Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) and Plain Old Telephone Service (POTS) are two methods that enable voice communication, each using different mediums and technologies. This blog will explore the differences between VoIP and POTS, providing you with a clear understanding of each to better inform your telecommunication choices.
What is VoIP
Voice over Internet Protocol is a modern telecommunications technology that enables voice communication and interactive media exchanges over Internet Protocol (IP) networks. Unlike the traditional POTS, VoIP overcomes geographical limitations, allowing you to make and receive calls via broadband internet instead of a standard telephone line.
This technology converts analog voice signals into digital packets of data, facilitating continuous transmission through the web to any location in the world with internet access.
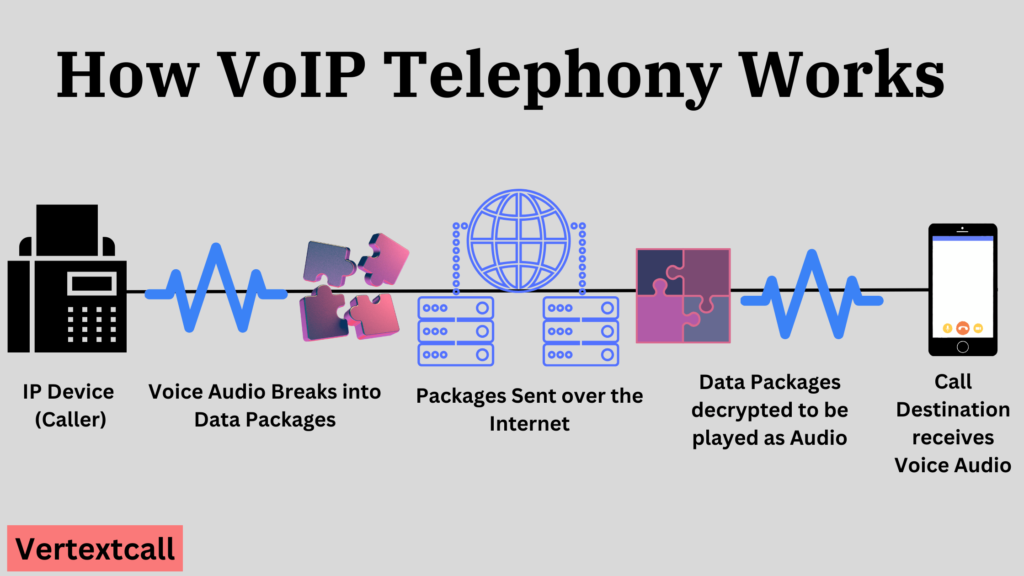
By using existing data networks, VoIP systems reduce operational costs and enhance functionality with features like voicemail to email, call forwarding, and video conferencing, making it a compelling choice for businesses looking for comprehensive and scalable communication solutions.
What is a VoIP line?
A VoIP line is a single voice transmission pathway provided by a VoIP service, functioning over a data network like the Internet. Similar to a traditional phone line, it enables making and receiving calls. However, what sets it apart is the ability to handle multiple calls simultaneously using the same Internet connection. In addition to voice calls, it can facilitate digital communication such as video calls and text messages.
What do POTS mean in telecommunication?
Plain Old Telephone Service (POTS), also known as the traditional telephone system, is a fundamental service that offers standard voice communication through copper wire networks established by telephone companies.
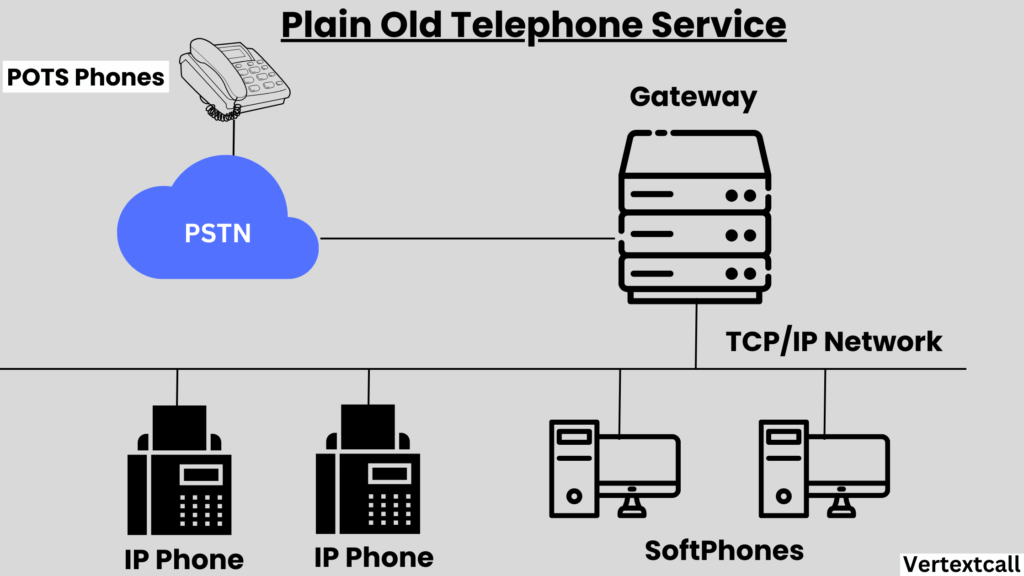
POTS has served as the foundation of voice communication since the late 19th century and is valued for its reliability. Even during power outages, POTS lines remain functional due to the voltage they carry, ensuring uninterrupted connectivity.
Operating with an analog signal, the system offers a consistent range of features centered on voice calls, fax, and basic services like dial-up Internet.
While it may lack the advanced functionalities of VoIP, POTS remains crucial in considerable regions for its proven reliability, particularly in rural or underdeveloped areas where internet services are less reliable.
The main difference between VoIP and POTS
When choosing between VoIP and POTS, a thorough comparison is crucial. Let’s analyze these communication methods across key aspects:
1/ Cost Comparison:
The cost of entry into VoIP can be significantly lower than POTS if your business is already equipped with reliable internet infrastructure. VoIP systems often require minimal additional hardware, making it a compelling option in the initial investment phase.
While POTS may have low initial setup costs, it can lead to higher operational expenses in the long run, particularly for long-distance or international calls. In contrast, VoIP, using internet connectivity, frequently presents significantly lower call fees, providing your business with a global reach and a competitive edge.
2/ Features and Functionality:
VoIP services provide a wide range of additional features beyond traditional voice communication. In addition to voicemail-to-email transcription, call routing, and video conferencing, VoIP platforms often include features like auto-attendant, call recording, and integration with CRM systems. These functionalities enhance the collaborative and communicative capabilities of your workforce, all within a unified ecosystem.
Conversely, POTS is straightforward and less feature-rich, focusing predominantly on providing a stable and clear voice call facility. While it lacks the advanced features of VoIP, POTS delivers consistency and reliability, particularly in regions where internet services are unpredictable or unavailable, thus ensuring that critical communications remain uninterrupted.
3/ Reliability and Call Quality:
When discussing call reliability and quality, both VoIP and POTS have their advantages. VoIP’s performance is closely dependent on the stability and speed of the internet infrastructure. Through improved internet connectivity and advanced VoIP technologies, call quality has been significantly enhanced, possibly reaching the level of traditional phone lines. However, service disruptions can occur if the internet connection is poor or during power outages.
Conversely, POTS is known for its dependability. The dedicated infrastructure of copper wires ensures that telephone service is often maintained even during power outages. This reliability factor is crucial for businesses that require uninterrupted communication channels. The analog nature of POTS and its established network traditionally deliver a high level of voice clarity, which is yet to be affected by varying internet conditions. However, analog lines are more open to noise interference, potentially reducing audio quality in certain situations.
4/ Flexibility and Scalability Considerations:
VoIP’s built-in architecture enables smooth scalability, allowing your business to add or remove lines, integrate with mobile devices, and incorporate advanced features as required. This adaptability can be transformative for businesses experiencing rapid growth or fluctuations. Additionally, VoIP offers the flexibility to connect teams across different geographic locations, facilitating effective and efficient remote collaboration.
On the other hand, POTS infrastructure has limited expansion and flexibility. The addition of new lines or services often needs extra hardware, leading to higher costs and increased complexity. While this may not be problematic for businesses with consistent size and demand, it could be less suitable for those expanding or implementing a more modern business approach. Nevertheless, the reliability of POTS can be beneficial for operations prioritizing stability over growth, particularly in regions with limited technological infrastructure.
5/ Security and Privacy Concerns:
Security and privacy play a crucial role in the domain of business communications, each system bringing its unique challenges and strengths. VoIP, being internet-based, faces similar threats as other online services like hacking, phishing, and denial-of-service attacks. Yet, through the use of advanced encryption protocols and secure network configurations, VoIP security can be greatly enhanced to safeguard sensitive data and communications. Additionally, privacy features are often customizable, enabling your business to align its VoIP systems with specific regulatory compliance standards.
On the other hand, POTS’s infrastructure offers a level of security due to its physical nature; it’s not exposed to internet-based threats and there’s a reduced risk of digital eavesdropping. However, analog signals can still be intercepted, and the technology lacks the advanced encryption methods available in digital systems. Privacy on POTS is more about physical security, ensuring that the lines cannot be tapped and conversations remain confidential. Businesses operating under demanding privacy regulations may find the inherent security features of POTS favorable, even though they are becoming increasingly challenged by digital security solutions.
VoIP vs POTS: Pros and Cons
VoIP: Pros and Cons
Pros | Cons |
Lower costs for local and international calls. | Quality may suffer if the connection is unreliable. |
Easily scalable and adaptable to changing business needs. | Call quality may vary depending on network conditions. |
Offers advanced features such as video conferencing, virtual numbers, and more. | Open to security threats such as hacking. |
Integrates with other business applications, enhancing productivity. | Requires power and may not function during outages. |
Can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection, offering flexibility. | May not always provide accurate location information. |
Related Reading: What is the advantage of VoIP over traditional telephone lines
POTS: Pros and Cons
Pros | Cons |
Known for high uptime and reliability. | Higher costs for long-distance and international calls. |
Accessible in most areas, including remote locations. | Typically offers basic calling features and lacks advanced functionality. |
Provides accurate location information to first responders. | Aging infrastructure with declining support and potential disruptions. |
Straightforward setup, requiring minimal equipment. | Less adaptable and scalable compared to VoIP. |
Generally considered more secure compared to VoIP. | May become obsolete as technology advances. |
How does the POTS line work
POTS operates by establishing a dedicated circuit between two points for the duration of a telephone call through the public switched telephone network (PSTN).
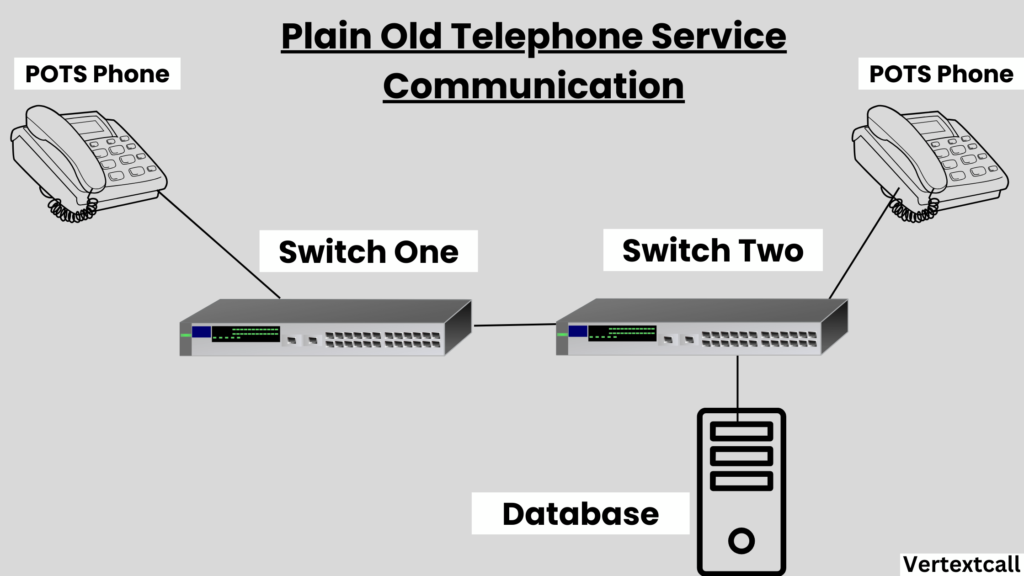
This means that when you make a call, a direct connection is created exclusively for that conversation. The system functions by converting the sounds of a voice into electrical signals using analog technology, allowing for the transmission of your voice over the network of wires and exchanges to reach the recipient.
While POTS is considered a reliable method of communication due to its simplicity and proven track record over many decades, it is becoming increasingly outdated with the rapid advancements in digital communication technologies.
What is an example of a POTS line?
A classic example of a POTS line is the traditional home landline telephone. This phone system is installed at a fixed location and has a dedicated phone number associated with it.

In businesses, fax machines are another example of devices that frequently utilize POTS lines, using a stable connection to transmit documents over long distances.
Elevator emergency phones and alarm systems also commonly rely on POTS lines to ensure a dependable means of initiating communication in critical situations.
These applications showcase the reliability of POTS in scenarios where a stable connection is crucial, reflecting its continued relevance in specific contexts despite the rise of digital alternatives.
Related Reading: Elevator phone line VoIP
Why are POTS lines going away?
The gradual discontinuation of POTS lines reflects the rapid technological advancements in digital communication. While POTS has been dependable, its infrastructure—copper wire networks—is expensive to maintain and lacks the flexibility of modern solutions. The rise of VoIP and subsequent innovations represent a shift towards more integrated, cost-effective communication platforms tailored to a digital-first era.
Additionally, the telecommunications industry has seen a significant shift in consumer behavior, with a preference for mobility, advanced features, and service integration, areas where POTS falls short. While analog lines were once the standard for voice communication, they are unable to meet the increasing need for rapid data transfer, leading to their outdated status.
Regulatory changes also play a role in this transition. As governments and regulatory bodies update policies to favor and facilitate digital communications, the support for legacy analog systems is in decline.
For instance
“On August 2, 2019, the FCC issued Order 19-72A1. This order required that by August 2, 2022, all traditional analog copper phone lines (POTS) in the U.S. must be replaced with a different service. The FCC announced this change with the headline ‘FCC Grants Relief from Outdated and Burdensome Regulations Governing Plain Old Telephone Service’.” (Source)
Funding previously allocated for maintaining POTS is now being redirected to enhance digital infrastructure, causing POTS lines to become scarce in the era of continuous digital advancement.
Why VoIP is better than POTS
When comparing VoIP to POTS, the advantages of VoIP become clear, showcasing its superiority in multiple areas of telecommunication. Here are several reasons why VoIP is often considered better than POTS:
1/ Unified Communications: VoIP plays a crucial role as a foundational element in unified communications, combining various modes of communication, such as voice, video, and messaging, into a unified and efficient system. This approach differs significantly from the traditional Plain Old Telephone Service, which primarily focuses on voice communication alone.
Related Reading: Unified Communications vs VoIP
2/ Remote Work Compatibility: As the trend towards telecommuting continues to rise, VoIP systems play a crucial role in facilitating effortless communication for remote workers. These systems enable your employees to access the business phone system from any location, promoting a high degree of flexibility that traditional analog systems lack due to their integral limitations tied to physical office setups.
Related Reading: Business VoIP phone system for remote workers
3/ Enhanced Data Integration: VoIP integrates with a variety of digital services such as CRM systems and email platforms, enhancing communication strategies and enabling more effective communication methods. This integration allows your business to streamline its communication channels, merging voice, video, and data services into a unified ecosystem. As a result, VoIP’s compatibility with data analytics tools offers advanced business intelligence, providing valuable insights into communication trends that can inform strategic decision-making.
4/ Regulatory Compliance: Modern VoIP services are increasingly designed with regulatory compliance in mind, aligning with standards such as GDPR and HIPAA. This ensures that communications remain private and data protection regulations are met, addressing a gap that traditional POTS systems did not initially cover.
5/ Higher Voice Quality: Modern VoIP services provide exceptional voice quality through advanced high definition (HD) voice capabilities, exceeding the traditional POTS with its analog limitations. By utilizing digital technology, VoIP ensures clear audio transmission, making communication more efficient and reliable for users across various platforms and devices.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1) What is the difference between POTS and VoIP lines?
Ans: The main difference between Traditional POTS and VoIP lines is that POTS lines connect through the publicly switched telephone network (PSTN) using analog signals and dedicated copper wires. On the other hand, VoIP lines offer the flexibility to use a wide range of devices, such as computers, VoIP phones, or even mobile devices, and they include advanced features like voicemail to email and call forwarding.
Q2) What is the difference between VoIP and POTS dial peer?
Ans: Within digital telephony systems, ‘dial peers’ serve as programmed endpoints for voice traffic on a network. In VoIP networks, a VoIP dial peer acts as the entity directing calls to a specific destination. This involves routing protocols, codecs, and packetization. In contrast, POTS dial peers relate to traditional routing over the PSTN without the need for packetization or digital codecs. POTS dialing is typically hard-wired and doesn’t possess the dynamic routing capabilities of VoIP, requiring manual or physical changes for adjustments.
Q3) What is POTS in VoIP?
Ans: POTS within a VoIP refers to the integration of the Traditional Plain Old Telephone Service in a Voice over Internet Protocol environment. This integration typically involves the use of devices like analog telephone adapters (ATAs) that allow standard telephones, which typically operate over PSTN to be used with VoIP technology. The concept aims to combine the reliability and familiarity of POTS with the advanced features and flexibility of VoIP systems.
Q4) What is IP POTS?
Ans: IP POTS is a modern adaptation of the classic telephone system that combines traditional POTS lines with the benefits of Internet Protocol technology. This integration allows for regular landline phones to connect to a digital network through an Analog Telephone Adapter (ATA) or a VoIP gateway. While these devices still provide the reliability and user experience of a conventional telephone system, they also enable additional functionality such as direct inward dialing and compatibility with modern VoIP features.
Q5) What is the difference between a VoIP phone line and a normal landline?
Ans: The core difference between a VoIP phone line and a traditional landline is that a VoIP phone line sends and receives calls over the internet by converting voice into digital packets, enabling additional functionality such as video calls, messaging, and file sharing within an integrated communication platform. On the other hand, a traditional landline operates over dedicated copper wiring, transmitting analog signals directly from one telephone to another.
Q6) Is VoIP better than PSTN?
Ans: VoIP and PSTN offer different advantages and the choice between them depends on your specific requirements. VoIP is often preferred for its flexibility, cost-efficiency, and advanced features like video calling and instant messaging, particularly beneficial for businesses frequently using the internet for communication. PSTN, on the other hand, demonstrates reliability with a solid infrastructure that can be invaluable in areas lacking stable internet access or during power outages where VoIP services may lapse. Thus, while VoIP offers modern communication solutions that cater to digital advancements, PSTN remains a reliable choice for those requiring a durable phone service.

