In today’s fast-paced business domain, selecting the right communication system is more crucial than ever before. With the rise of modern technology, Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) has emerged as a strong contender against traditional landline phones.
This comprehensive comparison guide explores deep into the key distinctions between VoIP and landline telephones, providing you with valuable insights to make an informed decision tailored to your business requirements.
Table of differences between VoIP and Landline
Aspect | VoIP | Landline |
Technology | Transmits voice calls over the internet. | Uses traditional copper wires or fiber optic cables to transmit voice signals. |
Cost | Generally lower cost, especially for international calls. | Higher cost, especially for long-distance and international calls. |
Equipment | Requires a stable internet connection and VoIP-compatible hardware such as IP phones or software-based clients. | Uses traditional telephones connected to a physical phone line. |
Flexibility | Offers more flexibility in terms of mobility and scalability. | Limited mobility, typically tied to a fixed physical location. |
Features | Offers advanced features like video calling, voicemail-to-email, and conference calling. | Basic features such as call waiting, Speed Dialing, and caller ID. |
Reliability | Susceptible to internet outages or quality issues. | Generally more reliable with minimal service disruptions. |
Accessibility | Accessible from any location with an internet connection. | Limited to areas with physical phone line infrastructure. |
Installation | Generally easier to set up, often plug-and-play with minimal installation required. | Requires professional installation of physical phone lines and equipment. |
Integration | Integrates well with other internet-based services and applications. | Limited integration with other digital services. |
Security | Might be open to cybersecurity risks such as hacking or eavesdropping. | Generally considered more secure due to dedicated physical infrastructure. |
Future Outlook | Declining usage, gradual transition to digital | Declining due to emergence of newer technologies |
What is VoIP
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) revolutionizes voice communication by utilizing a broadband internet connection instead of the conventional analog telephone system. This innovative method converts your voice signals into digital data, allowing for phone calls to be made from computers, specialized VoIP phones, or traditional telephones with specialized adapters.
VoIP also offers practical features beyond voice calling, including call forwarding, voicemail, and even faxing capabilities. This technology provides better connectivity and cost-effectiveness, particularly for businesses requiring global communication.
By converting voice into data packets, VoIP eliminates the need for traditional telephone lines or cellular networks, offering a flexible and scalable communication solution.
How does VoIP work
VoIP functions by taking your voice signals and turning them into digital packets. These packets travel through the internet just like any other type of data, such as email or a web page. Here’s how this happens in a step-by-step:
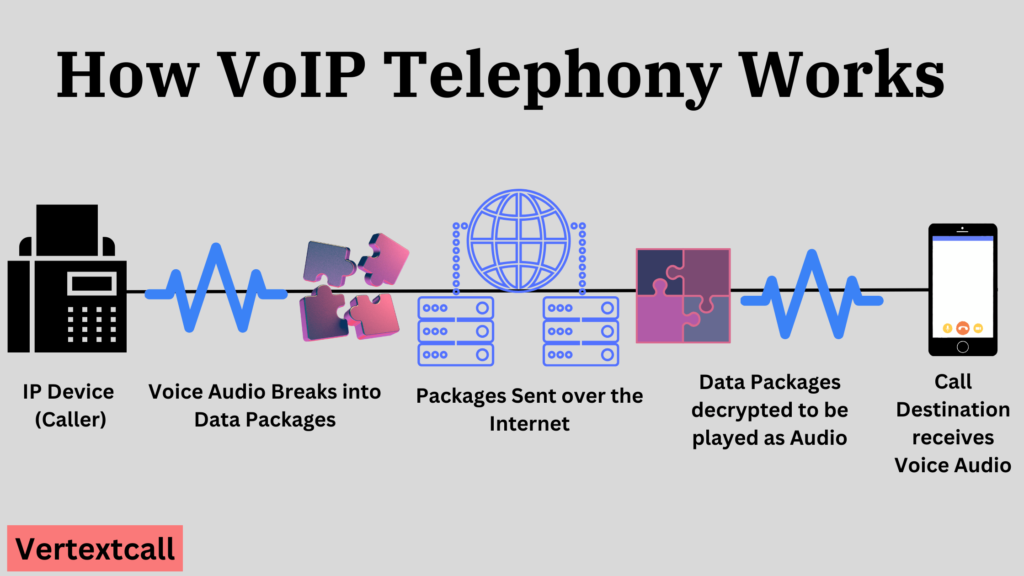
- Voice Conversion: When you talk into a VoIP-enabled device, your voice gets captured and transformed into digital data.
- Data Transmission: Next, these digital data packets are sent across the internet to their intended recipient. This process is similar to sending an instant message; only instead of text, it’s your voice being sent.
- Reconversion to Voice: Once these packets arrive at their destination, they are reconverted back into voice signals. This allows the person on the other end to hear what you said, just as if you were speaking on a traditional phone.
Through this process, VoIP allows for a more cost-effective way of handling calls, especially beneficial if your businesses need to stay connected both locally and globally.
What is a Landline
A landline is a conventional telephone system that relies on a network of fixed physical wires to enable communication. This system, known as the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN), operates through copper wires and fiber-optic cables that cover regions, connecting individual homes and businesses through underground or overhead lines.
The PSTN transmits voice data using a circuit-switched model, which establishes a dedicated channel for the duration of the call between two points. This ensures consistent and stable connections, independent of internet bandwidth.
Related Reading: Difference between VoIP and PSTN
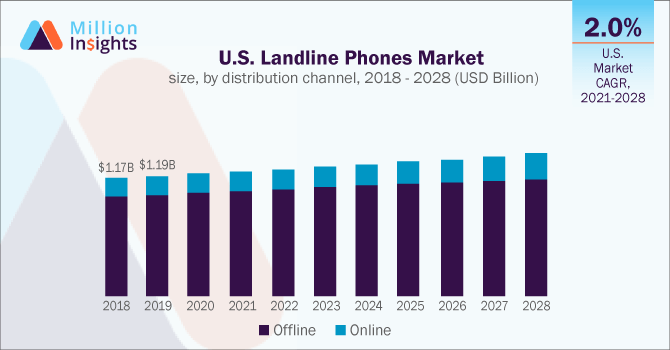
The global landline phone market was valued at USD 6.8 billion in 2020, with a projected CAGR of 2.8% from 2021 to 2028, dominated by developed countries like the UK and the US.
How does Landline Works
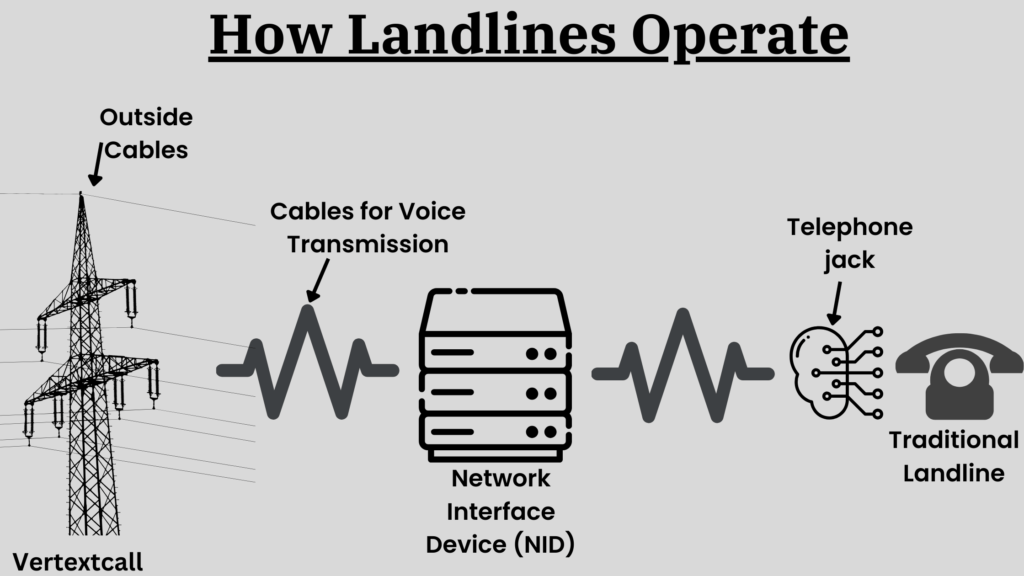
Landline telephony operates by the transmission of sound waves as electrical signals through a network of wires. When you speak into a landline telephone’s receiver, your voice is captured by a microphone, which converts the sounds into analog electrical signals. These signals travel through the phone’s internal wiring to the telephone network via a series of exchanges.
Each telephone is linked to a local exchange through what is termed the ‘local loop’. At the local exchange, the analog signal can be routed to another local user directly or to a long-distance exchange if the call is to a remote location.
This system employs circuit switching also called Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN), which dedicates a physical path for the duration of the call.
The receiving telephone translates the analog signals back into audible sound through a speaker, allowing the recipient to hear the caller’s voice with clarity.
The main differences between VoIP and landline
1/ Cost-Effectiveness Comparison:
VoIP tends to be the more cost-effective solution, offering lower setup costs, almost no maintenance, and minimal call charges. Its scalability makes it a sensible choice if your business is growing or needs to accommodate fluctuating call volumes.
Landlines, on the other hand, often have significant setup costs, including the need for physical infrastructure. While they might have lower monthly fees compared to VoIP, call charges can add up, especially for international or long-distance calls, which are often much higher than VoIP charges.
2/ Features and Functionality:
VoIP services provide a range of features that are either not available with landlines or come at an additional cost. These can include call analytics, advanced call routing, call recording, and integration with other software systems you may have in your business operations.
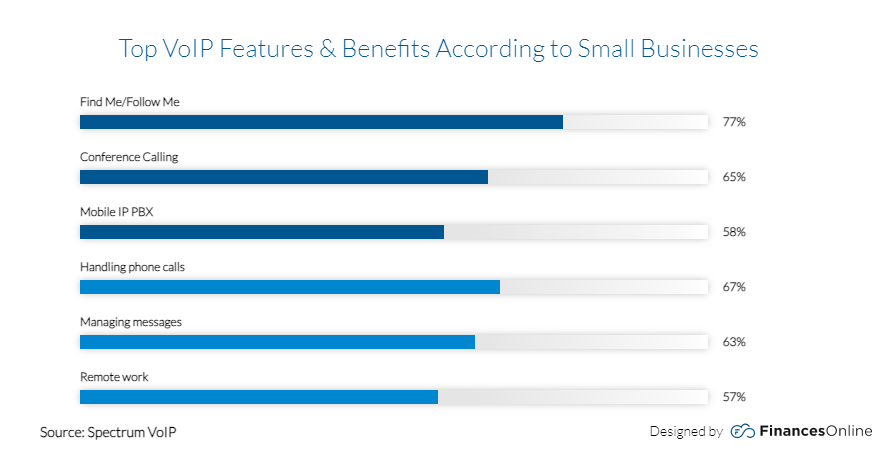
Landlines offer their own set of features, such as caller ID, call waiting, and call forwarding, but they are generally more static and don’t provide the same level of flexibility or integration possibilities as VoIP systems.
3/ Call Quality:
The call quality of a VoIP system can be affected by various factors such as your internet connection, the quality of service provided by your VoIP provider, and any network congestion. However, advancements in technology and Internet speeds have significantly improved VoIP call quality, with many systems achieving HD voice standards.
The quality of landline calls is traditionally more consistent and higher, primarily due to the dedicated copper wires used specifically for voice communication. Calls are usually clearer and have less risk of interruptions or latency issues.
4/ Scalability and Flexibility:
As businesses experience growth and expansion, VoIP systems provide an integrated solution for adding phone lines, ensuring scalability and flexibility. With the ability to accommodate remote workers, these systems offer equal access and connectivity for both on-site and off-site employees. This enables your business to optimize its communication infrastructure, developing collaboration and efficiency across the organization.
whereas with a traditional landline, you are physically limited by the number of phone lines you have installed. This means that if you need to make multiple simultaneous calls or expand your phone system for a growing business, you would need to invest in additional physical lines, which can be costly and time-consuming to set up.
5/ Transmission Medium:
VoIP utilizes the internet or private data network connections for voice call transmission, making it highly adaptable and modern technology. Data packets transmitted over the internet allow for more dynamic routing and easier handling of large volumes of calls without the need for additional hardware.
In contrast, landlines rely on copper phone lines to directly transmit analog voice signals without digital conversion. The reliance on physical infrastructure in landlines can limit flexibility and scalability compared to internet-based VoIP.
6/ VoIP Vs Landline: Hardware comparison:
Hardware Component | Landline Phones | VoIP Phones |
Connection Method | Requires PSTN wiring and telephone jacks. | Internet connection (broadband, Wi-Fi, or cellular). |
Handset | Corded handset is connected to the base unit. | Corded or cordless handset connected to the VoIP adapter or IP phone. |
Base Unit | The Physical base unit is connected to the network. | VoIP adapter (analog telephone adapter) or IP phone. |
Network Interface | Relies on PSTN circuitry | Converts analog signals to digital; communicates via Internet protocols. |
Difference between VoIP and traditional landline services when making long-distance calls
When it comes to making long-distance calls, the mechanisms of VoIP and traditional landlines differ, which can influence your choice depending on your needs.
Landline calls are routed through a network of physical wires and switchboards. This established technology has historically provided a high level of reliability. However, it often results in higher charges for long-distance calls due to the infrastructure involved in connecting these calls over vast distances.
On the other hand, VoIP calls are transmitted over the internet. This approach can lead to substantial cost savings, particularly for long-distance and international calls, as it avoids the traditional telephone network’s lengthy routing process. Additionally, many VoIP service plans include long-distance calls as part of their package, eliminating additional charges.
However, it’s important to note that the call quality of VoIP can be affected by internet bandwidth and stability. In areas with poor internet service, you may experience lower call quality compared to landlines during long-distance calls.
The bandwidth requirement for VoIP
VoIP Usage | Bandwidth Requirement |
Minimum bandwidth per VoIP line | 100 Kbps |
VoIP telephone calls (optimal performance) | 5-25 Mbps download speed |
Email and web browsing | 1 Mbps download speed |
File downloading | 10 Mbps download speed |
HD video teleconferencing | 6 Mbps download speed |
Key components of VoIP
The key components of VoIP systems include various elements that work together to facilitate voice communication over IP networks. These components include:
- Internet Connection: A strong and dependable Internet connection is the foundation of any VoIP system. It plays a crucial role in determining the quality of calls and overall system performance.
- VoIP Software: The software responsible for voice conversion, call routing, and feature deployment. This can be a third-party app or an integrated tool.
- VoIP Hardware: While VoIP is known for its software-based capabilities, physical devices such as IP phones and adapters are still critical components in a VoIP setup.
- PBX or Virtual PBX: A Private Branch Exchange in the cloud that routes internal and external calls through the VoIP network, facilitating advanced call-handling features.
Advantages and Disadvantages of using a VoIP call
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) calls offer several advantages and disadvantages compared to traditional phone calls. Here’s a breakdown:
Advantages of a VoIP call
1/ Cost Savings:
One of the most immediate and compelling advantages that VoIP offers over traditional landlines is significant cost savings. Unlike the conventional landline system, which involves costly infrastructure and long contracts, VoIP is a cloud-based solution that not only cuts down on hardware and maintenance fees but also eliminates the need for physical phone lines.
With VoIP, your business can experience the flexibility of making and receiving calls from any device connected to the internet, making it a highly scalable and cost-effective communication solution.
2/ Lower Monthly Phone Bills:
VoIP services are known for their cost-effective calling options, providing affordable rates for both domestic and international calls. This is made possible by leveraging the internet to transmit voice data, bypassing the traditional telecommunication infrastructure that landlines rely on. In fact, if you run a small business VoIP can assist in significantly reducing your business communication system expenses by up to 90%.
3/ No Additional Hardware Costs:
With Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP), your business can easily scale its communication infrastructure without the hassle of extensive physical network changes. This flexibility allows for the addition of new lines and handsets, enabling seamless expansion without the high upfront investment typically required for traditional landline expansions.
4/ Affordable International Calls:
Small businesses with global clients find VoIP particularly attractive for its significantly lower international calling rates. This cost-effective solution can lead to substantial savings over time compared to traditional landline tariffs. With VoIP, your business can connect with its international clients, expanding its reach and developing stronger relationships.
Additionally, the flexibility and scalability of VoIP systems allow small businesses to adapt and grow without the limitations of traditional phone systems.
5/ Integration with Other Communication Tools:
Voice over Internet Protocol offers the unified integration of customer relationship management (CRM) systems, as well as various software applications. This advanced integration allows your business to enhance its communication experience by seamlessly connecting different departments and streamlining operations.
6/ Easy Setup and Configuration:
The plug-and-play nature of VoIP systems allows for easy setup. Often, all that’s needed is a stable internet connection and compatible devices, cutting down setup times from weeks to mere hours.
Disadvantages of a VoIP call
1/ Reliability and Call Quality:
One of the most critical concerns for businesses considering the switch to VoIP is the reliability and call quality of the new system. Unlike traditional landlines that have a dedicated line for each user, VoIP systems share bandwidth with other internet services in the organization.
Potential Issues with VoIP Call Quality-
Jitter – VoIP signals that arrive out of order due to varying network latencies can cause jitter, leading to disjointed audio during calls.
Latency – Excessive delay on VoIP networks can result in lagging conversations, a particular disturbance for critical business calls.
Packet Loss – The dropping of voice data packets during transmission due to network congestion can cause parts of conversations to go unheard or misheard.
2/ Dependence on Internet Connection:
Another disadvantage of VoIP communication is that it is entirely dependent on the Internet, and any issues with the connection can significantly hamper business operations. During outages, VoIP systems are rendered unusable, unlike landlines which receive power through the telephone line, making them operable even during power cuts.
In addition:
- VoIP requires consistent and high-speed internet to function optimally. In cases where bandwidth is limited, such as peak usage times, calls may suffer.
- Businesses with unreliable internet connectivity will see a direct impact on their ability to make and receive calls consistently.
3/ Security Risks:
As cyber threats rise, the security of business communications is more critical than ever. VoIP systems present a new set of vulnerabilities that traditional landlines do not, such as
Data Breaches – VoIP data, when not encrypted, are as vulnerable as any other internet-based communication, leaving your business open to data breaches.
Denial of Service Attacks – VoIP services can also be the target of malicious attacks that overpower systems, making them inoperable.
4/ Power Dependency:
Unlike traditional landline phones that can rely on power supplied by the telephone line, VoIP phones require a constant and separate power source to operate effectively. The impact of power outages on VoIP communication is significant. During blackouts, unless there is a backup power source in place, VoIP services are disrupted.
While battery backups can provide a temporary solution, they require regular maintenance and may not offer indefinite operation, particularly during extended crises.
5/ Emergency Services and E911:
For VoIP calls, the 911 emergency call system works differently. It’s essential to understand the protocols and regulations related to emergency services to ensure your system’s setup complies with the law and provides proper emergency service access.
VoIP systems may not accurately report the location of a caller, which can be critical for using emergency services. In contrast, landlines are directly linked to a physical address, facilitating the quick deployment of help.
Pros and Cons of Landline
Landline phones have been a pillar of communication for decades, offering both advantages and disadvantages compared to newer technologies like VoIP. Here are the pros and cons of using a landline:
Advantages of using landlines
1/ Dependable Quality of Service:
Landlines are known for their reliable connection quality, with minimal disruptions and clear audio. This is because landlines use dedicated copper wires, a time-tested technology that has proven to be less susceptible to interference and compression.
Unlike Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP), which relies on internet bandwidth that can vary in stability, landlines provide a consistent and uninterrupted communication experience. With landlines, your conversations will be free from the potential dropouts that can occur with other communication methods.
2/ Greater Security:
The chances of eavesdropping on landline calls are considerably lower than with VoIP. This is because intercepting landline communications typically requires physical access to the wires, which adds an extra layer of security. The physical nature of landline connections provides a level of protection against remote interception and unauthorized access.
3/ No Need for Power:
Landline phones, draw their power directly from the telephone exchange. This means that they can continue to provide uninterrupted service even during electrical outages, ensuring that you stay connected when you need it the most. Whether it’s for emergency calls or important conversations, the reliability of landline phones makes them an essential communication tool in any business. Therefore you can always count on your landline phone to keep you connected.
4/ Easy Integration:
Landlines offer the advantage of seamless integration with various systems, including fax machines and security systems, without the need for additional configurations. This means that you can easily connect your landline phone to your existing fax machine or security system, allowing for convenient communication and enhanced security without any hassle.
Whether you need to send important documents or ensure the safety of your premises, landlines provide a reliable solution that can effortlessly integrate with other essential systems.
5/ Reliable Emergency Services:
With a landline, you have a direct line to emergency services that is not dependent on internet connectivity or electrical power. This reliable and essential communication tool ensures that even during disruptions or emergencies, you can always reach out for help securely. Whether it’s a power outage or a loss of internet connection, your landline ensures that you can stay connected when it matters most.
Disadvantages of using landlines
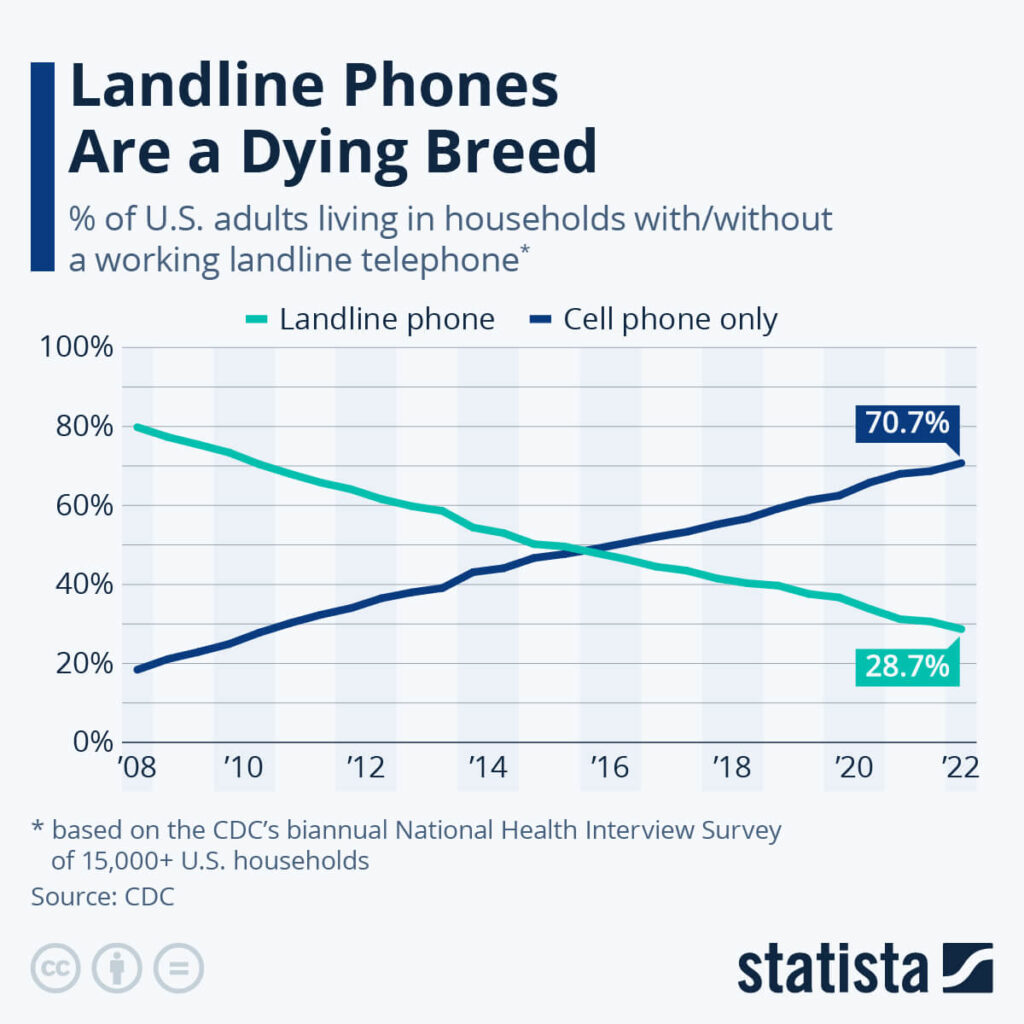
1/ Limited Mobility:
A clear downside of landline phones is that they keep you tied to one spot. Unlike VoIP phones, you can only make or answer calls from the exact location of your landline.
This traditional restriction means you can’t take your office calls on the go and may miss important conversations when away from the desk.
2/ Additional Costs for Advanced Features:
Many of the advanced features that come standard with VoIP services, such as auto-attendant, call forwarding, and voicemail-to-email, can incur additional costs when using a traditional landline or might not be available at all.
This could potentially lead to increased operational costs for a business looking to maintain a modern and efficient communications system, especially when considering the need for expensive hardware and maintenance.
3/ Upfront Investment:
When it comes to installing a landline system, there’s usually a significant initial investment required for purchasing the necessary hardware and availing professional installation services. This can be quite costly, especially when compared to the hassle-free setup of Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) solutions.
With VoIP, you can simply use your current internet connection and a device, like a computer or a smartphone, to access VoIP services. This convenience not only saves you money but also eliminates the need for additional equipment and complex technical installations.
4/ Lack of Advanced Integrations:
Landline phone systems, although reliable, often lack the essential integration with digital tools and business software that VoIP systems provide. This limitation can result in communication workflows that are less efficient and a missed opportunity to fully leverage modern technology for streamlining operations.
The two types of Landlines
There are two main types of landline phones: corded and cordless

Corded landline phones maintain a physical connection between the handset and the base unit through a cord. This design ensures reliability as these phones do not rely on batteries and generally provide clear and consistent call quality.
On the other hand, cordless landline phones utilize radio signals to connect the handset and the base unit, allowing you to move freely within a specified range.
Hardware associated with landline
When setting up a landline phone system, several hardware components are required. The most fundamental piece of equipment is the telephone itself, which comes in various styles ranging from traditional dial phones to modern push-button models with LCDs and speakerphone capabilities.
Each phone must be physically connected to a telephone jack installed on the premises, which in turn is connected to the wiring that runs to the telephone network outside your building.
Additionally, for multi-line operations, businesses often invest in a Private Branch Exchange (PBX) system. This is essentially a private telephone network used within a company that allows for free calls between users and provides features like call transfers, voicemail, call queues, and conference calling—though with additional costs for using these capabilities. The PBX system needs to be maintained and occasionally upgraded, representing an ongoing investment.
The infrastructure for landlines also involves the public switched telephone network (PSTN), which requires a vast and costly web of physical circuitry to connect calls.
Copper wires, fiber optic cables, switching centers, and other network interfaces and devices are part of this traditional setup.
How to convert a landline into VoIP
Converting a traditional landline to a Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) system is a process that requires both strategic planning and a basic understanding of the technology involved. Here’s how to embark on this transformation:
1/ Selecting a VoIP Provider: Start by researching and selecting a VoIP provider that fits your business needs. Pay close attention to their service plans, features, reliability ratings, customer support, and costs to ensure they align with your company’s communication requirements.
2/ Analog Telephone Adapter (ATA) Setup: If you wish to retain your current phones, purchase and install an ATA, which converts analog signals into digital data that can be transmitted over the internet. This step allows you to utilize your existing telephone handsets with the new VoIP service.
3/ Testing: Run a parallel setup with your current landline system alongside your new VoIP setup. Test the VoIP service to ensure that call quality and features are working as expected and that your internet connection can handle the additional load.
4/ Porting Phone Numbers: Collaborate with your selected VoIP provider to transfer your current phone numbers. This ensures business continuity and prevents any disruption to your communication lines.
5/ Finalize the Switch: Once you are satisfied with the performance of the VoIP setup and all numbers are ported, you can finalize the transition and decommission your traditional landline service.
It’s important to note that the specific steps may vary depending on the VoIP service provider and the equipment you choose.
Choosing the Right Option for Your Business
Selecting the phone system that best suits your business isn’t just about comparing lists of features. It’s about evaluating what your business needs, now and in the future, and finding a solution that aligns with your goals and operational realities.
1/ Factors to Consider
Several key factors will influence your decision. These include the size of your business, the nature of your work, your long-term financial outlook, your current technological environment, and the importance of mobility and additional features for your communications strategy.
2/ Assessing Business Needs
Conduct a thorough assessment of your business’s communication requirements. Are most of your calls local or long-distance? Do you need robust call center capabilities? How quickly do you see chances for business expansion? By focusing on these needs, you can ascertain which system will best support your business.
Is a landline better than VoIP?
As discussed above, the choice between a landline and a VoIP system depends on the specific needs of your business or personal use. Traditional landlines offer the reliability of long-established technology, with consistent call quality, an independent power supply, and a sense of familiarity for many users.
On the other hand, VoIP technology excels in cost-effectiveness and a wide range of features that landlines cannot match. Which often include video calls, messaging, and seamless integration with other business applications, all while generally offering a lower monthly bill.
In conclusion, if your priorities prioritize traditional reliability and you operate in an area with uncertain internet service, a landline might be a better choice. However, if you are seeking modern features, scalability, and cost-effective integration with technology, VoIP is a viable option.
Frequently Asked Questions?
Q1) Do I need a landline if I have a VoIP?
Ans: Not necessarily. VoIP systems are designed to provide phone services over the Internet, which allows for many of the same functionalities as traditional landlines, often with additional features like voicemail-to-email and call forwarding. For businesses or individuals seeking modern telecommunication solutions with potentially lower costs and greater flexibility, a VoIP service can often replace traditional landlines. However, some may choose to maintain a landline as a backup for emergencies or in areas with unreliable internet connections.
Q2) How do I know if I have a landline or VoIP?
Ans: To determine if your phone system is a traditional landline or VoIP, you can look at the hardware and service setup. Landline phones are typically connected to a series of physical wires within the phone system or run on the public switched telephone network (PSTN). VoIP phones, on the other hand, require an internet connection, and the hardware usually includes Ethernet ports that link directly to a router or network.
Q3) Can I use a VoIP phone as a regular phone?
Ans: VoIP phones can indeed be used similarly to regular phones. They allow you to make and receive calls much like traditional handsets. However, they utilize internet connectivity instead of traditional phone lines.. This enables VoIP users to access additional features that standard phones might not support, such as the ability to integrate with other applications or software, video calling, and transferring calls to other devices.
Q4) Can I use my Landline phone for VoIP?
Yes, you can use your existing landline phone for Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) with the help of an adapter called an Analog Telephone Adapter (ATA). This device connects your traditional phone to your internet network, allowing digital signals to be converted into a format that your phone can understand. It’s a cost-effective way to upgrade your home or business communication system.
Q5) Will VoIP replace Landlines?
The trend in telecommunication shows a marked shift towards VoIP due to its cost-efficiency and feature-rich services. Despite this evolution, landlines still remain in certain sectors that require a dedicated and reliable line, such as for emergency services or in rural areas with limited internet service. While VoIP could potentially become the predominant phone service choice, it is not expected to completely replace landlines in the foreseeable future.
Q6) Why is VoIP cheaper than using a telephone?
VoIP is generally cheaper than traditional telephone services because it uses your existing internet connection, eliminating the need for costly phone line installations and maintenance. Additionally, VoIP providers typically offer more competitive pricing due to lower overhead costs and the nature of digital service delivery. However, it’s worth noting that VoIP cost savings can vary based on your service plan, provider, and usage patterns.
Q7) Can VoIP call a landline?
Yes, VoIP users can make calls to landline phones seamlessly. The VoIP service converts the call from a digital format to an analog format compatible with the PSTN, allowing communication between VoIP and traditional phones.

