In the space of business communications, the decision between a digital phone system and Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) is crucial. Both have their merits and limitations but choosing the right one can give your operations a significant edge.
This guide will explore the key differences between digital phone systems and VoIP which will help you make a better choice that aligns with your business objectives and communication needs clearly and thoughtfully.
What is VoIP & its Functionality
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) transforms communication by utilizing the Internet to transmit voice data. Unlike traditional digital phone systems using circuit-switched networks, VoIP encodes voice into data packets for transmission over an IP network, removing the dependence on conventional telephone lines.
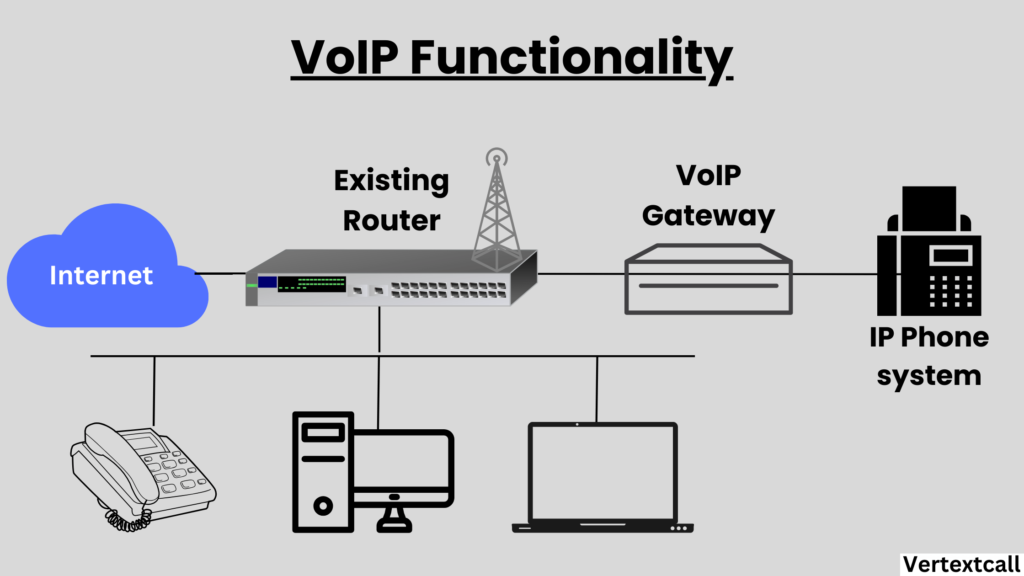
This technology provides your business with various features like virtual meetings, call forwarding, file sharing, voicemail-to-email transcription, CRM system integration, video conferencing, and auto-attendant services, enhancing operational efficiency and communication capabilities.
Furthermore, the flexibility of VoIP supports remote work, driving its increasing popularity among businesses looking for cost-effective, scalable, and advanced communication options.
What is a digital phone system?
A Digital Phone System functions by converting voice into digital signals, which are then transmitted over a dedicated network used for the company’s internal communications. By employing digital switch technology, these systems ensure reliable voice quality and offer scalability with digital line infrastructure.
Many businesses favor digital phone systems for their consistent call quality, and features like call forwarding, call waiting, and voicemail. However, it’s important to note that these systems still depend on physical lines and require onsite hardware maintenance, potentially affecting flexibility and cost-effectiveness.
Key Differences between Digital Phone Systems and VoIP
Digital phone systems and VoIP systems are used for voice communication within businesses, but they operate in distinct ways. Here are the key differences between the two:
1/ Infrastructure and Setup Considerations:
When you compare the infrastructural requirements of Digital Phone Systems and VoIP, you’ll notice significant differences in their setup and ongoing maintenance needs. Digital Phone Systems demand a reliable physical infrastructure, including in-house wiring, phone hardware, and a PBX setup housed within your business premises. This leads to higher upfront costs and requires a dedicated space for the hardware.
On the other hand, VoIP services primarily operate through an internet connection, with minimal onsite equipment needed. The simplicity of installation and the option to use your existing computers or smart devices for communication significantly reduces initial investment and physical space requirements. This streamlined setup is appealing to businesses looking for a more modern, flexible communication network.
2/ Transmission Methods:
Digital systems operate on a reliable circuit-switched network, allocating a dedicated line throughout your call to ensure consistent call quality.
In contrast, VoIP functions on a packet-switched network, breaking your voice data into digital packets transmitted over the internet and reassembled upon arrival. This approach enables flexible resource allocation, maximizing your network efficiency.
Although both systems prioritize clear communication, VoIP’s performance is linked to your internet bandwidth.
3/ Managing Maintenance:
Maintenance demands vary significantly between digital phone systems and VoIP. As someone managing a business’s communication infrastructure, you must balance the traditional upkeep of a digital system with the more dynamic requirements of VoIP. Digital systems may require more maintenance due to physical components such as wires and switches that may wear out or need to be updated. Resources should be allocated for potential hardware repairs or replacements.
On the other hand, VoIP maintenance primarily focuses on software updates and network configurations rather than hardware. As VoIP operates over the internet, ensuring strong cybersecurity measures and reliable internet connections are crucial for its maintenance. While setting up a VoIP system initially may be complex, long-term maintenance can be simpler with a solid IT infrastructure in place.
4/ Assessing Scalability and Flexibility:
When you address the scalability and flexibility of communication systems, it’s essential to understand how each system adapts to your business’s growth and changing needs. Digital Phone Systems are somewhat limited in this aspect due to their dependence on physical lines and hardware. To scale up, you need to install additional lines and equipment, which could be both time-consuming and costly.
With VoIP, scalability is more adaptable and less resource-intensive. You can easily add or reduce the number of users as your operations expand or downsize, all with minimal physical modifications required. Moreover, VoIP’s compatibility with various devices supports a mobile and increasingly remote workgroup, offering flexibility to your workforce.
5/ Cost Implications:
The investment in Digital Phone Systems includes not just the purchase of hardware, but also installation costs, ongoing maintenance, and the potential for future upgrades as technology progresses. These expenses add up, making it a substantial consideration, particularly for small to medium-sized enterprises.
On the flip side, VoIP services offer a cost-effective alternative. Since VoIP relies on your existing internet connection, the need for physical phone lines and hardware is greatly minimized, leading to reduced upfront costs. Moreover, with most VoIP service providers offering subscription-based models, you can anticipate and budget your expenses more effectively.
Such models often include software updates, reducing the likelihood of redundancy and the need for expensive hardware replacement. This can result in significant cost savings and a more predictable expenditure over time.
6/ Bandwidth Requirements:
When examining bandwidth, it’s crucial to evaluate your business’s data needs. For a Digital Phone System, bandwidth isn’t a primary concern since the system functions on traditional copper wire technology, providing dedicated communication lines that minimize interference risks.
Conversely, with VoIP, bandwidth is a key consideration. Given that VoIP relies on the Internet for voice calls, it’s vital to ensure your network can handle increased data flow without compromising call quality.
VoIP bandwidth requirement
VoIP Usage | Bandwidth Requirement |
Minimum bandwidth per VoIP line | 100 Kbps |
VoIP telephone calls (optimal performance) | 5-25 Mbps download speed |
Email and web browsing | 1 Mbps download speed |
File downloading | 10 Mbps download speed |
HD video teleconferencing | 6 Mbps download speed |
7/ Power Capacity:
Traditional Digital Phone Systems typically obtain power from the same copper wire network that transmits the voice signal, affording them operational durability even during an electrical outage. This can be an invaluable feature for your business if constant availability is critical.
In contrast, VoIP systems depend on power from your local electricity supply to run the necessary equipment like modems, routers, and the phones themselves. This means that without proper backup solutions, such as uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), a loss of local power can lead to a complete communication shutdown.
You need to assess the power reliability in your area and consider whether your business requires operational measures to guard against power interruptions that could affect your VoIP system.
What are the advantages of IP phones?
IP (Internet Protocol) phones offer various advantages for your business over digital phones. Here are some key benefits:
- Cost Efficiency: VoIP systems excel in cost management, offering your business an economically viable solution for global communication. Although the initial investment in internet-based phone systems may exceed that of traditional setups, the operational expenses often surpass the startup costs. VoIP enables free or significantly reduced rates on long-distance and international calls.
- Enhanced Call Management: VoIP systems often include advanced call management features such as call routing, queuing, and analytics for detailed oversight and optimization of communication strategies.
- Quality of Service (QoS): Technologies dedicated to improving VoIP call quality, such as advanced codec algorithms and QoS optimizations, ensure high-quality audio and video communication.
- Easy Integration: Many VoIP systems can integrate with other business software, providing a continuous workflow and enhancing the synergy between communication and business processes.
- Flexibility and Mobility: The Inbuilt flexibility of VoIP is a significant advantage for your mobile employees and distributed workforces. It allows for calls and other communications across various devices, accessible from any location with an internet connection.
What are the disadvantages of IP phones?
- Dependency on Internet Connectivity: With IP phones effective communication relies heavily on the dependability and speed of your Internet connection. Any interruption in internet service can directly affect the functionality of your VoIP system.
- Security Concerns: It’s crucial to recognize that VoIP systems, being internet-based, are open to cyber threats like phishing, malware, and Denial of Service (DoS) attacks. You need to have strong security protocols to safeguard your systems.
- E911 Limitations: E911 services are crucial when implementing VoIP solutions. Unlike traditional telephony, VoIP systems lack fixed physical locations for emergency responders due to their internet-based nature. Your organization must implement Enhanced 911 (E911) to link a physical address with the caller’s number.
- Quality of Service Variances: Despite advanced QoS technologies, VoIP call quality can still suffer from latency, jitter, and packet loss if your network is not correctly optimized or if bandwidth is insufficient.
- Compliance and Privacy Issues: Ensure that your selected VoIP solution aligns with industry regulations and standards, particularly in terms of data sovereignty and privacy.
To know more check out our detailed article on: Advantages and disadvantages of IP phones
Why are digital phones better?
Digital phones offer several advantages that make them a favorable choice for many businesses, depending on their needs and circumstances. Here are some reasons why digital phones might be considered better in certain situations:
- Enhanced Audio Quality: You can experience superior audio clarity with digital phones due to advanced digital signal processing that removes static and interference.
- Greater Scalability: As your organization grows, you can scale your digital phone system more efficiently, adding lines and features easily without extensive hardware upgrades.
- Mobility and Flexibility: Digital phones enable you with the ability to move freely and remain connected, as they can be used anywhere with a broadband connection, making remote work uninterrupted.
- Easier Integration: You can seamlessly integrate digital phones with various business applications like Slack, Zoom, and Microsoft Teams. This integration not only improves workflows and boosts productivity but also ensures a more efficient exchange of information across different departments within the organization.
- Cost Savings: Over time, you’ll find that digital phones are more economical due to reduced call costs—especially for long-distance and international calls—and because they require less physical infrastructure.
- Enhanced Security: With the right protocols in place, digital phone systems can offer you better security against eavesdropping and other security threats compared to analog systems.
What is the difference between VoIP and a virtual phone system?
The following table provides a brief overview of the differences between VoIP and a virtual phone system, highlighting their respective technologies, infrastructures, scalability, cost structures, and feature sets.
Aspect | VoIP | Virtual Phone System |
Definition | Voice over Internet Protocol is an innovative tech enabling voice call transmission via Internet connectivity. | A virtual phone system is a cloud-based communication platform that offers business phone services over the Internet. |
Cost Structure | Costs may include initial setup fees for hardware and software, along with ongoing service fees from VoIP providers. Long-distance and international calls may have separate charges. | Usually functions using a subscription model, where pricing levels are determined by the user count and necessary features. Some providers offer all-inclusive plans with unlimited calling. |
Usage | Can be used for various applications, from personal calls to enterprise-level phone systems. | Primarily used by businesses for managing calls, integrating with CRM systems, setting up virtual numbers, etc. |
Hardware | Requires VoIP-compatible devices like IP phones, ATA adapters, or softphones installed on computers or smartphones. | Does not necessarily require specific hardware; can often work with existing phones or softphones, but may offer compatible hardware for more features. |
Features and Scalability | Offers basic calling features like call waiting, caller ID, and voicemail, but more advanced features depend on the service provider. Scales with the capabilities of the VoIP system. | Typically includes a wide range of features such as call forwarding, auto-attendants, analytics, and integrations with other business tools. Easily scalable with subscription plans often offering tiered levels of service. |
Related Reading: Difference between VoIP and virtual phone systems
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1) What is the difference between IP phones and digital phones?
Ans: The main difference between IP phones and digital phones is that IP phones use voice over internet protocol technology to send and receive voice communications via the internet. They convert audio into data packets, which are transmitted over a data network, enabling use on any internet-connected device globally. Digital phones, on the other hand, convert sound into digital signals but still operate over traditional PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network) lines with dedicated digital infrastructure.
Q2) What is the difference between a digital phone and a landline?
Ans: The difference between a digital phone and a landline is that a landline typically refers to traditional analog phone systems that use copper wires for transmitting voice signals. In contrast, a digital phone, although falling under the landline category, operates by transmitting digital instead of analog signals. This means that voice signals are converted into digital data before transmission over the network. Digital phones provide better voice quality and can offer more features than analog landline phones due to this digital transmission.
Q3) Is VoIP considered digital?
Ans: Yes, VoIP is considered a form of digital telephony, as it involves the encoding of voice into digital data which is then transmitted over the internet. Unlike conventional telephony using circuit-switched networks, VoIP functions on packet-switched networks. This enables the utilization of data networks to handle voice calls, making the transmission inherently digital.
Q4) Are digital phones the same as VoIP?
Ans: No, digital phones are not the same as VoIP. Although both use digital signaling to improve call quality the way they transmit voice data differs. Digital phones typically use digital signals over the established Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN), whereas VoIP transmits voice data via the Internet. Each system has unique infrastructure and connectivity requirements, which results in differing advantages and limitations based on specific business needs.
Must Read: Difference between VoIP and PSTN

