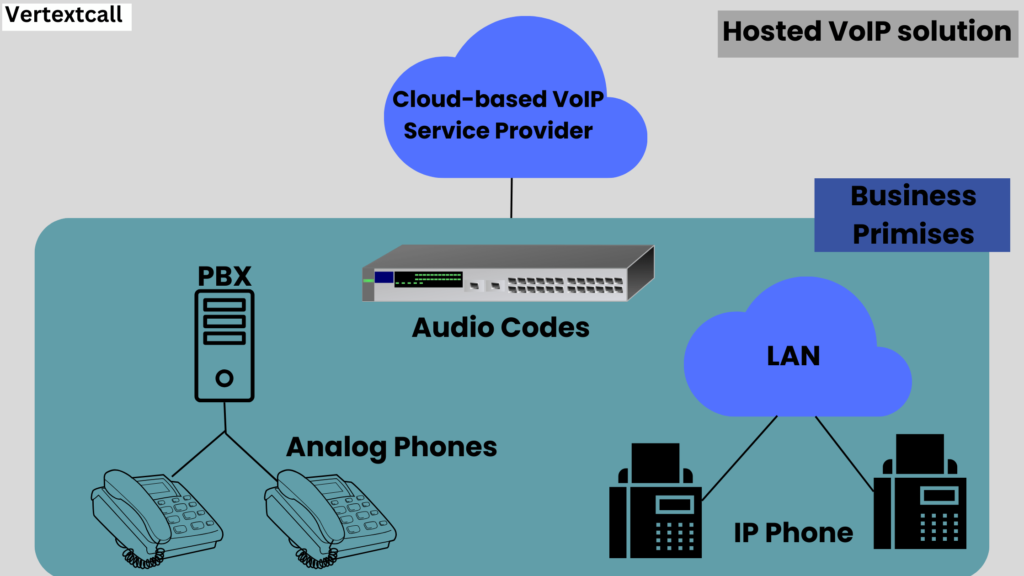
This model is particularly appealing for small to medium-sized businesses looking for advanced communication features with minimal investment in infrastructure.
2/ In-house VoIP Systems: Alternatively, an in-house or on-premises VoIP system places the control and responsibility of the VoIP infrastructure within the organization.
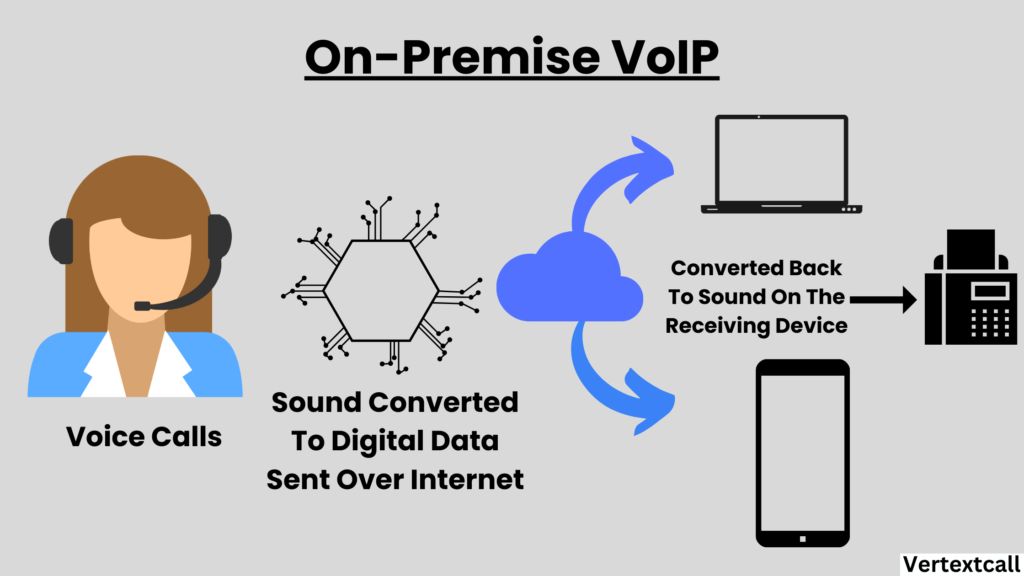
This approach is suited for larger businesses or those with specific compliance requirements, offering complete customization and control at the cost of increased investment and management.
3/ Hybrid VoIP Services: Hybrid VoIP services merge traditional telephony systems with VoIP technology, providing a transitional pathway for businesses upgrading their communication structures. This service allows corporations to maintain existing PSTN lines while incrementally integrating VoIP, offering a balance of reliability and innovation.
4/ Business VoIP Services: Specifically designed to meet the demands of corporate communication, business VoIP services offer a comprehensive suite of tools including, but not limited to, call forwarding, conferencing, voicemail to email, and CRM integration. These services cater to enhancing operational efficiency and connectivity in a professional setting.
5/ SIP Trunking: Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Trunking is a direct approach to VoIP that connects a business’s PBX system to the internet. Unlike traditional VoIP services, SIP Trunking utilizes a virtual connection, avoiding the need for physical phone lines and providing scalability and flexibility for growing businesses.
Related Readings:
VoIP Examples & Implications
1/ Enhancing Customer Service and Satisfaction:
Startups, more than any other business, rely on client relationships. VoIP tools enhance customer service with features like call routing, which ensures calls are directed to the most appropriate team member, and IVR, which allows for a personalized, automated response to customer queries.
2/ Remote Work Enablement:
VoIP significantly enhances the capability for remote work, which is a critical aspect of modern business operations. This technology empowers telecommunications, allowing employees to connect effortlessly to their office systems regardless of their physical location, via the Internet. VoIP for remote workers ensures they can access the full suite of office communication features from home or on the move, ensuring business continuity and efficiency.
3/ Advanced Analytics and Reporting:
With advanced analytics and reporting capabilities, VoIP technology enables businesses and IT professionals to monitor call quality, analyze usage trends, and evaluate customer interactions. By using this data, companies can make strategic decisions to enhance their communication strategies, boost customer satisfaction, and ultimately, drive business growth.
What are the advantages of VoIP?
Below are the primary advantages that make VoIP a better choice for businesses and individuals searching for efficient communication solutions:
- Cost Efficiency: VoIP offers a compelling benefit with its potential for substantial cost savings. Unlike traditional phone systems with high installation, maintenance, and call charges, VoIP significantly reduces expenses by utilizing internet connectivity. This cost-effective solution is particularly advantageous for long-distance and international calls.
- Portability: The global nature of the internet means VoIP services are not restricted by geographic location. Using your existing numbers, you can make or receive calls from any internet-connected spot — a crucial benefit for mobile workers and international businesses.
- Integration with Business Systems: VoIP technologies can integrate with existing business systems, such as Customer Relationship Management (CRM) tools, email, and conferencing platforms. This integration streamlines workflows, enhances productivity, and ensures a unified communication experience.
- Enhanced Security: With advanced encryption protocols and security measures, VoIP systems offer enhanced security for your communications. This is crucial in protecting sensitive information in current times where data breaches and eavesdropping are rising concerns.
- Scalability: With VoIP, you have the unique advantage of scalable communication solutions. Depending on your business’s growth and the fluctuation of your needs, you can easily adjust your VoIP system. This means that as you expand or scale down, your communication capabilities can easily adapt, ensuring you’re always equipped with the right tools without the need for substantial additional investments.
What are the downside of VoIP?
Despite the benefits offered by VoIP technology, you should also be aware of its limitations and challenges.
- Dependency on Internet Connectivity: The most fundamental requirement for VoIP is a reliable and fast Internet connection. This means, slow, inconsistent, or frequently interrupted internet connections can impact your VoIP call quality and reliability. This may result in dropped calls and poor voice clarity.
- Quality of Service (QoS) Management: Ensuring consistent call quality requires effective Quality of Service (QoS) configurations. In networks with heavy data traffic, prioritizing VoIP traffic to prevent delay (latency), jitter, and packet loss requires sophisticated network management, which can be a complex task for some organizations.
- Emerging Security Vulnerabilities: Although VoIP provides advanced encryption and security features, it remains vulnerable to cyber threats. Like all internet-based technologies, VoIP systems are at risk of hacking, phishing attacks, and security breaches. Organizations must be vigilant in implementing and upholding security measures to protect against these VoIP vulnerabilities.
- Power Outages: Unlike traditional landline phones that operate on a separate power supply, VoIP systems depend on power for the internet router and VoIP phone hardware. During power outages, VoIP services become inoperable unless equipped with backup power solutions, making communication impossible.
- Compatibility Issues: Integrating VoIP with current traditional telephony systems or specific business software platforms can present compatibility hurdles. Resolving these challenges might necessitate further hardware or software solutions investments to overcome the technological divide.
To know more check out our detailed article on: Advantages and disadvantages of voice over Internet protocol
What do you need for VoIP setup?
To establish a VoIP setup, several key components and requirements must be in place to ensure a smooth and efficient operation.
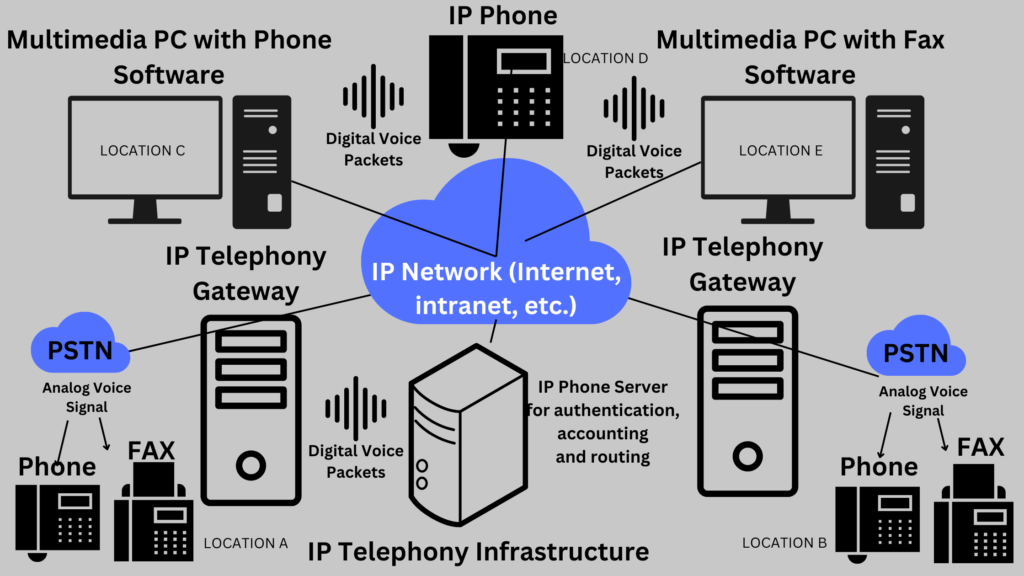
Firstly, a reliable internet connection with sufficient bandwidth is critical, as VoIP relies on the internet to transmit voice data. The quality and speed of your internet connection directly affect the clarity and reliability of VoIP calls.
Secondly, appropriate hardware is necessary. This may include IP phones, which are designed specifically for VoIP communication, or conventional telephones paired with an Analog Telephone Adapter (ATA) to convert analog signals into digital format.
For setups preferring not to use physical telephones, Softphones installed on computers or mobile devices can serve as an alternative, requiring only a microphone and speakers or a headset. VoIP cables, such as Ethernet cables, are also essential for connecting IP phones or other VoIP devices to your network.
A VoIP service provider is another critical requirement. Choosing a reputable provider will ensure access to necessary services and support for VoIP technology. This provider will offer the VoIP servers and gateways that allow your VoIP system to connect and communicate with other phone networks worldwide.
Furthermore, an internal network infrastructure that includes routers and switches is vital to manage the data traffic within your VoIP setup. This infrastructure must be capable of prioritizing VoIP traffic to maintain call quality over other types of internet usage.
Lastly, setting up VoIP may require specific software or applications, particularly if using Softphones or managing a VoIP system for a business. These tools offer features such as call routing, voicemail, and conference calling capabilities.
Traditional Phone Systems vs. VoIP
Features | Traditional Phone Systems | Voice over Internet Protocol |
Technology | Utilizes copper wires and analog signals for communication. | Employs internet protocol to transmit digital voice data. |
Installation and Maintenance | Requires physical infrastructure, which can be complex and costly to install and maintain. | Easier and less expensive to install and maintain because it uses existing internet infrastructure. |
Mobility | Limited mobility; tied to physical location of installed lines. | High mobility; calls can be made from anywhere with an internet connection. |
Scalability | Adding lines or expanding the system can be expensive and cumbersome. | Easily scalable with minimal cost; can adjust quickly to changing needs. |
Features | Basic features like call waiting, caller ID, and voicemail may require additional fees. | Comes with a wide range of features, such as video calls, text, voicemail-to-email, and more, often at no extra cost. |
Call Quality | Consistent call quality, but subject to interference from weather and infrastructure aging. | Call quality is high but can be affected by internet speed and bandwidth availability. |
Check out our detailed guide on: VoIP vs Traditional Phone Services
Protocols for VoIP
As mentioned earlier in the article within the VoIP ecosystem, certain protocols play a crucial role, including:
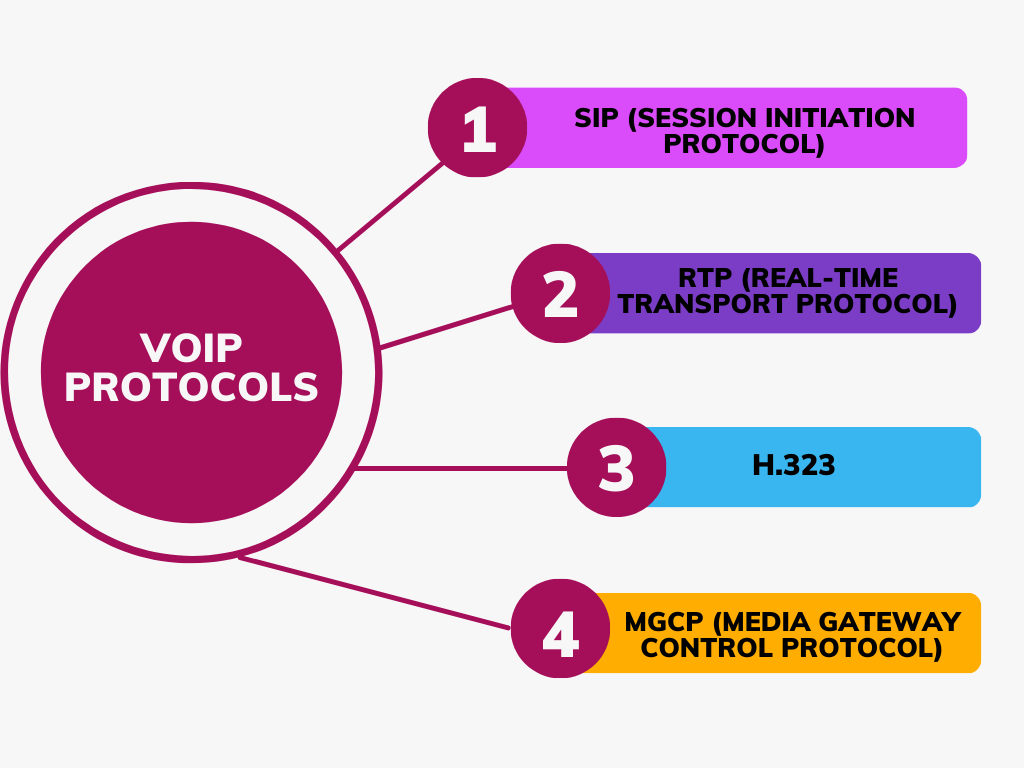
- SIP (Session Initiation Protocol): SIP stands for Session Initiation Protocol, which is a crucial standard used in VoIP systems to initiate, manage, and terminate voice communications over the Internet. It plays a fundamental role in establishing connections between two or more participants, ensuring smooth and efficient call setup, adjustment, and teardown.
- RTP (Real-time Transport Protocol): RTP is designed for delivering audio and video over the internet in real-time. It is used with SIP or other signaling protocols to manage the actual data transfer during a VoIP call.
- H.323: H.323 is one of the oldest VoIP protocols and provides specifications for real-time audio, video, and data communication over packet-switched networks such as the Internet. Although SIP has become more prevalent, H.323 is still used, especially in enterprise environments.
- MGCP (Media Gateway Control Protocol) and MEGACO/H.248: Both protocols are used for controlling media gateways on the internet. MGCP and MEGACO, the newer version of MGCP, play a crucial role in converting data from the traditional phone system to VoIP and vice versa, managing the flow and directing the voice data between networks and devices.
Must Read: What protocol does VOIP use
How does the FCC regulate VoIP?
To ensure the balance between innovation and public welfare, the FCC’s regulations are vital in guiding VoIP providers and users. Here are key directives from the FCC that must be followed to maintain compliance in the VoIP realm:
I. E911 Requirements:
In a traditional landline system, 911 services automatically detect a caller’s location. VoIP, however, presents unique challenges due to its mobile nature. Recognizing that every second counts in an emergency, the FCC mandates that VoIP providers enable E911 capabilities, ensuring that calls are accurately routed to public safety answering points (PSAP) operators who can dispatch help promptly.
II. Number Portability Regulations
Porting phone numbers, or transferring them between service providers, is a fundamental right for phone service subscribers. VoIP providers must follow FCC’s Local Number Portability (LNP) rules, ensuring that switching between VoIP and traditional services does not cause unnecessary disruptions for consumers.
III. Disability Access Requirements
The FCC promotes accessibility by requiring VoIP service providers to ensure that individuals with disabilities have equal access to telecom services. This includes supporting technologies like Telecommunications Relay Services (TRS) and ensuring compatibility with assistive devices.
IV. Consumer Protection Rules
To prevent fraud and abuse in the VoIP sector, the FCC establishes guidelines for fair practices, transparent pricing, and empowering users with control over service features. Providers are required to safeguard consumers’ calling records’ privacy and implement procedures for addressing customer complaints and resolving disputes.
Troubleshooting problems with a VoIP service
Follow these steps to troubleshoot the most common VoIP issues with confidence.
Step 1: Perform Basic Checks
When a VoIP call fails to connect or suffers from poor quality, begin with the simplest checks:
- Verify Hardware Setup: Confirm that all equipment, from the handset to the router, is powered on and properly connected.
- Validate Internet Connection: Ensure that your internet is operational and check its speed to confirm it meets VoIP requirements.
- Review Equipment Settings: Ensure that all VoIP hardware and software are configured correctly.
Step 2: Check for Interference
External factors can significantly impact VoIP performance. Troubleshoot by:
- Identifying Network Overload: High network usage or unreliable connections can affect VoIP quality.
- Seeking Out Network Security Issues: Firewalls and security settings can mistakenly block VoIP traffic.
- Addressing Environmental Interference: Environmental factors such as power lines or other electronics can cause interference.
Step 3: Narrow Down the Issue
If the problem persists, use a process of elimination to pinpoint the cause:
- Switch Hardware: Test with different phones and use standard analog phones to verify problems are not device-specific.
- Isolate Network: Connect your VoIP system to a separate network to discover if the issue is network-related.
- Consult Manuals: Manufacturers often include detailed troubleshooting steps in their product manuals; always consult these resources.
Implementing these steps systematically is your best approach to resolving VoIP service problems.
Choosing a VoIP provider
Choosing an appropriate VoIP provider is a pivotal step for any organization, and affects both its internal operations and the quality of customer interactions. When selecting a VoIP service, evaluating several key factors is essential to ensure that your decision supports current needs and future growth.
1/ Reliability: Seek providers with a proven track record of uptime and dependability. Your business communication relies on consistent service without interruptions.
2/ Quality of Service (QoS): High-quality audio is non-negotiable. Providers should offer superior QoS controls to prioritize VoIP traffic, ensuring clear calls even during network congestion.
3/ Customer Support: Choose a provider that offers reliable customer support, including 24/7 availability. Quick and competent support can minimize potential service disruptions.
4/ Scalability: Your VoIP solution should grow with your business. Look for providers that offer easy scalability options, allowing you to add or remove services as your business needs progress.
5/ Security Features: Given the sensitive nature of voice communications, ensure your provider offers advanced security features, including encrypted calls and protection against common cyber threats.
6/ Pricing and Plans: Evaluate the cost-effectiveness of different plans. Consider not only the monthly fees but also the cost of additional features and international calling rates, ensuring there are no hidden charges.
Frequently asked questions
Q1) What is VoIP and What is its purpose?
Ans: Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) is a technological advancement that transforms the way we communicate. It allows audio and video calls to be made through various internet-connected devices without the need for a conventional phone service. Its purpose is to provide a more flexible and cost-effective communication option for both personal use and businesses.
Q2) Can you get VoIP for free?
Ans: Yes, there are free VoIP services available; however, their features and capabilities are often limited compared to paid versions. Free VoIP solutions may be suitable for individuals or small-scale uses like staying connected with close ones or for budget-conscious small startups.
Q3) Can I use a VoIP phone as a regular phone?
Ans: No, a VoIP phone cannot be used exactly as a regular phone, which is connected through traditional landline service. VoIP phones are designed to work over the Internet by converting voice signals into digital data. However, they often resemble traditional phones in appearance and functionality, offering similar features such as call forwarding, voicemail, and even directory services.
Q4) Does VoIP work with Wifi?
Ans: Yes, VoIP works well with Wi-Fi. This compatibility is one of the key features that makes VoIP highly preferable for modern businesses and personal use. When connected to Wi-Fi, VoIP phones and devices can send and receive voice data over the Internet, allowing for communication without traditional phone lines.
Q5) How does VoIP connect to a cell phone?
Ans: VoIP can connect to a cell phone through a VoIP application installed on the device. Essentially, the application allows the cell phone to act as a VoIP phone, enabling it to send and receive calls over the internet instead of the cellular network. To use VoIP on a cell phone, you need a stable internet connection, either via Wi-Fi or their mobile data plan, and a subscription to a VoIP service provider.
Q6) How much does it cost to install VoIP?
Ans: The cost of VoIP installation varies based on deployment scale, service provider choice, and hardware needs. Initial expenses may include subscription fees of $25 to $35 per line per month and optional handset purchases ranging from $50 to $400 each.

