When it comes to telecommunications, there are two main methods for handling calls in a business setting: VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) and PBX (Private Branch Exchange) systems. VoIP uses internet connectivity to transmit voice data, which completely changes the way we think about traditional telephony.
On the other hand, PBX is a private network that allows calls to be routed to different extensions from external lines. In this guide, we’ll explore the differences between these technologies and how they can impact businesses in terms of scalability, cost-effectiveness, and integration capabilities.
Table of differences between VoIP and PBX
Aspect | PBX | VoIP |
Infrastructure | Hardware-based system, often on-site | A software-based system, relies on the internet |
Cost | Higher initial setup and maintenance costs | Lower initial setup costs, potential savings in the long term |
Scalability | Limited scalability, may require hardware upgrades | Highly scalable, easy to add or remove lines/users |
Flexibility | Limited flexibility for remote work and mobile integration | Flexible, supports remote work and mobile integration |
Features | Basic features such as call routing, voicemail | Rich features including video conferencing, virtual numbers |
Reliability | Generally more reliable due to dedicated hardware | Reliability may depend on internet connection quality |
Maintenance | Requires regular maintenance and updates | Software updates can be applied remotely |
Integration | Limited integration with other software systems | Seamless integration with CRM, email, and other business tools |
Geographic Restrictions | Limited to a physical location | No geographic restrictions, global connectivity |
Use Cases | Suitable for established businesses with specific regulatory or compliance requirements | Ideal for businesses with remote workforce, scalable communication needs, and integration with CRM and other business applications |
Disaster Recovery | May require separate disaster recovery plan | Built-in redundancy and disaster recovery features |
Regulatory Compliance | Compliance may require additional effort | Service provider ensures compliance with regulations |
PBX & VoIP Meaning:
What is VoIP
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) is an advancement in telecommunications that utilizes internet connectivity to transmit voice data. Unlike traditional telephone lines, VoIP converts voice signals into digital packets and routes them through the Internet. This means you can have high-quality calls, continuously integrate with other communication technologies, and save costs by utilizing existing IP networks.
From an analytical standpoint, the primary advantage of VoIP is its scalability, allowing your business to add lines or features without major infrastructure changes easily. Operationally, VoIP unifies communication systems and unlocks advanced functionalities such as voicemail-to-email transcription and direct inward dialing. These capabilities enhance communication in a way that fulfills the needs of your modern business.
Types of VoIP
The VoIP ecosystem can be divided into two main categories:
Fixed VoIP and Non-Fixed VoIP.
Fixed VoIP is tied to physical addresses and offers reliable security protocols, making it a popular choice for businesses that value a reliable connection similar to traditional landlines.
On the other hand, Non-Fixed VoIP provides flexibility, allowing you to make and receive calls without being tied to a specific location. This is particularly advantageous for remote employees and organizations with a global presence.
Related Reading: Learn more about fixed VoIP vs. non-fixed VoIP
What is PBX
A Private Branch Exchange (PBX) is a dedicated telephone network used by organizations to efficiently manage incoming and outgoing calls. With a PBX phone system, employees share a set number of external lines for outgoing calls, ensuring smooth communication within the office environment.
This reliable technology has been the preferred choice for decades, offering enhanced call management capabilities and facilitating uninterrupted connectivity for businesses of all sizes. By utilizing a PBX system, your organization can streamline its telecommunication processes, improve efficiency, and enhance overall productivity.
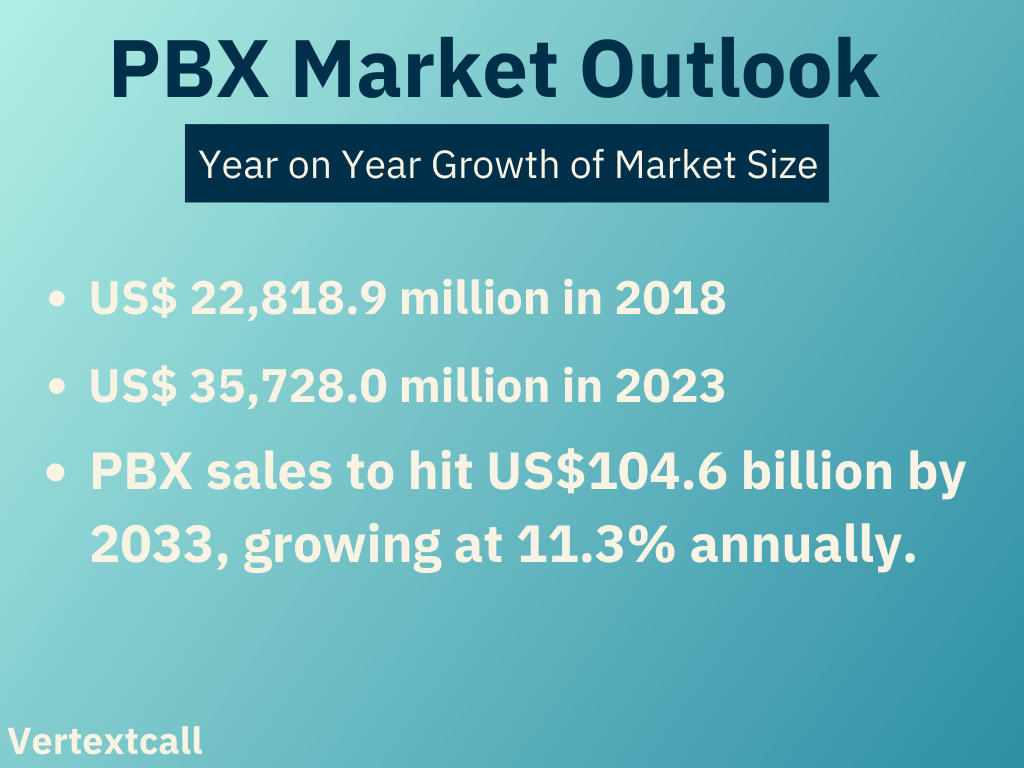
PBX sales revenue is forecasted to grow at an 11.3% CAGR from 2023 to 2033, reaching US$104.6 billion by 2033.
Types of PBX
Apart from the Traditional PBX Systems discussed above, There are several types of PBX systems, each with its features and functionalities. Here are some common types:
IP PBX Systems
IP PBX is an updated version of PBX technology that leverages IP data networks for call routing and switching. It offers advanced communication features and seamlessly integrates with other internet-based communication methods, providing scalability and potential cost savings.
Hybrid PBX Systems
Hybrid PBX systems combine the reliable features of traditional PBX with the advanced capabilities of IP technology. This type of system offers your business the flexibility to use both digital and analog communication methods, making it highly adaptable.
Hosted PBX Systems
Cloud-based hosted PBX solutions are managed offsite by a third-party service provider, offering your business the advantages of a PBX system without capital expenses or equipment maintenance.
The main difference between VoIP and PBX
VoIP and PBX are both technologies used for managing telephone calls within an organization, but they serve different purposes and operate in different ways. Here’s the main difference between the two:
1/ Infrastructure comparison:
VoIP mainly operates through software-driven technology, requiring minimal physical setup and relying primarily on internet infrastructure. On the other hand, PBX systems can utilize various technologies, including traditional copper lines or ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network), providing a more stable and reliable network connection.
These technologies ensure uninterrupted communication and enable businesses to have a dedicated phone system within their premises. While VoIP offers flexibility, PBX offers a tried and tested solution for those seeking a stable and dependable network for their communication needs.
2/ Communication Medium:
VoIP transmits voice data as packets over the Internet, which can occasionally result in quality issues due to transmission delays. Conversely, PBX traditionally employs dedicated phone lines, providing consistent and clear voice communication with minimal interference. By utilizing dedicated phone lines, PBX systems ensure reliable and high-quality voice transmission, making them the preferred choice if your business prioritizes uninterrupted communication.
3/ Business Scalability:
When deciding between VoIP and PBX, scalability plays a crucial role from an analytical standpoint. Voice-over Internet Protocol offers built-in scalability, allowing your business to effortlessly add or remove lines with minimal adjustments to the infrastructure. This flexibility provides a significant advantage to growing companies that require quick adaptability.
On the other hand, a Private Branch Exchange (PBX) system often requires a predetermined physical infrastructure, resulting in additional hardware costs and potential downtime when scaling up or down. While PBX can be scaled, the processes involved are typically more complex and resource-intensive compared to the streamlined scalability offered by VoIP solutions.
4/ Features and Functionality:
Both VoIP and PBX systems offer advanced features to streamline communication. These include call routing for efficient call management, voicemail-to-email for convenient message retrieval, and call queuing to ensure callers are attended to in an organized manner.
However, one key advantage of VoIP is its unified integration with a wider range of software tools. This integration opens up possibilities for additional functionality that can greatly enhance productivity and customer service. From CRM integration to advanced analytics and reporting, VoIP supports businesses with the tools they need to deliver exceptional service and maximize efficiency.
5/ Reliability and Call Quality:
VoIP call quality can sometimes be affected by internet issues such as bandwidth limitations or network congestion, resulting in drops in call quality or service interruptions. On the other hand, PBX systems, especially those that do not rely on the Internet for connectivity, tend to offer more consistent call quality and reliability. This is because PBX systems utilize dedicated phone lines or local networks, ensuring a stable and uninterrupted communication experience for users.
6/ Ongoing Expenses:
The financial implications of choosing between VoIP and PBX can have a significant impact. VoIP generally has lower startup costs, primarily due to minimal hardware requirements and easy setup. On the other hand, PBX systems often require larger initial investments, especially for large enterprises with substantial infrastructure needs.
However, when considering long-term costs, a different perspective arises. VoIP provides scalability and affordable international calling, which helps offset the expenses for upgrades and maintenance that PBX systems may require.
7/ Protecting Communication:
When assessing the security of VoIP and PBX systems, it is crucial to consider various threats and protective measures. Since VoIP services operate over the internet, durable cybersecurity practices are essential to prevent potential digital breaches. This includes the deployment of firewalls, encryption, and regular security updates to ensure comprehensive protection.
On the other hand, PBX systems are generally considered to be less open to cyber threats due to their use of dedicated lines. However, they are not completely immune and require protective strategies, such as implementing physical security measures and controlling access to the hardware. In terms of ensuring the safety and privacy of communications, both systems must be carefully managed.
8/ Enhanced Interoperability and Innovation:
PBX systems are widely used in businesses and are known for their standardized approach and adherence to defined protocols. While this ensures interoperability, it can sometimes limit the scope for innovative communication solutions.
On the other hand, VoIP technology continues to evolve, offering a broader range of features and integrations. With standards like SIP (Session Initiation Protocol), VoIP enables seamless communication and facilitates the integration of various business applications, resulting in enhanced efficiency and productivity.
Related Reading: Learn more about SIP vs VoIP
9/ Maintenance and Support:
VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) systems are generally easier to maintain and troubleshoot compared to traditional phone systems due to their digital nature. On the other hand, PBX systems may require specialized technicians for installation and maintenance, but they offer a higher level of support and reliability that some businesses find reassuring.
What is the difference between VoIP gateway and PBX?
A VoIP gateway is a network device that converts telephony traffic into IP to be transmitted over a data network. It serves as a vital link between the traditional Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) and VoIP system by efficiently translating analog voice signals into digital data packets and vice versa.
This functionality allows organizations to use their existing telephony infrastructure while enjoying the advantages of IP telephony.
On the other hand, a PBX serves as a dedicated telephone network within an organization, to manage inbound and outbound calls, as well as internal communication. A traditional PBX system can be based on analog or digital technology and does not essentially utilize IP technology for voice transmission.
However, modern IP-PBX systems employ VoIP technology and are designed to handle the routing and switching of calls between a VoIP network and traditional telephones.
The main difference can be found in functionality: a VoIP gateway primarily focuses on converting signals between different formats. On the other hand, a PBX offers a more comprehensive set of call management features, including call forwarding, voicemail, call queues, and conferencing, within an organization’s private phone system.
While a VoIP gateway can integrate into a PBX system during the transition to IP telephony, it lacks the internal networking and call management capabilities that a PBX provides.
PBX Vs Cloud VoIP
The below table provides a concise overview of the differences between PBX and Cloud VoIP across various aspects:
Aspect | PBX | Cloud VoIP |
Infrastructure | On-premises hardware | Hosted in the cloud |
Initial Cost | Higher upfront costs for hardware | Lower upfront costs; often subscription-based |
Features | Typically includes basic calling features | Broad range of features including video conferencing, virtual receptionist, mobile integration, etc. |
Reliability | Dependent on local infrastructure and maintenance | Relies on the reliability of the internet connection and service provider |
Accessibility | Tied to physical location | Accessible from anywhere with an internet connection |
Implementation Time | Longer implementation time due to hardware setup and configuration | Quick setup; can be operational within hours |
Updates and Upgrades | Manual updates and upgrades may be required | Automatic updates and upgrades provided by service provider |
Regulatory Compliance | Compliance may require additional effort | Service provider ensures compliance with regulations |
Hosted PBX Vs Hosted VoIP
Feature | Hosted PBX | Hosted VoIP |
Infrastructure | Uses IP-based infrastructure managed off-site | Relies on IP networks managed off-site |
Hardware | Requires physical PBX hardware on-premises | Does not require physical PBX hardware |
Cost | May involve higher initial investment and maintenance expenses | Generally offers cost savings due to lower infrastructure and operational costs |
Integration | Limited integration capabilities | Seamless integration with other software applications and services |
Features | Generally provides basic call management features | Offers a broader range of features and functionalities, including video conferencing, instant messaging, and mobility features |
Flexibility | Limited customization options | Highly flexible, customizable to meet specific business needs |
Reliability | Relies on the reliability of on-premises hardware | Relies on the reliability of off-site servers and network infrastructure |
Use Cases | Suitable for established businesses with specific regulatory or compliance requirements | Ideal for businesses with remote workforce, scalable communication needs, and integration with CRM and other business applications |
Disaster Recovery | May require separate disaster recovery plan | Built-in redundancy and disaster recovery features |
Regulatory Compliance | Compliance may require additional effort | Service provider ensures compliance with regulations |
Why do companies use PBX?
As PBX serves as a private telephone network within an organization, it provides an efficient way to manage calls with more control and flexibility. There are several compelling reasons why companies choose to incorporate PBX systems:
1/ Minimum Dependence on Internet Quality: PBX systems, operate independently of Internet connectivity. This means that they are not affected by the variable quality of Internet service, which can sometimes lead to call issues. This reliability is especially crucial in environments where uninterrupted communication is essential, such as call centers or emergency services.
2/ Centralized Communication Control: Companies also choose PBX systems to have a single, centralized system that efficiently directs all incoming and outgoing calls, ensuring smooth communication flows.
3/ Cost-Effectiveness: By consolidating communications into one system, businesses reduce the need for multiple phone lines and minimize operational costs, providing a fiscal advantage to the organizations.
4/ Advanced Features: Utilizing PBX allows companies to leverage advanced call features such as voicemail, call forwarding, and conferencing, which are crucial for enhancing both productivity and collaboration within the workforce.
5/ Improvement in Customer Experience: Features like call queuing and direct extension dialing improve customer interaction and satisfaction, playing a pivotal role in competitive industries.
6/ Adaptability: As enterprises grow and communications technologies evolve, PBX systems offer the flexibility required to integrate new functionalities and update the existing setup to meet changing needs.
What are the disadvantages of PBX?
While traditional PBX systems do provide reliable performance and control, it’s important to consider their inherent disadvantages.
1/ Inflexibility to Scaling: One of the challenges of PBX infrastructure is the inflexibility to scaling. Unlike VoIP, which offers more flexibility, scaling a PBX system can be difficult and expensive. It often involves the need for new hardware and installation work, which adds to the complexity and cost. This limitation can pose obstacles if your business requires a scalable communication solution.
2/ Upfront Investment: Implementing PBX systems typically requires a significant initial investment in hardware and installation. This can include the cost of purchasing the necessary equipment, such as servers, routers, and phones, as well as the expenses associated with setting up and configuring the system. If you are running a startup or small business, this financial commitment can pose a barrier, especially when you are operating on limited budgets and trying to allocate your resources effectively.
3/ Limited Remote Capabilities: Traditional PBX systems often lack the necessary flexibility for remote work, which hampers workforce adaptability. This limitation can result in inefficiencies and difficulties for remote employees, who may require additional solutions to effectively collaborate and communicate outside of the office environment.
4/ Limited Advanced Features: Traditional PBX systems offer fewer advanced features and integrations compared to modern VoIP systems. This lack of flexibility can hamper communication efficiency for certain businesses. For instance, while traditional PBX systems may have basic call-forwarding capabilities, they may not support advanced features such as call recording, voicemail-to-email transcription, or integration with customer relationship management (CRM) software.
What advantages does VoIP offer over PBX?
When comparing VoIP and PBX systems, VoIP stands out for its technologically advanced advantages. Some of these include
1/ Improved Cost-Efficiency: VoIP systems offer enhanced cost-effectiveness compared to traditional PBX systems, both during initial deployment and in the long run. This is achieved by leveraging existing internet resources, eliminating the need for dedicated phone lines, and reducing expenses associated with long-distance and international calls.
2/ Simplified Infrastructure: VoIP simplifies the infrastructure by utilizing internet connectivity for communication. This integrated approach enhances communication processes by seamlessly integrating voice and data, reducing the complexity of managing separate networks. It also helps to reduce maintenance needs, as there is no need for extensive on-site hardware installations or regular hardware upgrades. By eliminating the dependence on physical hardware, VoIP provides businesses with the ability to scale and adapt to evolving communication needs effortlessly.
3/ Mobility and Remote Compatibility: VoIP technology facilitates users to connect and communicate efficiently from virtually anywhere, making it an essential feature in today’s remote work environment. The built-in flexibility of this solution strengthens employees to maintain productivity and develop effective collaboration, regardless of their geographical location. By utilizing VoIP, your organization can ensure a consistent level of service and support for its workforce, driving efficiency across the board.
Related Reading: VoIP for remote workers support
How to connect PBX to VoIP
Integrating a traditional Private Branch Exchange (PBX) system with VoIP technology can be done in various ways.
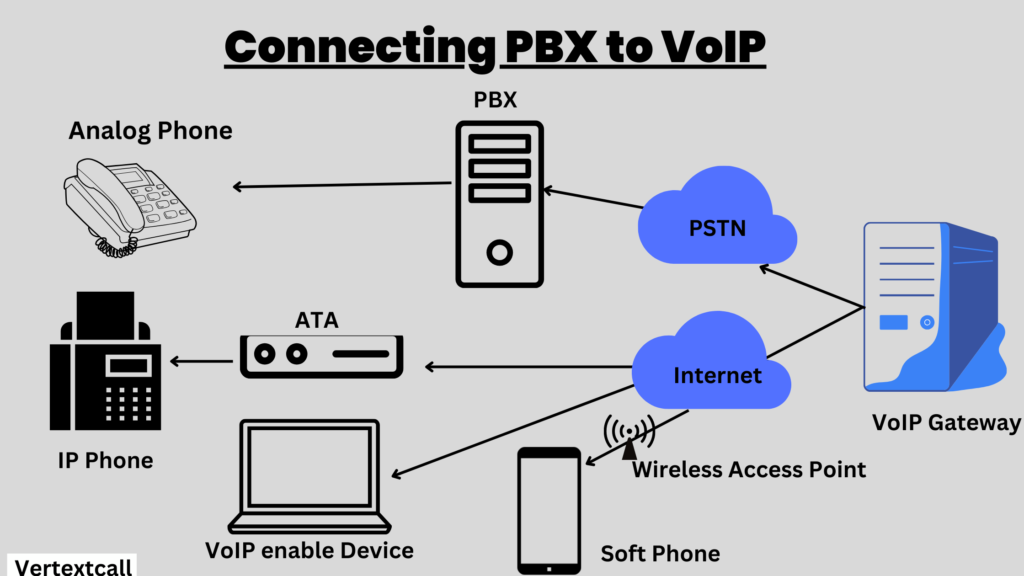
One common approach is to use an IP Media Gateway, which acts as a bridge between the PBX’s analog or digital signals and the digital VoIP network. This gateway converts voice traffic into IP packets that can be sent over the internet.
To make sure the existing PBX equipment and the gateway are compatible, your organization should carefully analyze technical specifications and conduct thorough testing. Also, implementing Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) trunking aligns the public switched telephone network (PSTN) with internet-based telephony service.
This allows direct communication between the PBX and the VoIP provider, leading to potential cost savings and increased functionality.
When planning this integration, it’s important to consider possible interoperability challenges, bandwidth requirements, and security protocols to ensure a smooth connection that improves business communications.
Which is better PBX or VoIP
Choosing the right telephony solution that aligns with your business goals and operations is a crucial decision. Let us guide you through the selection process:
Factors to Consider
When considering the options, take into account the following factors:
- Current and future call volume: Assess the expected number of calls and the patterns of usage over time. Understanding these aspects will help determine the appropriate solution to handle the communication needs effectively.
- Internet and network capabilities: Evaluate the quality and reliability of your internet and network infrastructure to ensure seamless operation and implementation of (VoIP) systems. Strong internet and network capabilities are crucial for ensuring clear and uninterrupted communication.
- Budget constraints: Take into consideration your budget limitations and the availability of capital for investing in a communication solution. Consider both upfront costs and ongoing expenses to align with your financial resources.
- The flexibility required by your organization: Analyze the level of flexibility needed by your organization in terms of scalability, remote work capabilities, and integration with other systems. Having a communication solution that can adapt to the changing needs of your organization is essential for long-term success.
By taking these detailed factors into account, you can make a more informed decision regarding the optimal communication solution for your organization.
Assessing Business Needs and Goals
When it comes to deciding which option is best for your business, it ultimately comes down to your specific needs and long-term goals. If flexibility is a priority for you and you’re willing to handle occasional connectivity issues, then VoIP might be the right choice.
On the other hand, if call quality and reliability are important and you have the necessary resources for a larger upfront investment, a PBX system could be the optimal solution for you.
Frequently Asked Question
Q1) What is IP PBX and VoIP?
Ans: An IP PBX (Internet Protocol Private Branch Exchange) is a telephony system that uses IP data networks to facilitate voice communications. It combines the traditional PBX functionalities with modern VoIP features, allowing calls to be transferred over a network on the internet or local network.
VoIP is a comprehensive term that includes voice transmission over the internet, rather than traditional telephone lines. VoIP technology is commonly integrated into IP PBX solutions to facilitate these transmissions. Its functionality involves converting analog voice signals into digital packets, which then travel over IP networks to reach their destination. Upon arrival, they are converted back into voice sounds.
Q2) Does VoIP require a PBX?
Ans: VoIP does not necessarily require a PBX to function; it simply needs an internet connection and the appropriate VoIP software/hardware. VoIP can be used with various communication systems, such as a hosted PBX, IP PBX, or even without any PBX setup, as observed in direct peer-to-peer VoIP calls.
Q3) Is PBX Obsolete?
Ans: No, the PBX system is not completely obsolete. While technological advancements have led to a significant shift towards IP-based systems like VoIP, PBX systems have also evolved into IP PBX with VoIP capabilities. Traditional PBX remains relevant in situations where reliable communication is crucial, particularly in areas with limited internet access or for organizations that prefer to maintain their communication systems on-premises due to privacy concerns or specific industry regulations.
Q4) Is PBX Outdated?
Ans: PBX systems may appear to be outdated when compared to the latest cloud-based VoIP services that offer greater flexibility and a broader range of features. However, they remain in use due to their reliability and control over the communication process. Companies that have invested in strong infrastructure and PBX systems can still derive significant benefits from their usage.
Q5) What is a VoIP-hosted PBX Solution?
Ans: A VoIP-hosted PBX solution is a telephony system that operates in the cloud, combining the Private Branch Exchange functionality with the service provider’s data servers instead of being located on the business premises. By utilizing VoIP technology, it allows for making and receiving calls without the need for physical hardware or traditional telephone service lines. This setup offers advanced features like automated attendants, call forwarding, voicemail, call recording, and integration with various business applications—all managed through the Internet.

