Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) has transformed our connectivity, yet not all VoIP solutions are equal. This article explores the difference between Proximity VoIP and Normal VoIP, examining their features and the technological foundations that set them apart. With this insight, your business can make well-informed decisions tailored to your specific communication requirements.
Table of differences between Proximity VoIP and Normal VoIP
Th following table provides a clear overview of the distinctions between Proximity VoIP and Traditional VoIP across various aspects of their operation and infrastructure.
Aspect | Proximity VoIP | Traditional VoIP |
Routing Method | Based on the physical location proximity of users | Fixed server routing |
Geographic Routing | Directs calls to the nearest data center or server | Centralized routing through a fixed server |
Load Balancing | Dynamic load balancing based on real-time data | Limited or manual load balancing |
Call Quality | Generally higher due to reduced latency | May experience higher latency in some cases |
Scalability | Highly scalable with seamless expansion | Scaling may be complex and require infrastructure updates |
Redundancy | Often includes redundancy and failover measures | Less reliable redundancy and failover mechanisms |
Configuration | Automatic configuration based on proximity | Requires manual or predetermined server settings |
Maintenance | Less manual intervention for routing optimization | More manual configuration and maintenance |
What is Normal VoIP
Voice over Internet Protocol, or Traditional VoIP, is a communication system that allows your businesses to communicate multimedia over Internet networks. This technology enabled the transmission of voice calls, video calls, and other communication forms without relying on traditional telephone lines.
Through packet-switched networks, conventional VoIP transforms analog voice signals into digital data. This digitized data is subsequently transmitted across the Internet or private data network infrastructures.
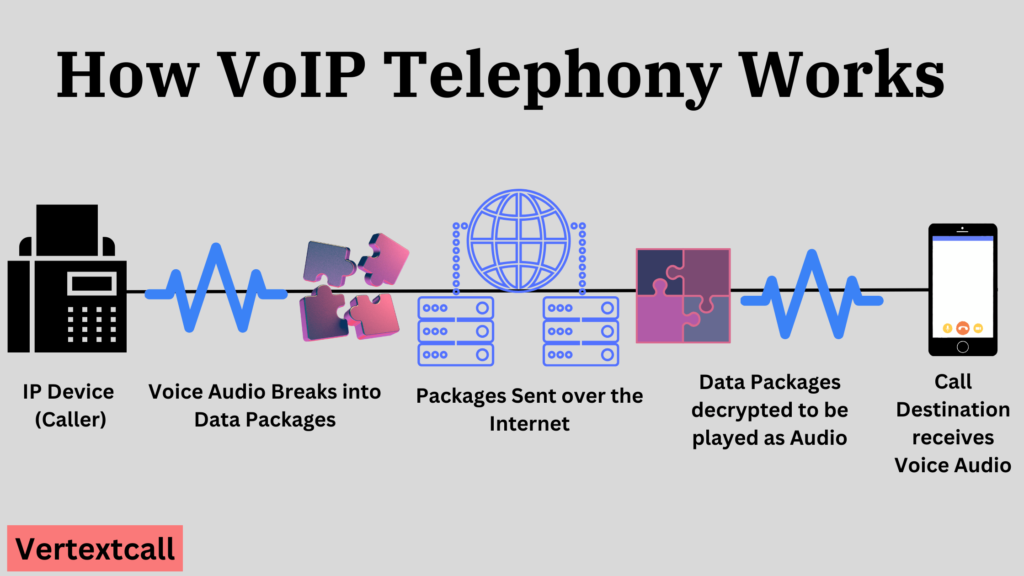
In addition to fundamental features such as call forwarding, caller ID, voicemail, conference calling, and fax-to-email, VoIP offers advanced functionalities that improve flexibility and integration with other business tools.
While VoIP delivers benefits like cost savings and scalability, it’s essential to consider potential drawbacks like dependency on internet connection quality and exposure to power outages.
What is VoIP chat?
VoIP chat is a segment of VoIP communication tech that allows real-time text messaging over internet protocol networks. Unlike standard instant messaging, VoIP chat is usually integrated into VoIP applications, enhancing communication beyond traditional telephony limits. It merges quick text exchanges with the full VoIP suite, offering the flexibility to switch to voice or video calls instantly.
Related Reading: What is the difference between VoIP and Video conferencing
What is Proximity VoIP
Proximity VoIP is a specialized version of VoIP technology tailored to prioritize connectivity in nearby networks, like within your building or local area. This system identifies your physical proximity to optimize communication and provide high-quality audio with less delay.
Unlike Traditional VoIP, which works globally regardless of your location, Proximity VoIP aims to enhance your experience when you and the other party are close by. You can benefit from local network infrastructure with Proximity VoIP, improving call quality and stability by reducing data travel distance.
This advantage is especially useful in places like busy events or commercial places where internet connectivity may be challenging. However, Proximity VoIP can enhance call quality in specific situations, it might not have the universal reach of Traditional VoIP. Its effectiveness could rely on local network setup.
Key Differences between Proximity VoIP and Traditional VoIP
Proximity VoIP and Traditional VoIP differ primarily in their approach to routing calls and the way they handle network infrastructure. Here are the key differences between the two:
1/ Infrastructure: Centralized vs. Distributed
Traditional VoIP relies on a centralized infrastructure where voice data and processing flow through one or a few main data centers. Proximity VoIP, on the other hand, employs a distributed architecture, spreading data processing among multiple servers located closer to users to reduce data travel distances.
The centralization of Traditional VoIP may lead to obstructions based on the capacity and effectiveness of the single or main data center. In contrast, Proximity VoIP’s distributed approach provides redundancy and better manages peak loads without significantly declining performance.
2/ Latency in Calling:
Voice data packets in normal VoIP often travel long distances to reach a central server before being directed to their final destination. This travel time can cause noticeable delays in communication, impacting call quality.
On the other hand, Proximity VoIP utilizes strategically located data centers to maintain voice data packets on a more direct path. This approach significantly reduces latency problems, ensuring a smoother conversation flow comparable to traditional phone lines. By leveraging the proximity factor, Proximity VoIP enhances the responsiveness of VoIP communication while aiming to preserve high accuracy in every interaction.
3/ Quality of Service:
Quality of Service (QoS) stands as a critical benchmark for telecommunications solutions, directly affecting the end-user experience. With Traditional VoIP, QoS can vary based on factors such as bandwidth availability and internet traffic, leading to inconsistency in call quality. As network conditions fluctuate, you may encounter disruptions or variable call clarity, which can undermine the perceived reliability of the service.
Proximity VoIP offers a solution to address these issues by leveraging a network of localized data centers. This setup promotes a more stable and uniform QoS by minimizing the variables that typically affect traditional VoIP services. The localized approach facilitates a reliable network condition, ensuring greater consistency in voice communication quality. By strategically distributing data centers, the aim is to provide a consistent communication experience that remains reliable even during fluctuating network traffic.
4/ Scalability:
Scalability stands as a fundamental element in any communication technology. While traditional VoIP can scale to a degree, it often demands significant infrastructure investments with growing user needs. Consequently, this complexity and potential failure points may arise as the centralized system expands.
On the other hand, Proximity VoIP solutions offer a simpler scalability approach by allowing the addition or removal of local service points based on specific requirements, providing flexibility and ease of management.
5/ Geographical Dependency:
Proximity VoIP, known for its efficiency in reducing travel distance for voice packets, is particularly advantageous in specific geographic regions. This optimization helps minimize latency and enhance call quality, making it a preferred choice for businesses with distributed teams.
On the other hand, Traditional VoIP, while also offering reliable communication, is less influenced by geographic factors due to its established infrastructure and widespread accessibility across various regions globally.
Advantages of proximity VoIP
Proximity VoIP offers several advantages over traditional VoIP systems, particularly in terms of call quality, reliability, and scalability. Here are some of the key advantages of Proximity VoIP:
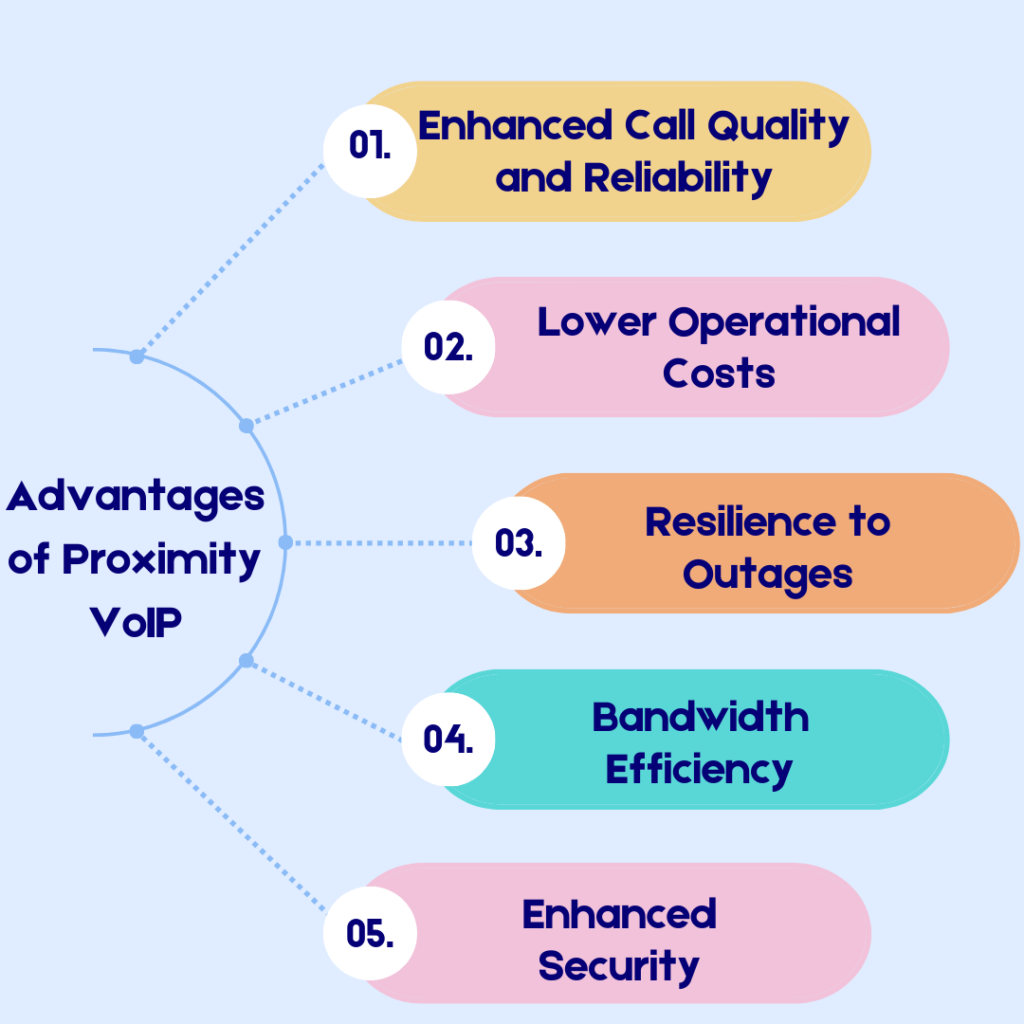
1/ Enhanced Call Quality and Reliability: Proximity VoIP’s localized data processing effectively minimizes latency and jitter, leading to enhanced voice quality and reduced call drops. This reliability is vital for businesses relying on uninterrupted communication for customer service and operational success.
2/ Lower Operational Costs: Businesses using Proximity VoIP could experience lower operational costs. By reducing reliance on centralized infrastructure and utilizing current internet access, your business can notably decrease hardware investments and maintenance expenses.
3/ Resilience to Outages: The decentralized nature of Proximity VoIP means that a failure at one node has less impact on the network’s overall functionality, maintaining strength and guaranteeing continuous availability.
4/ Bandwidth Efficiency: Utilizing local data centers reduces bandwidth needs for transmitting voice data across long distances. This decrease can ease network congestion and enhance overall performance efficiency.
5/ Enhanced Security: A decentralized infrastructure can provide increased security by ensuring that communication data is not centralized in one location, thus lowering the likelihood of extensive data breaches.
How does Proximity Voice chat work
Proximity VoIP operates on the principle of minimizing latency and maximizing voice quality by routing voice packets through the shortest path possible. It achieves this by decentralizing the necessary processing – distributing it across various nodes, typically closer to the network edge.
This ensures that data travels a minimal distance, reducing the time for voice packets to reach their destination, thus enhancing real-time communication capabilities.
As discussed above, proximity VoIP is especially advantageous in scenarios where users are geographically spread out, as it leverages local internet resources to facilitate high-quality voice transmission with fewer delays and jitter than traditional VoIP systems that rely on a central server hundreds or thousands of miles away.
What is the difference between VoIP and Voice chat
VoIP and voice chat are both technologies used for transmitting voice communication over the Internet, but they differ in several key aspects:
1/ Intended Use: VoIP is primarily tailored for professional environments, offering a wide range of features ideal for business phone systems. On the other hand, voice chat is commonly found within instant messaging platforms, catering to informal and spontaneous conversations.
2/ Call Quality and Reliability: VoIP services typically focus on ensuring high call quality and reliability. They utilize advanced codecs and protocols to enhance voice clarity, making them ideal for formal corporate communications. On the other hand, voice chat may prioritize convenience and quick connectivity over quality.
3/ Features and Integrations: VoIP platforms are typically loaded with features – including conference calling, call forwarding, voicemail, and CRM integrations – that support complex business operations. In comparison, Voice chat applications offer a more streamlined set of features focused on ease of use and quick casual communication.
4/ Infrastructure and Scalability: VoIP solutions are established on a reliable infrastructure to meet scalability and enterprise-level needs. In contrast, voice chat services run on a flexible, often cloud-based platform that can quickly adapt to changing user numbers with less emphasis on scalability.
5/ Cost Implications: VoIP services are tailored to suit business budgets, providing cost-effective communication solutions on a larger scale. While voice chat services may be free or cheaper, they might lack the comprehensive features needed for professional use without additional premium options.
6/ Security and Compliance: VoIP solutions are designed with secure security measures and regulatory compliance like HIPAA or GDPR. In contrast, voice chat apps targeting a wide user base may not meet the same data protection and regulatory standards.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1) Is VoIP the same as Proximity Chat?
Ans: No, VoIP and Proximity chat are not the same. VoIP is a broad term that refers to any voice communication transmitted over the internet, which is primarily used for purposeful and ongoing communication typical in business and professional environments. Proximity chat, however, is usually a feature within a broader voice communication system that enables you to engage in voice interactions based on your virtual or physical proximity to other users.
Q2) Is Facetime considered VoIP?
Ans: No, FaceTime isn’t typically classified as VoIP. While it enables voice and video communication over the Internet, it differs from typical VoIP services in several ways.
Q3) How do I use my analog phone with VoIP?
Ans: To use an analog phone with VoIP, you will need an Analog Telephone Adapter (ATA). This connects your traditional phone to the digital network used by VoIP services. Once connected, the ATA converts the analog signal from your phone into digital data for transmission over the Internet.
To initiate this setup, connect the ATA to your router or internet connection, then plug your phone into the ATA. After configuring the device according to the VoIP provider’s instructions, you should be able to use your analog phone for VoIP calls. It is important to ensure that the chosen ATA is compatible with your VoIP service for seamless operation.
Q4) What is Proximity in the context of VoIP communication?
Ans: In the context of VoIP communication, Proximity refers to a network design approach that aims to enhance call quality by reducing latency. This is achieved by strategically placing interconnected nodes to create shorter routing paths for voice data packets.
The focus on proximity aims for clearer voice quality and quicker connections. However, this setup requires a strong security protocol due to its decentralized nature, adding complexity to network management.

