In this blog, we’ll take a deep look into the history of Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) and its transformation since 1870. Starting from its initial opposition to the monopolistic practices of traditional telephone companies to the present day where VoIP stands as a pillar of global communication, we’ll explore the significant milestones and technological advancements that have shaped its evolution.
History of technologies for VoIP existence
To understand the history of VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol), we need to look at two key inventions. The first is the telephone, an essential tool for voice communication over distances. The second critical development is the Internet, a broad network for sharing information globally.
The Invention of the Telephone in the 1870
In the 1870s, two inventors, Alexander Graham Bell, and Elisha Gray, played important roles in creating the telephone. This device allowed people to talk to each other from long distances for the first time, using wires to carry their voices.

The fundamental concept of telephony was to convert sound waves into electrical signals. These signals can be transmitted over extensive distances and then converted back into sounds that can be heard.
From then on, voice communication became an integral part of human interaction and business transactions. Over time, the telephone evolved into a more advanced and reliable technology, enabling us to communicate with each other across countries.
Strowger’s Automatic Switch
In 1889, Almon B. Strowger from Kansas City, came up with an idea for a new kind of switch. This wasn’t just any switch—it was a major advancement that would change how telephone calls were made.

Before this invention, connecting a call required a human operator to manually connect wires. Strowger’s switch allowed these connections to be made automatically, making it quicker and easier for people to talk to each other over the phone. This advancement was a big step forward in making telephone communication more efficient.
Shannon’s Binary Revolution: Transforming Communication
In 1943, Dr. Claude Shannon published a seminal paper that would become the foundation for the digital communications revolution.
His work introduced the concept of using binary digits to represent information, a principle that is the foundation of all modern digital communication, from cellular phones to the extensive scope of the Internet.
Shannon’s theories on information and communication essentially transformed the way data is transmitted, stored, and processed. This new development set the foundation for internet-based voice calling (VoIP) and many other tools that form our current digital environment.
Entry of TouchTone Dialing in Telecommunications
In 1963, utilizing the work of Dr. Claude Shannon, AT&T introduced “TouchTone” dialing, a system that significantly advanced the field of telecommunications.
This technology replaced the traditional circular dialing method with a push-button interface, enabling faster and more reliable call setup.
The TouchTone system used a form of in-band signaling, where different frequencies were assigned to each button on the keypad, allowing for dual-tone multi-frequency (DTMF) signaling.
This innovation was not only about improving user experience; it also increased the efficiency and capacity of the telephone network.
The Evolution from ARPANET to the Internet
In 1968, ARPANET, a research project funded by the U.S. Department of Defense, took foundational steps toward creating the Internet. ARPANET’s development represented the beginning of interconnected computer networks, which enabled various computers to communicate.

This was a significant advancement in the field of computer science and telecommunications, as it introduced the concept of packet switching—a method for efficiently transmitting data over a network.
This innovation allowed data to be broken down into packets, sent to their destination through various routes, and then restored upon arrival. The successful implementation of ARPANET initiated the process for the global network of networks, known today as the Internet.
The Internet’s creation provided a new platform for communication, including voice communication, which would later evolve into technologies like VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol).
The Rise of Time-Sharing Systems in Computing
During the 1970s, alongside the development of the Internet, another significant technological advancement took place with the introduction of time-share computing systems.
This revolutionary concept transformed the way computing was conducted, allowing users to utilize a single computer system at the same time but from various terminals.
Time-sharing systems were designed to optimize the use of mainframe computers, which were expensive and not widely accessible at the time.
By allowing multiple tasks to be processed in an overlapping mode, time-sharing maximized efficiency and significantly reduced the cost and physical space requirements previously associated with computer usage.
This development played a crucial role in making computing resources more accessible to universities, research institutions, and businesses, developing an environment of increased collaboration, innovation, and productivity.
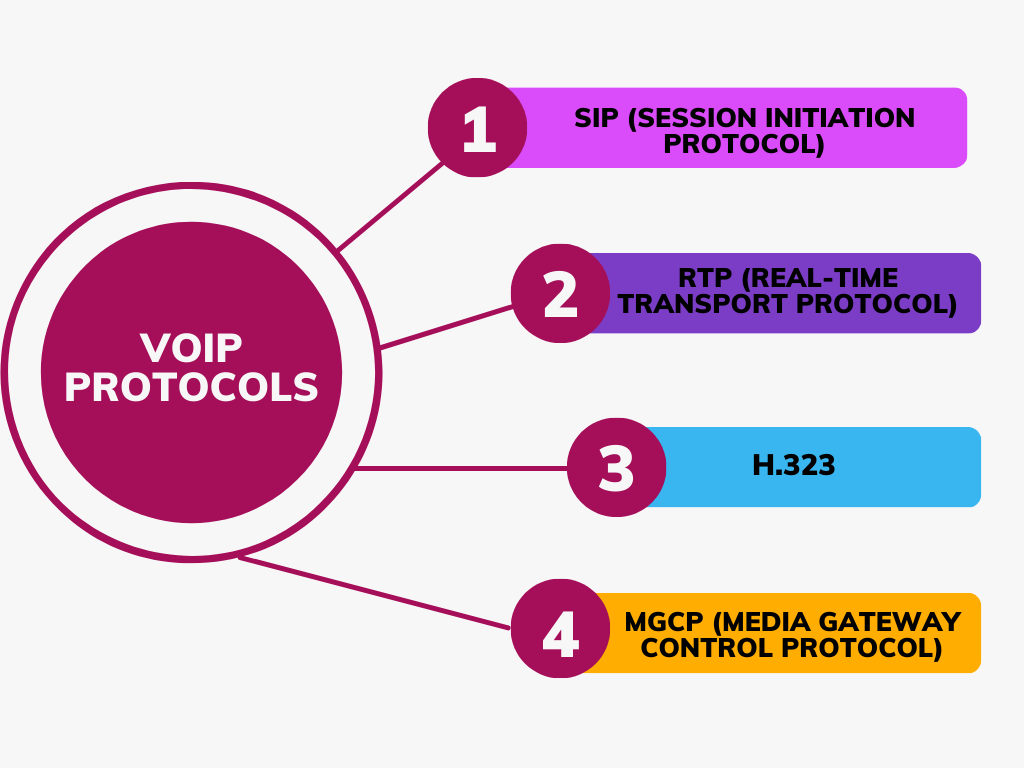
Introduction of VoIP Protocols
In 1972, Dr. Vint Cerf contributed to the field of digital communication by inventing the Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), which would become the foundational protocol for VoIP technologies and Internet connectivity.
The Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) plays a pivotal role in ensuring the reliable, sequential, and error-free exchange of data streams between applications on different devices connected through the Internet.
By standardizing how data is exchanged over the Internet, TCP/IP enabled the creation of a globally interconnected network of computers, —essentially, the internet as we know it today.
The protocol set was divided into two layers: TCP, which segments a message or file into smaller packets for transmission and reassembles them at the destination, and IP, which directs each packet to its correct destination by tagging it with a destination address.
This innovative approach not only promoted the development of VoIP technologies, enabling voice and multimedia content transmission over the internet but also significantly transformed telecommunications by offering a cost-effective and adaptable alternative to traditional phone networks.
Invention of VoIP
VoIP, or Voice over Internet Protocol, started in February 1995 with the initiative of VocalTec, Inc., a small company from Israel.
This technology significantly changed how we communicate by using the Internet to transmit voice calls instead of traditional and costlier telephone networks.
VoIP functions by transforming voice signals into digital data packets, transmitting them across the Internet, and then re-transforming them into voice signals for the receiver.
This method reduces the cost of long-distance and international calls and increases the flexibility in making or receiving calls from different locations.
VoIP Communication and Business Dynamics
By 1998, VoIP technology had evolved from its early ideas, with experts realizing its potential for business and its ability to change the telecom industry.
Entrepreneurs started to offer VoIP solutions that changed how we use voice communication. These included services that let people make calls from a computer to a regular phone, and services allowing calls from one phone to another over the Internet.
This was a big step forward. It showed that VoIP could move from being just a new idea to a useful way to communicate, proving it could replace or add to old phone systems. The development of computer-to-phone and phone-to-phone VoIP showed it could be a cheaper option for calling overseas or long distances, helping to make VoIP a normal part of communication networks.
This stage was key in showing what VoIP could do and making it important for both personal and business use around the world.
VoIP Cultural History
The cultural history of VoIP is based on several key factors that drove its development and adoption globally. Initially, its rise was partly due to the lack of accessible traditional phone services, as highlighted by the Association of African Internet Service Providers (AfriISPA).
Experts like Daniel Berninger have argued that VoIP was created to avoid traditional telephone companies’ monopolistic control over communication, offering a cheaper alternative to avoid costly per-minute charges. Above cost-saving, the core belief in the universal right to communicate was fundamental to VoIP’s cultural significance.
From a business perspective, multinational corporations quickly saw the value in VoIP for reducing communication expenses and streamlining their information infrastructure. This technology also supported the globalization of the workforce, as seen in instances where
American call center jobs were transferred to India, impacting cultures on both ends. Indian call center workers, for example, were often trained to adopt Western mannerisms and accents, a process criticized for its cultural implications.
VoIP Economic History
When VocalTec Communications introduced InternetPhone in 1995, big companies like Bell Laboratories had not yet explored using the Internet to make phone calls. By 2004, VoIP had become a major focus of telecom research and development.
This innovation offered a cheaper alternative to traditional phone services, reshaping the telecom industry. Initially, the monopoly held by AT&T over telecommunications and computing prevented any significant competition.
However, key events in 1968, including regulatory decisions and technological advancements, began to break down this monopoly, opening doors for VoIP and other telecommunications innovations.
These changes encouraged companies to reduce costs by integrating their voice and data networks, despite initial concerns over call quality. Internet Telephone Service Providers (ITSP) saw a business opportunity to improve call quality for a fee.
VoIP services become mainstream (from 2000s onwards)
Entry of major players like Skype
In the early 2000s, Skype became a key player in the VoIP space, changing how people connect worldwide.
It made internet calls accessible to many, allowing for free international communication. Skype was easy to use and supported voice, video calls, and messaging, making it more than just software – it became a symbol of global connection.
Its success showed the possibilities of VoIP technology, representing a big step in digital communication’s growth. Skype used the internet to offer an alternative to traditional phone systems, hinting at a future where voice and video chats could be as easy as sending an email.
Transforming Communication Through Mobile Devices
The expansion of VoIP technology to mobile phones in 2005 significantly changed how we communicate. This change meant that people could now use internet-based calls directly from their smartphones, offering a convenient and cost-effective alternative to traditional phone services.
Through applications designed to support VoIP, users can conduct calls over the internet from their mobile devices, enhancing connectivity and reducing costs.
The current state of VoIP technology
Today, Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) technology is a fundamental part of how we communicate, both in personal and professional settings.
With its well-to-do history and rapid development, VoIP has revolutionized communication, making it cheaper, more accessible, and more adaptable.
With the rise of smartphones and mobile internet, VoIP became even more accessible. Recent research indicates that more than 31% of businesses have shifted to VoIP as their main method of communication, highlighting its growing importance.
Moreover, projections suggest the global VoIP market will hit $55 billion by 2025, showcasing the technology’s rising value and adoption levels.
What we expect to be the future of VoIP
Looking ahead, the way we make calls using the Internet is expected to get even better and more common. With technology always getting better, internet calls (or VoIP) will become more common in our daily lives, both for chatting with personal networks and for work meetings.
Additionally, businesses are discovering the various benefits of Internet calls, which offer significant cost savings and enhanced functionalities.
Shortly, we can expect even more innovative features, such as 3D video calls or compelling experiences that recreate being in the same room as the person you’re interacting with.
Moreover, as this technology gains wider adoption, the costs associated with it are decreasing, making it more accessible to everyone.
Related Reading: What Did VoIP Replace?

