The telecommunication industry keeps changing, especially with new technology. Similarly, the way businesses manage phone systems has transformed significantly. Gone are the days when traditional ISDN lines were the only option.
Today, we have the flexibility to choose between ISDN systems and the increasingly preferred VoIP solutions for our businesses. In fact, the global mobile VoIP user base has exceeded 3 billion.
But how do these two options differ, and which one is right for you?
We will compare VoIP and ISDN systems, looking at their advantages and disadvantages. This comparison aims to help your business understand its options in communication technologies better.
What is VoIP
In simple terms, VoIP technology allows us to make regular phone calls with the help of an internet connection, instead of using a traditional phone line
Essentially, VoIP converts your spoken voice into digital signals, transmits them across the internet, and then converts them back on the other end so the person you’re calling can hear you as if you were using a regular phone.
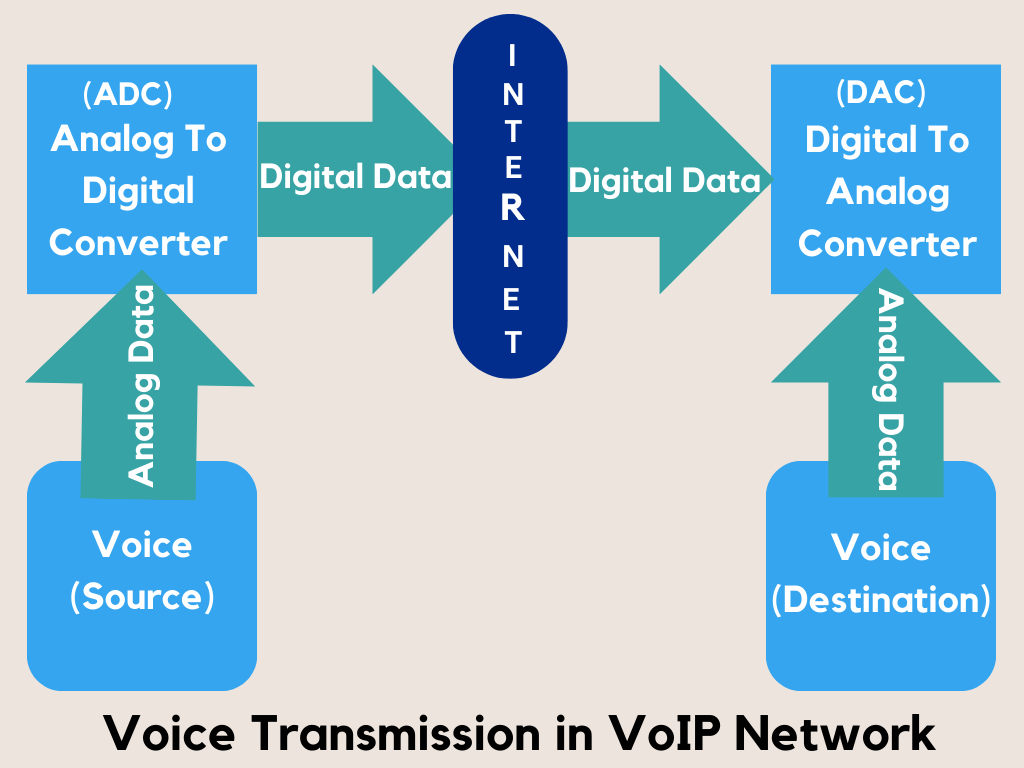
Additionally, you can make VoIP calls directly from your daily-use laptop, a VoIP phone, or other data-driven devices, offering a flexible and often less expensive alternative to the costlier traditional phone systems.
Check out our detailed guide on: What is VoIP
What is ISDN
ISDN, or Integrated Services Digital Network, is a more traditional form of telecommunications technology. It’s a method of transforming your standard phone line into a high-speed digital office for your voice, data, and video communications.
Unlike VoIP technology, ISDN provides a reliable digital transmission through dedicated lines, ensuring a level of service quality that internet-based services can have difficulty matching.
This technology enables multiple digital channels to be operated together over the same regular copper phone wires. This means you can host video conferences, transfer large files, and simultaneously carry out voice calls without experiencing a quality decline.
Difference between ISDN and VoIP
The key difference between ISDN and VoIP is the technology they use to transmit voice and data communications. Below we have discussed 5 main aspects that differentiate the two technologies:
1/ Call Quality:
ISDN provides premium call quality by transmitting voice, video, and data over dedicated digital lines. This ensures you get clear, high-quality communication without the interruptions or quality issues sometimes experience with internet-based services. ISDN’s reliability makes it ideal if your business prioritizes consistent communication quality, especially if you are operating in areas with less stable internet services.
VoIP technology offers a highly flexible and cost-effective solution for your communication needs. However, it’s important to understand that maintaining optimal call quality can sometimes present a challenge, primarily due to its dependence on your internet connectivity. This reliance means that VoIP’s performance is directly influenced by the quality of internet service, including bandwidth availability, latency rates, and the potential for packet loss.
2/ Flexibility and Scalability:
ISDN systems are relatively inflexible, requiring you to have physical lines installed and removed to adjust to your business needs. Each PRI (Primary Rate Interface) line handles 23 voice channels, which might be too much for your small business or too little if you are running a larger operation.
VoIP technology gives you better flexibility and scalability for your business’s communication needs. Unlike traditional ISDN systems, which require physical installation or removal of lines to scale, VoIP allows you to adjust the number and type of services you use through a simple online management platform. Whether you need to add more lines, or you’re scaling down, VoIP adapts to your needs without the need for extensive physical infrastructure changes.
3/ Cost-Effectiveness:
ISDN requires a physical infrastructure, meaning there are initial setup costs and ongoing maintenance expenses. For each PRI line, you’re investing in a dedicated connection that can handle up to 23 (or 30, depending on your location) simultaneous calls. You’ll also need to consider the cost of installation, potential equipment needed, and any maintenance fees.
With VoIP, your cost efficiency significantly increases. As VoIP operates over your existing internet connection you can avoid many of the upfront installation fees, costly equipment, and maintenance charges that come with traditional telephony systems.
4/ Reliability and Redundancy:
ISDN phone lines are not affected by electricity power outages and are generally viewed as a stable and reliable means of communication. For businesses where a phone line failure is unacceptable, ISDN’s dependability is a key factor.
VoIP setup allows for immediate rerouting of calls to alternate locations or devices in case of an internet outage, ensuring your business communication remains uninterrupted.
5/ Additional Features and Integration:
ISDN systems come with a range of functionalities such as caller ID, call forwarding, and three-way calling, alongside more advanced features like call queuing and conferencing. Additionally, it offers the capability to integrate with your current telecom and network infrastructures for a personalized level of customization.
VoIP phone system offers features like advanced call routing, virtual numbers, and an online management platform that allow for easy adjustments and scalability to match your changing business needs. Additionally, VoIP technology supports call management options including voice and video calls, message services, call waiting, caller ID, voicemail to email transcription, conference calling, and mobile app integration.
Why should I switch to VoIP?
There are many reasons why you should be switching over to VoIP from ISDN (later in the article, we have also listed the steps to do so). Here are some of the reasons for opting for VoIP for your business operations.
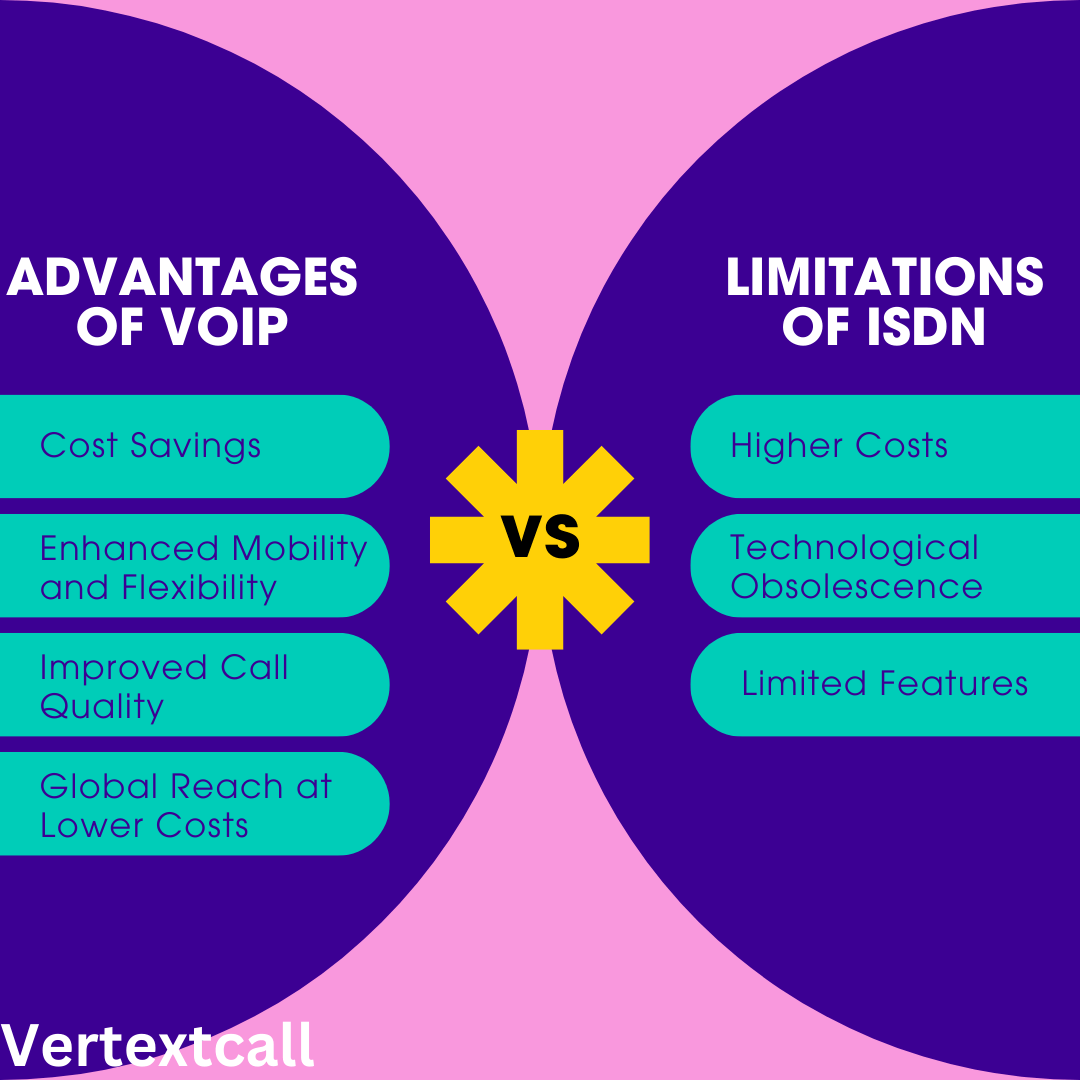
Advantages of VoIP
1/ Cost Savings:
One of the foremost benefits VoIP offers you is significant cost savings. By using your internet infrastructure, VoIP reduces many of the initial setup and ongoing maintenance expenses associated with traditional ISDN systems.
2/ Enhanced Mobility and Flexibility:
VoIP technology enables your employees to stay connected from their remote locations. Through internet connectivity, employees can access their phone system anywhere, offering a level of mobility that traditional phone systems simply can’t match. This means that whether your team members are working from home or traveling for business, they remain connected, improving overall business responsiveness and productivity.
3/ Improved Call Quality:
While VoIP call quality can be influenced by internet connectivity, advancements in technology and bandwidth have greatly enhanced the clarity and consistency of VoIP calls. With proper internet service and network settings, VoIP can deliver superior sound quality and reliability comparable to traditional ISDN lines.
4/ Global Reach at Lower Costs:
VoIP enables you to assign virtual numbers that appear local to any geographical location you choose, regardless of where your business is based. This functionality not only enhances your market reach but also makes it more cost-effective for your customers and business partners to contact you.
Disadvantages of VoIP
1/ Dependence on Internet Connection:
As discussed above, VoIP’s performance heavily depends on your internet connectivity. Poor internet speed or an unstable connection can negatively affect call quality, leading to dropped calls or unsatisfactory audio and video quality.
2/ Latency and Jitter:
These issues can occur due to the nature of internet data transmission. Latency and jitter can cause delays and uneven communication flow during VoIP calls, impacting your overall call experience.
3/ Emergency Call Limitations:
VoIP services can sometimes have limitations when making emergency calls. This issue mostly arises when you use a non-fixed VoIP phone number in your business, as it may not automatically transmit your exact location to emergency services.
4/ Potential Additional Costs for High-Quality Internet:
If you are aiming to achieve the best VoIP call quality, a high-speed internet connection is essential, which might lead to additional costs for upgrading your existing internet service.
To know more check out our detailed guide on: Benefits of VoIP over traditional telephony
Benefits of ISDN
ISDN, or Integrated Services Digital Network, offers several benefits that are particularly valuable for businesses prioritizing stability and quality in their communication systems:
1/ Guaranteed Quality and Reliability:
ISDN provides you with a dedicated circuit for each connection, ensuring consistent quality for your voice and data transmission without any fluctuations.
2/ Faster Data Transmission Speeds:
Compared to traditional analog phone systems, ISDN offers you faster data transmission rates, making it suitable for sending large files or video conferencing.
3/ Enhanced Security:
Since ISDN is a dedicated line service, it offers you a higher level of security compared to VoIP systems, reducing the risk of eavesdropping and data breaches for sensitive communications.
Limitations and drawbacks of ISDN
1/ Higher Costs:
ISDN typically incurs higher monthly costs compared to VoIP services. This is due to the need for dedicated lines and specialized equipment, which also contribute to higher installation and maintenance expenses.
2/ Technological Obsolescence:
As technology advances, ISDN is becoming increasingly outdated and going to be completely shut down by the year 2025. The telecommunications industry is moving towards more all-purpose cost-effective, and efficient digital services, leaving ISDN behind.
3/ Limited Features:
ISDN lacks the advanced features and integrations offered by VoIP systems, such as virtual numbers, mobile app integration, and the ability to conduct video calls, which can limit a business’s ability to adapt to modern communication needs.
Types of ISDN
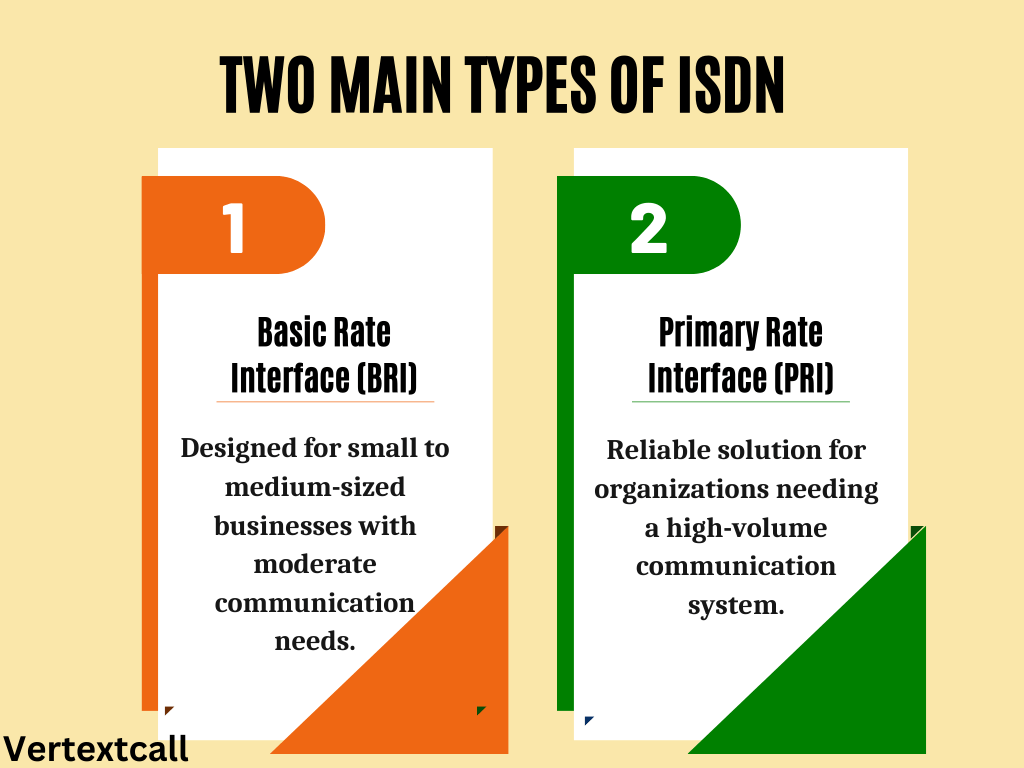
ISDN services are primarily differentiated into two types: Basic Rate Interface (BRI) and Primary Rate Interface (PRI).
1/ Basic Rate Interface (BRI)
The Basic Rate Interface, or BRI, is designed for small to medium-sized businesses with moderate communication needs. BRI essentially provides two 64 Kbps B-channels for voice or data services, and one D-channel at 16 Kbps for signaling and call setup. This setup, also known as 2B+D, allows for two simultaneous voice or data calls, making it an efficient choice for businesses that do not require the bandwidth that larger enterprises might.
2/ Primary Rate Interface (PRI)
Unlike BRI, PRI offers higher capacity, providing 23 B-channels for voice or data services, each at 64 Kbps, and one 64 Kbps D-channel for signaling. This setup, often referred to as 23B+D in North America and 30B+D in Europe and Australia, enables up to 23 (or 30) simultaneous transmissions of voice, data, or video traffic, making it a reliable solution for organizations needing a high-volume, high-quality communication system.
What protocols does ISDN use?
Here are the core protocols associated with ISDN:
- I.430 and I.431 Protocols: As discussed above these are the base physical layer protocols for ISDN BRI (Basic Rate Interface) and PRI (Primary Rate Interface) services, respectively. They define the physical and electrical conditions required for ISDN’s digital transmission.
- Q.921 (LAPD – Link Access Procedure for D-channel): This is a data link layer protocol used in the D channel of ISDN. It establishes, maintains, and terminates connections between network endpoints.
- Q.931: Operating at the network layer, this protocol is responsible for setting up, managing, and terminating calls over the D channel. It covers signaling aspects necessary for establishing connections between devices.
- DSS1 (Digital Subscriber Signaling System No.1): Also known as Euro-ISDN or ETSI (European Telecommunications Standards Institute) standard, DSS1 provides signaling protocols for efficient call setup and management in ISDN networks.
- BONDING Protocol (Bandwidth On Demand Interoperability Group): This protocol allows for the combination of multiple B channels to increase the data transmission rate, enabling higher bandwidth requirements.
- V.110 and V.120 Protocols: These protocols enable ISDN to carry non-ISDN signals, providing compatibility for services such as analog modems over digital networks.
Each of these protocols plays a critical role in ensuring that ISDN networks can deliver high-quality, reliable communication services across a wide range of applications, from voice calls to data transmission and video conferencing.
What protocols does VoIP use?
VoIP technologies also rely on various protocols and standards to ensure the reliable transmission of voice, video, and data services over IP networks. Key VoIP protocols and standards include:
- SIP (Session Initiation Protocol): SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) is a fundamental protocol used in VoIP technology. it works by sending messages in a request-response model between SIP clients and servers. These messages manage the setup, duration, and closure of calls or multimedia sessions, making SIP a crucial component within the VoIP ecosystem.
Related Reading: SIP Versus VoIP
- RTP (Real-time Transport Protocol): RTP (Real-time Transport Protocol) primary function is to ensure that digital media streams are delivered in real-time, with minimal delay, maintaining the quality and integrity of interactive communications. RTP works in coordination with RTCP (Real-time Transport Control Protocol) to provide feedback on data delivery quality, enabling adjustments necessary for optimizing performance.
- RTCP (Real-time Transport Control Protocol): Working in coordination with RTP, RTCP provides separate control information and feedback on the quality of service being provided by RTP, including data transmission speeds, packet loss, and network overload.
- SDP (Session Description Protocol): SDP is used within the SIP framework to describe multimedia sessions and invites participants to join a session. It provides information about the session’s attributes, such as the media format and IP addresses.
- MGCP (Media Gateway Control Protocol): MGCP (Media Gateway Control Protocol) is a protocol designed for controlling media gateways on voice-over IP (VoIP) networks. Its primary aim is to manage the signaling and session management needed for handling voice calls, multimedia streaming, and fax transmission.
Related Reading: VoIP protocols and standards
How to switch to VoIP
Here’s a streamlined process to guide you through the transition, ensuring an efficient switch to a more flexible and cost-effective telephony solution.
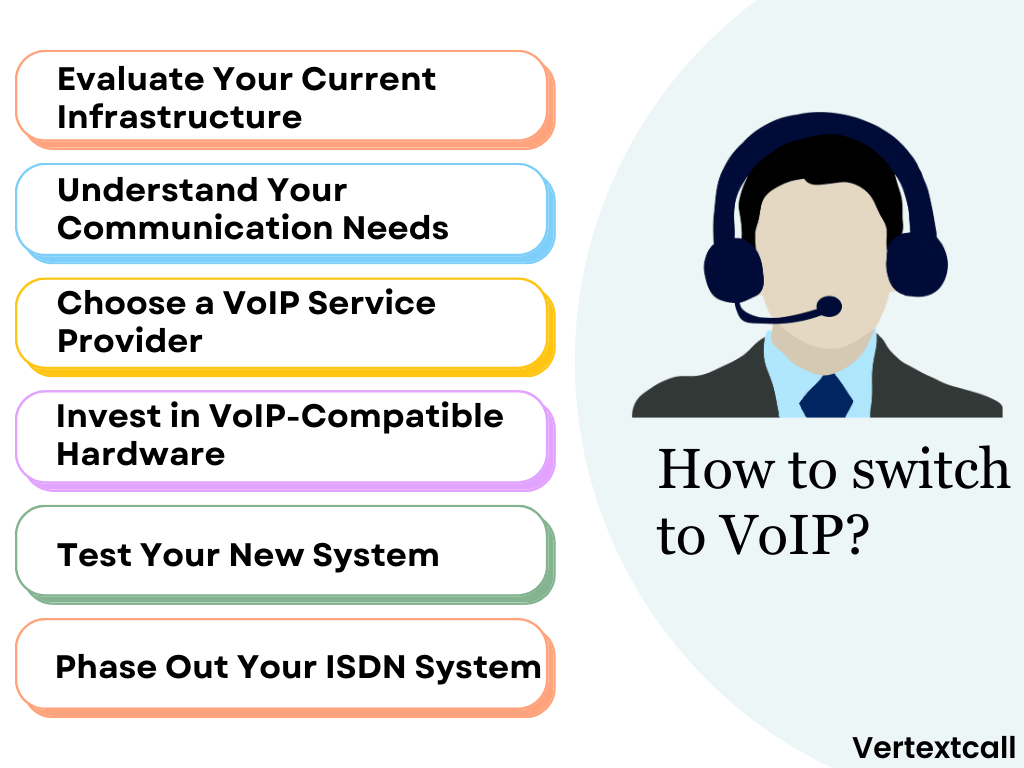
1/ Evaluate Your Current Infrastructure:
The first step would be to analyze your current telephony setup. Determine the aspects of your ISDN system that meet your needs and those that do not. This evaluation will help you understand the specific benefits VoIP can offer your business.
2/ Understand Your Communication Needs:
Identify your communication requirements. Consider factors such as the number of users, call volume, and whether you need advanced features like video conferencing, mobile apps, or integration with business tools.
3/ Choose a VoIP Service Provider:
Look for providers that offer reliability, quality customer support, and scalability. Compare plans, and pricing, and read reviews to make an informed decision.
4/ Invest in VoIP-Compatible Hardware:
While many VoIP systems work with existing telephony hardware, investing in VoIP-compatible phones and devices can enhance call quality and user experience.
5/ Test Your New System:
Test all functionalities of your new setup, including making calls and utilizing all available features. The testing phase is essential to identify and resolve any potential complications before fully implementing the VoIP system.
6/ Phase Out Your ISDN System:
Finally, once you are confident in the reliability and performance of your VoIP system, you can begin phasing out your old ISDN system.
Challenges and considerations when migrating from ISDN to VoIP
- It’s essential to ensure your network can handle the increased data traffic and maintain stable connectivity to avoid dropped calls or poor-quality audio.
- Prioritizing VoIP traffic on the network to maintain high-quality voice transmission is crucial. You may need to adjust your QoS settings to prevent latency and jitter.
- Ensuring that emergency call services work effectively with the VoIP system, including accurate location reporting, is a critical consideration.
- VoIP services are subject to different regulations in various countries or regions. Understanding these regulatory standards can help in avoiding potential legal challenges.
Is VoIP better then ISDN?
The question of whether VoIP is better than ISDN for your business comes down to what you need and value most in your communication systems. But if you are choosing VoIP, you’re opting for a technology that lets you make calls over the Internet, which can significantly reduce your phone bills, especially if you make a lot of international or domestic calls.
It also offers the flexibility to easily add or remove lines, and access to advanced features like video calls, instant messaging, and integration with business applications, which are not possible with ISDN.
On the other hand, ISDN is a more traditional method of telecommunication that runs on dedicated line systems. However, it is highly outdated and often comes with higher maintenance costs.
Ultimately, if you’re looking for a way to make your business’s communication systems more efficient and adaptable to future needs, VoIP is likely the better choice for you.
Frequently Asked Questions?
Q1) What is ISDN in VoIP?
Ans: In the VoIP context, ISDN can be seen as an alternative technology. VoIP technology enables the transmission of voice communications over Internet-based networks, which differs from ISDN’s use of the PSTN for such transmissions. While ISDN supports digital data transmission over standard telephone lines, VoIP converts voice data into packets and transmits them over the Internet or a private network.
Q2) Why is ISDN being phased out?
Ans: ISDN technology is being phased out globally due to the advancements in Internet Protocol (IP) technologies, specifically Voice over Internet Protocol and Unified Communications services. These technologies offer significantly more flexibility, scalability, and features at a lower cost than ISDN.
Q3) What is the difference between ISDN and SIP?
Ans: The main difference between ISDN and SIP is that ISDN is a circuit-switched telephone network system that provides digital transmission of voice and data over ordinary telephone copper wires, supporting both voice and data in a single line. In contrast, SIP is a signaling protocol used for initiating, controlling, and ending real-time sessions for multimedia communication, including audio, visual, and text exchanges, over Internet Protocol (IP) networks. Unlike ISDN, which is fixed to physical network infrastructure, SIP operates on a virtual level, utilizing the internet or private data networks for communication.
Q4) Is SIP or VoIP more secure?
Ans: In terms of security, both technologies face similar risks, including eavesdropping, fraud, and denial of service attacks. However, the security of either technology largely depends on the implementation of security measures. This includes the use of encryption protocols like TLS (Transport Layer Security) for SIP signaling and SRTP (Secure Real-time Transport Protocol) for VoIP calls, secure VPNs for network traffic, and adherence to strong, up-to-date security practices.
Q5) Does ISDN still exit?
Ans: Yes, ISDN still exists, although it is becoming increasingly rare and is in the process of being phased out in many countries.
Q6) Does VoIP use ISDN?
Ans: No, VoIP does not use ISDN directly. VoIP and ISDN are fundamentally different technologies for enhancing voice communications.