When it comes to selecting a Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) service, the decision-making process varies significantly for businesses and residential users.
It is crucial to understand the subtle differences between business and residential VoIP solutions to make an informed choice that aligns with your specific requirements. This blog post aims to uncover the key distinctions by examining factors such as call quality, features, cost-efficiency, and customer support.
Whether you are a startup, an established company, or a household, we aim to guide you in choosing the VoIP service that best suits your communication needs.
What is a business VoIP?
Business VoIP is a specialized service tailored to meet the communication needs of enterprises. Unlike traditional telephony, which relies on physical infrastructure, business VoIP utilizes high-speed internet and cloud-based platforms to deliver advanced functionalities crucial for corporate operations.
It goes beyond just call-making and receiving capabilities, offering features such as automated attendants, call routing, and conference calling (more details below) to enhance operational efficiency. By using VoIP, businesses can develop collaboration and drive efficiency, both in-office and for remote teams.
Key features and functionalities
As your businesses demand more than just the ability to make and receive calls. Business VoIP solutions come loaded with a range of features designed to enhance operational efficiency and communication effectiveness. Some of the key features include
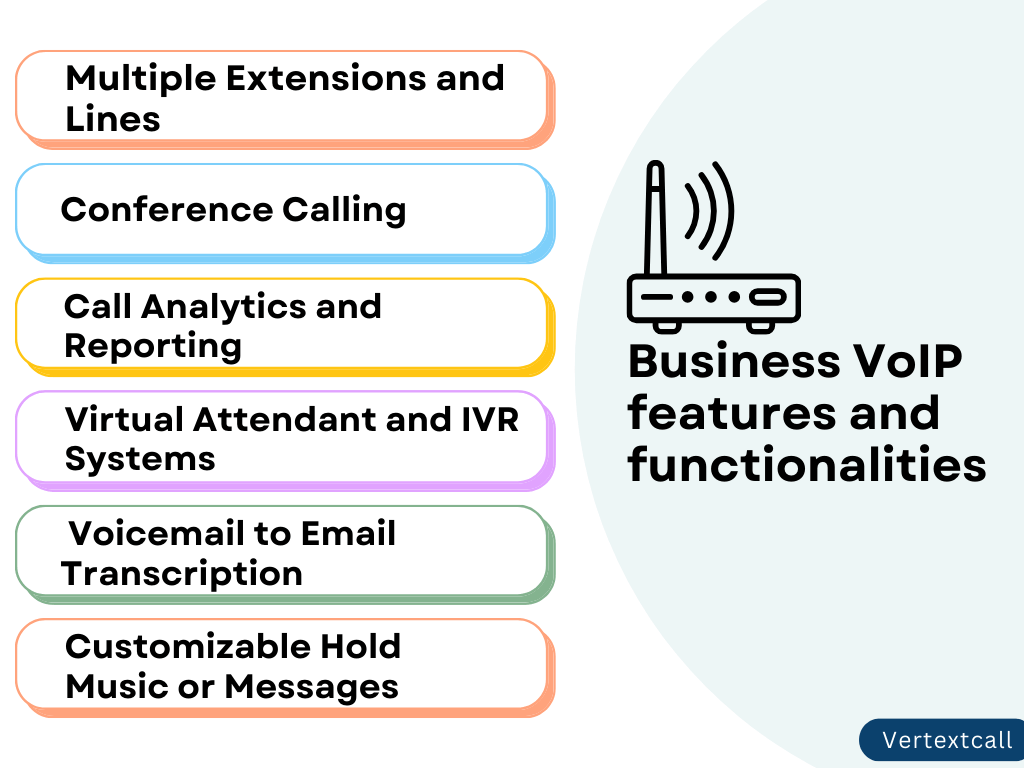
1/ Multiple Extensions and Lines: Business VoIP services provide the capability for multiple extensions and direct lines, which is important if your enterprise needs separate contact points for different departments or team members.
2/ Conference Calling: Conference call is an essential component of a business VoIP feature set, enabling uninterrupted communication among multiple parties. It plays a vital role in facilitating your meetings, discussions with remote workers, and cross-functional team collaborations. Implementing this technology is crucial for developing effective collaboration and ensuring smooth communication across all fronts.
3/ Call Analytics and Reporting: Business VoIP systems produce comprehensive analytics and reports on call volume, duration, wait times, and other essential performance metrics. This data can provide valuable insights to help optimize your communication strategies.
4/ Virtual Attendant and IVR Systems: A Virtual Attendant, or Interactive Voice Response (IVR) System, enhances your customer experience by directing callers to the appropriate services or information they require. These automated attendants can handle a high volume of calls simultaneously.
5/ Voicemail to Email Transcription: Voicemail-to-email services streamline message management by automatically transcribing voicemails to text and delivering them straight to your email. This efficient process not only speeds up response times but also ensures that you never miss out on critical information, even when you’re away from your desk.
6/ Customizable Hold Music or Messages: Businesses can enhance customer engagement during wait times by customizing hold music or messages. This feature presents an opportunity to share valuable information about promotions, services, or other announcements, effectively transforming idle time into a powerful marketing tool.
What is a residential VoIP?
Residential VoIP is a solution specifically designed for home use. It utilizes the same foundational technology that converts voice into a digital signal for internet transmission. However, the services and features are customized to cater to the needs of households rather than businesses.
Residential VoIP offers a cost-effective way for you to connect with your family and friends, often including international calling plans at a fraction of the cost of traditional landline services. While it may lack the advanced features and scalability found in business VoIP, residential VoIP services still provide essential functionalities such as caller ID, voicemail, and call waiting. This ensures a user-friendly communication experience for everyday users.
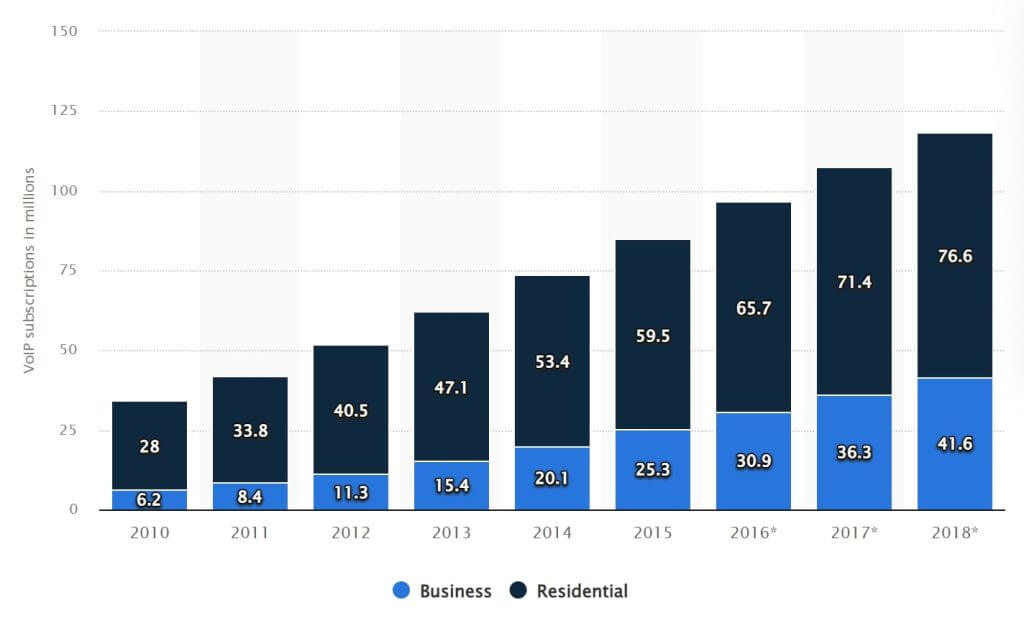
Between 2010 and 2018, the count of residential VoIP lines increased from 28 million to 76.6 million.
Main features and benefits
Residential VoIP offers various features and benefits that make it an attractive option for households:
1/ Mobility in calling: Residential VoIP services offer the flexibility of making and receiving calls from multiple devices, as long as you have a reliable internet connection. Whether it’s your smartphone, laptop, or tablet, you can stay connected wherever you are, at home or on the move.
2/ User-Friendly Setup: Residential VoIP services are designed to be user-friendly and simple to set up, ensuring accessibility even for non-technical users. Typically, all you need to get started is an internet connection, a subscription to the service, and a compatible device like a router or dedicated VoIP phone.
3/ Cost Efficiency: Residential VoIP is widely known for its cost-effectiveness, significantly reducing the expenses associated with traditional telephone services. As a home user, you can enjoy the advantages of low monthly fees and often unlimited domestic calls, along with competitive international rates. These economical solutions provide substantial monthly savings, highlighting the importance of budget-conscious communication for households.
4/ Value-Added Features: While not as comprehensive as the extensive range of business VoIP features, residential services still provide essential functionalities that cater to the needs of individuals. These include caller ID to identify incoming calls, voicemail to receive and manage messages and call forwarding to redirect calls to another number or device. These features ensure that as a residential user, you can experience a convenient and efficient communication experience.
The key difference between business and residential VoIP
The main difference between business and residential VoIP revolves around their target users, pricing, and feature sets:
A. Pricing Models and Plans:
When it comes to business VoIP, it commonly functions on tiered plans that can be scaled based on the specific features and number of users required. On the other hand, residential VoIP typically follows a flat-rate pricing model that offers unlimited usage, allowing you to experience uninterrupted communication without worrying about usage limits or additional charges.
B. Service Level Agreements (SLAs):
For business VoIP, Service Level Agreements (SLAs) play a crucial role in ensuring reliability. These agreements provide your business with a contractual commitment to performance standards and uptimes, serving as a protective barrier. By defining precise metrics for call quality, SLAs ensure minimal interruptions and quick issue resolution, thereby upholding the professionalism of communication channels.
Residential VoIP, on the other hand, typically does not require such formal agreements. This is primarily because the potential impact of service outages is generally less significant in non-commercial settings. Moreover, residential users typically have alternative means of communication, such as mobile phones or landlines, which reduces the impact of any potential service interruptions.
C. Customization and Scalability Options:
Business VoIP solutions provide extensive customization options to meet the diverse needs of various industries. These solutions can be tailored to fit the unique operational processes of organizations, with personalized call flows, integrations, and advanced analytics. Furthermore, they are designed to effortlessly scale, allowing for seamless expansion as businesses grow, including the addition of new users, departments, or international branches.
On the other hand, residential VoIP services prioritize simplicity and ease of use rather than deep customization. While they may provide basic personalization options like app-based controls or customizable voicemail messages, they emphasize the simplicity and reliability needed for household communication.
D. Security and Privacy Considerations:
In environments where sensitive corporate information is constantly being transferred, business VoIP services are equipped with advanced security protocols to mitigate the risk of cyber threats. These services incorporate secure encryption methods, precise network security measures, and defined user access controls, to safeguard against breaches and uphold regulatory standards.
In contrast, residential VoIP services cater to the security needs of individual users. They employ standard encryption and safeguard personal data. While their security features are comprehensive, the focus is on providing straightforward, user-friendly protection that defends against common threats without the complexity typically associated with enterprise-level security. This ensures that you can confidently use VoIP services with the assurance of privacy and protection.
E. Quality of Service Metrics:
When it comes to business VoIP, ensuring high-quality service is crucial. Quality of Service (QoS) metrics play a vital role in tracking and maintaining the necessary transmission quality for professional interactions. These metrics cover various aspects such as latency, jitter, and packet loss, which contribute to the overall performance and reliability of the service. By implementing specific priority rules, your business can ensure call quality even during periods of high network traffic, guaranteeing uninterrupted communication flow.
On the other hand, residential VoIP providers also prioritize delivering a high-quality service experience. However, they may not offer the extensive and customizable QoS settings commonly found in business environments. Instead, they focus on maintaining sufficient quality standards that meet the needs of day-to-day communication without overwhelming users with technical details.
How does VoIP work at home?
VoIP technology at home transforms your voice into a digital signal using a series of systematic steps. Understanding these steps can clarify the process and showcase the finesse behind convenient home communication:
- Call Initialization: When a VoIP call is initiated at home, the analog voice signal from the user is captured by a VoIP-enabled device, such as a computer, smartphone app, or analog telephone adapter (ATA) connected to a traditional phone.
- Analog-to-Digital Conversion: The VoIP device then converts this analog voice signal into a digital format. It utilizes a codec, a program that encodes and compresses the audio signal for efficient transmission over the Internet.
- Data Packetization: The digital audio is packetized, meaning it is divided into smaller, manageable packets of data. Each packet carries a segment of the voice signal, along with data about its origin, destination, and sequence in the call.
- Transmission Over the Internet: These packets are transmitted over the user’s broadband Internet connection. They travel through various network pathways to reach their destination, determined by routing protocols that find the most efficient path in real-time.
- Reassembling and Decompression: Once the packets arrive at their destination, they are reassembled in the correct sequence and decompressed. This process converts them back into a continuous audio stream that can be understood by the receiver.
- Digital-to-Analog Conversion: If the recipient is using a traditional phone, the digital signal is converted back into an analog signal for the receiver to hear the message, using an ATA or similar device.
Throughout the conversation, this process occurs symmetrically in near-real time, allowing for seamless communication as if the parties were using traditional telephony.
What type of business needs VoIP
Voice over Internet Protocol is beneficial for various types of businesses, particularly those that rely heavily on communication. Some examples of businesses that can benefit from VoIP include:
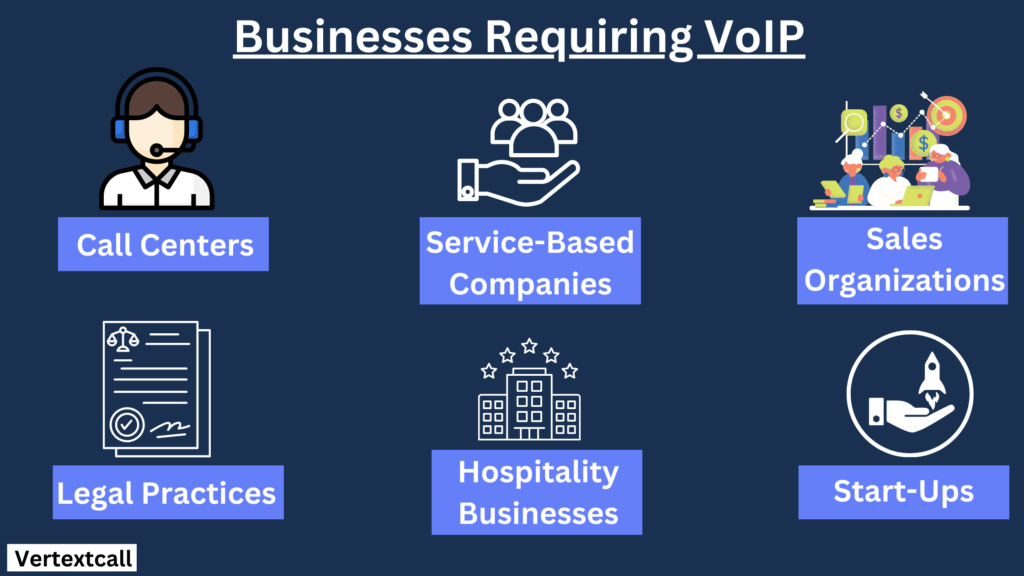
1/ Call Centers: VoIP is integral for call centers, providing them with advanced features such as call queuing, automatic call distribution, and interactive voice responses, which are essential for handling high call volumes efficiently.
2/ Service-Based Companies: For businesses that deliver services such as IT support, consulting, or home repairs, VoIP enables employees to communicate effectively with clients, regardless of their location, developing superior customer service.
3/ Sales Organizations: VoIP is an essential tool for sales professionals in fast-paced environments, enabling smooth communication with prospects and customers. With the freedom to connect anytime, anywhere, without being confined to a desk, VoIP facilitates sales teams to accelerate the sales process and achieve remarkable results.
4/ Legal Practices: Law firms benefit from VoIP through features such as call recording and e-fax, ensuring the accurate documentation and transfer of sensitive legal communications.
5/ Hospitality Businesses: The hospitality industry, including hotels and resorts, leverages VoIP for streamlined operations, such as booking, guest services, and event management.
6/ Start-Ups: Growing businesses require flexible communication solutions such as VoIP, which can adapt to rapid growth and change without significant capital investment.
How much does business VoIP cost
The cost of business VoIP services can vary significantly based on various factors, including the provider, feature set, and scale of operation. Generally, VoIP service prices are customized to suit the size and requirements of businesses.
Basic plans for startups start at around $20 per user per month, while advanced packages with additional features can exceed $35 per user per month. Additional expenses like international calling or premium support may also affect the final cost for small-to-medium-sized businesses.
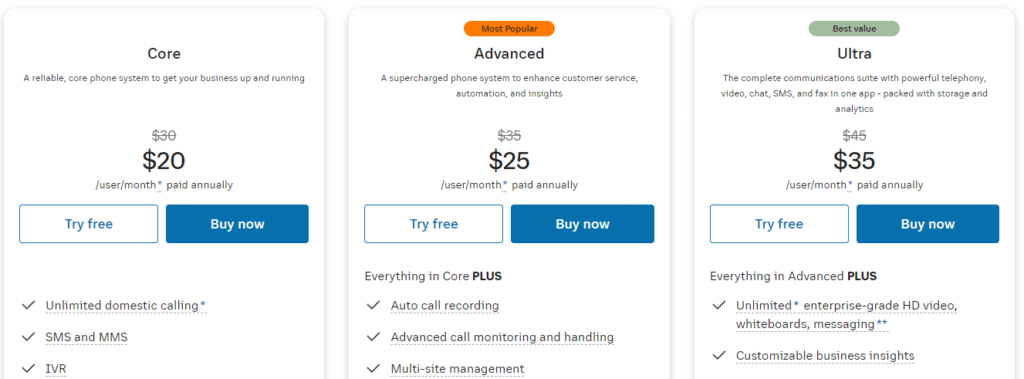
To ensure the chosen VoIP solution aligns with both financial constraints and communication needs, you should conduct a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis, considering potential savings from reduced infrastructure and operational costs.
Considerations for residential VoIP adoption
When considering the integration of VoIP technology in a home, it’s important to take several key factors into account for a smooth and effective transition from traditional telephony.
- Quality of Internet Connection: The quality of the internet connection is crucial for the performance of VoIP. It relies on the reliability and speed of your home internet service. A high bandwidth connection helps reduce latency and packet loss, ensuring superior call quality.
- Compatibility with Existing Hardware: You need to determine if your current devices support VoIP or if they require additional hardware, such as ATAs or specialized VoIP handsets, to convert the digital-analog signal.
- Emergency Services Accessibility: Establishing access to emergency services through VoIP, which includes accurate location information for 911 calls, is essential. You must verify that your VoIP provider supports Enhanced 911 (E911) services.
- Power Outage Contingencies: Unlike traditional phone lines, VoIP relies on a powered network. It is crucial to have an Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) or other power solutions in place to ensure uninterrupted communication even during power outages.
- Provider Selection: When considering VoIP services, it is crucial for you to thoroughly assess providers. Factors such as service plans, cost, customer support, and user reviews should be carefully evaluated to ensure alignment with your specific needs and expectations.
VoIP vs Home Phone
VoIP and Home Phone, also known as landline service, are both methods of making telephone calls, but they operate differently:
Aspect | VoIP | Home Phone |
Technology | Uses internet protocol for voice transmission | Utilizes traditional analog or digital phone lines |
Connection | Requires a stable internet connection | Needs a physical telephone line connection |
Cost | Often cheaper for long-distance and international calls | Typically involves higher costs for long-distance calls |
Equipment | Requires VoIP-enabled devices such as IP phones, computers, or smartphones | Utilizes standard landline telephones |
Flexibility | Offers greater flexibility in terms of mobility and scalability | Generally lacks mobility and scalability options |
Installation | Generally easier to set up, often through software installation or plug-and-play devices | May require professional installation and wiring |
Maintenance | Typically requires minimal maintenance, software updates may be needed | May require periodic line checks and repairs |
To know more check out the detailed guide on: Difference between VoIP and Landline
Business phone vs. personal Phone
Aspect | Business Phone | Personal Phone |
Purpose | Primarily for business use, facilitating professional communication | Mainly for personal communication and occasional professional use |
Integration | Integrates with business software like CRM systems, email clients, and office productivity tools | Lacks integration with business software but may sync with personal apps and accounts |
Support | Typically comes with dedicated customer support and service level agreements | Relies on general customer support services provided by the carrier or manufacturer |
Security | Emphasizes security features like encrypted calls, secure connections, and access controls | Focuses on basic security measures such as password protection and device encryption |
Customization | Offers customization options tailored to business needs, such as custom greetings, call routing rules, and branded interfaces | Limited customization options, usually confined to ringtone selection and contact management |
Reliability | Business-grade reliability with uptime guarantees and redundancy measures | Reliability may vary depending on carrier and network coverage, typically not guaranteed |
Future Outlook | Declining usage, gradual transition to digital | Declining due to emergence of newer technologies |
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1) What is the difference between business and residential phone lines?
Ans: Business phone lines are designed to handle higher call volumes and offer a range of professional features such as multi-line management, conference calling, automated attendants, and advanced call-forwarding. These features are specifically built to meet the challenging demands of corporations. On the other hand, residential phone services are designed for personal use, with an emphasis on ease of use, affordability, and basic features sufficient for everyday communication.
Q2) Is VoIP for business only?
Ans: No, VoIP is not limited to business use. VoIP technology is equally valuable in residential settings. Home users can benefit from VoIP’s cost-efficiency and experience features like voicemail, caller ID, and call waiting without the complexities associated with business systems.
Q3) Can I use my personal cell phone for business?
Ans: Yes, you can use your personal cell phone for business purposes. This is often seen in small businesses or startups where resources are limited, and personal assets are utilized for professional needs. However, it is important to consider that using a personal phone for business may not convey the same level of professionalism or offer the same organizational capabilities as a dedicated business line.
Q4) Can I have a business line on my personal cell phone?
Ans: Yes, it is possible to set up a business line on a personal cell phone. This is commonly done through virtual phone systems that utilize VoIP technology. Virtual numbers can be directed to your mobile device, thereby separating business from personal communications without the need for two separate phones. This solution provides flexibility and maintains a professional presence, with the convenience of managing all calls through a single handset.
Q5) Is VoIP worth it for a small business?
Ans: Yes, VoIP offers small businesses a compelling solution for cost-effective and scalable communication. Compared to traditional phone systems, VoIP requires a lower initial investment and can significantly reduce monthly phone bills. With its flexible features like voicemail to email, call forwarding and video conferencing, VoIP adapts to the diverse needs of small businesses, streamlining operations and developing team collaboration.

