VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) or cellular phone services is more than a choice of convenience; it’s about selecting a communication method that aligns with both our personal and professional needs.
Our detailed guide, “VoIP vs. Cellular Phone,” aims to provide a deep understanding of both technologies, delving into the complexities of digital communication to help you determine the service that best fits your requirements.
What is VoIP & How Does it Work
Voice over Internet Protocol, commonly referred to as VoIP works by transforming your voice into digital data, which is then transmitted over the Internet to the intended recipient.
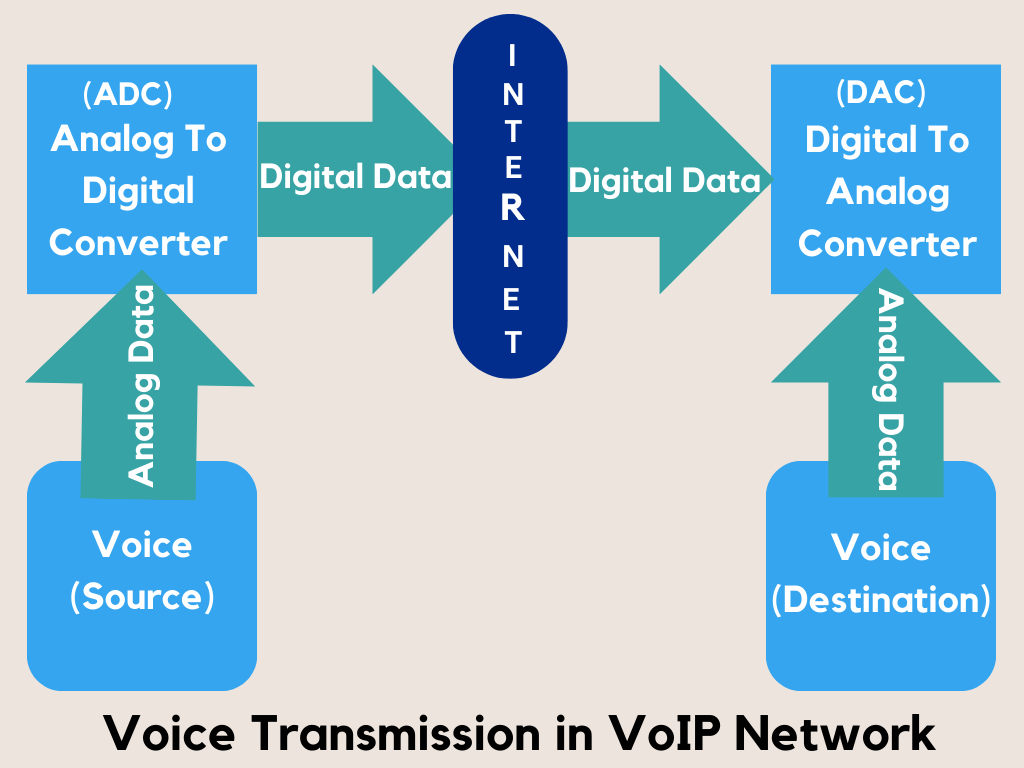
This conversion happens in real-time, using a codec to encode the voice signal into a digital format at the sending end, and then decode the digital packet back to a voice signal at the receiving end.
This enables more efficient utilization of bandwidth as data packets can travel through the quickest and most efficient routes, as opposed to PSTN, which requires a dedicated line for the entire duration of a call.
As a result, VoIP facilitates voice communication at a lower cost while offering the added flexibility of integrating with other internet-based services.
Related Reading: Key Differences Between VoIP and PSTN
What is a Cellular Phone & How Does it Work
A cellular phone, commonly known as a cell phone, is a wireless communication device that uses radio waves to connect to a network of cell towers. These cell towers facilitate the transmission of voice, text, and data, allowing you to stay connected wherever you go.
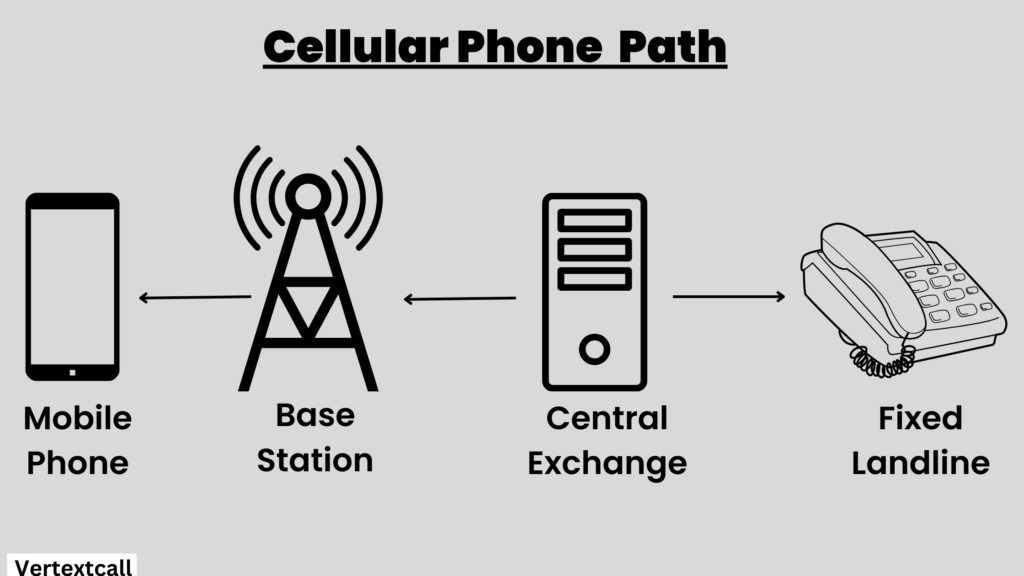
Unlike Voice over Internet Protocol, cell phones do not rely on an internet connection. Instead, they utilize the established cellular networks provided by mobile phone operators. Each cell tower covers a specific geographical area, referred to as a cell.
As you move, your calls are transferred from one tower to another, ensuring uninterrupted service. This process, known as cell handoff, enables individuals to stay connected without any disruption.
Over the years, cellular technology has evolved from 1G to the current 5G, bringing significant improvements in speed, capacity, and reliability. This advancement has not only enhanced voice communication but also opened up a whole set of multimedia services that can be experienced on the go.
Key differences between VoIP and Cellular phones
As discussed above, VoIP and cellular phones both enable voice communication, but they operate in different ways and have different characteristics. Here are the key differences between the two:
1/ Infrastructure and Network Requirements
VoIP systems utilize your current internet connection for voice communication, which can be advantageous in terms of efficient resource utilization. By utilizing the current internet infrastructure, VoIP streamlines communication, eliminating the necessity for dedicated phone lines and cutting down expenses.
However, it is important to consider that the quality and reliability of VoIP calls can be influenced by the strength and security of your network. If your network lacks sufficient bandwidth or is open to cyber threats, it may impact the overall performance of VoIP.
VoIP bandwidth requirement
VoIP Usage | Bandwidth Requirement |
Minimum bandwidth per VoIP line | 100 Kbps |
VoIP telephone calls (optimal performance) | 5-25 Mbps download speed |
Email and web browsing | 1 Mbps download speed |
File downloading | 10 Mbps download speed |
HD video teleconferencing | 6 Mbps download speed |
On the other hand, cellular phones rely on cell towers maintained by wireless service providers. These towers facilitate wireless communication by transmitting and receiving signals. While cellular networks offer wider coverage and mobility, the call quality and reliability may fluctuate based on variables like signal strength and network congestion.
2/ Call Quality and Reliability Factors
Voice communication quality and reliability vary between VoIP and cellular networks. The quality of VoIP calls heavily depends on internet connection stability and speed. A strong, high-speed broadband connection ensures clear, high-quality audio with minimal latency. However, a weak or unstable internet connection can result in dropped calls, delays, and lower audio quality.
On the other hand, cellular phone calls depend on the strength and coverage of the cellular network, which can be affected by proximity to cell towers and areas with signal interference. Generally, cellular networks offer consistent call quality and high reliability, especially in well-covered areas, making them a reliable option for communication, especially when traveling.
3/ Features and Functionality
VoIP technology not only facilitates voice communication but also offers a wide range of features such as video conferencing, call forwarding, voicemail-to-email services, instant messaging, virtual phone numbers, auto attendant, call recording, and remote collaboration tools. It integrates with widely used business apps like Slack, Microsoft Teams, CRM, etc, providing a unified communication platform suitable for corporate environments.
Cellular phones, on the other hand, prioritize providing reliable and essential communication services while utilizing the network’s mobility and the additional features of a smartphone. These include GPS navigation, on-the-go internet access, and multimedia capabilities.
4/ Cost Considerations
The costs of both systems can vary significantly based on various factors. VoIP systems typically have lower call costs and the added advantage of often no long-distance fees, as calls are routed over the internet. This can be particularly beneficial for your business to frequently make long-distance calls.
On the other hand, cellular plans can be more expensive, especially for international calls, but they provide a more predictable cost for users who may not have control over their internet service or need a reliable connection during travel.
5/ Mobility and Accessibility
When it comes to mobility, cellular phones naturally provide the convenience of communication almost anywhere. They operate on a network that doesn’t rely on a fixed internet connection, ensuring accessibility within the range of a cell tower. This means that even in remote areas or places with limited internet infrastructure, you can still rely on your cell phone to make calls.
On the other hand, for optimal VoIP service, a consistent and dependable internet connection is essential. This means that in areas with poor connectivity or no internet access, VoIP services may not be accessible. This difference is crucial if you require the freedom to make calls without the concern of internet access.
Advantages of VoIP over regular phone calls
VoIP technology transforms communication with its range of benefits compared to conventional phone calls. Key advantages include
1/ Cost-Effectiveness: VoIP significantly reduces the cost of communication by utilizing the Internet for call transmission, eliminating the need for expensive telephone networks or long-distance charges. Typical savings for a business using VoIP range from 30% to 50%.
2/ Flexibility in Number Choice: VoIP users have the advantage of choosing phone numbers from various area codes or even different countries. This flexibility is particularly advantageous for businesses looking to establish a strong local presence strategy, enabling them to connect with customers in diverse locations.
3/ Enhanced Quality: With the advancement of broadband technology, VoIP has transformed communication by providing exceptional call quality that can surpass traditional phone calls. This technology ensures clear voice transmission, eliminating any potential interference and enhancing the overall communication experience.
4/ Voice Quality Customization: VoIP technology offers customizable voice quality settings to meet diverse business requirements. This feature optimizes bandwidth usage, especially, which is particularly beneficial for businesses that prioritize cost-saving measures without compromising on communication standards.
Disadvantages of VoIP calling
While VoIP technology offers various advantages, however, users need to consider its potential drawbacks as well. Some of these disadvantages include
1/ Dependency on Internet Connectivity: VoIP services depend entirely on the availability of a stable Internet connection. When the connection is poor or gets interrupted, it can result in call drops and a noticeable decline in call quality. Ensuring a reliable internet connection is vital for uninterrupted and high-quality VoIP communication.
2/ Voice Quality and Latency Issues: While voice quality can be superior on VoIP, it is highly dependent on the bandwidth and quality of the internet connection. Poor internet leads to latency, jitter, and packet loss, resulting in below-par call quality.
3/ Emergency Calls Limitation: VoIP services may not always support traditional emergency number dialing or may not provide accurate location data to emergency responders, which could lead to critical delays in emergencies.
4/ Security and Privacy Risks: Voice-over IP calls, being reliant on internet-based communication, are exposed to various security risks. These include hacking attempts, eavesdropping on conversations, and exposure to cyber threats such as data breaches and unauthorized access.
5/ Compatibility Concerns: In some cases, older systems and software may not be fully compatible with VoIP, which is why it may be necessary to consider upgrades or replacements. This is because VoIP relies on modern technologies and protocols that may not be supported by outdated infrastructure. By making the necessary adjustments, organizations can ensure effortless integration and take full advantage of the benefits that VoIP has to offer.
Related Reading: Advantages and Disadvantages of VoIP phone system
Advantages of cellular phone
Cellular technology offers numerous advantages that make it a popular communication option globally. The following benefits emphasize the traditional strengths of cellular phones:
1/ Universality: Cell phones operate over a well-established global network called the cellular network. This network consists of interconnected base stations that allow mobile communication without the need for an internet connection. This means that wherever you are, as long as there is cellular network coverage, you can make calls and stay connected with ease.
2/ Reliability: Cellular networks are thoroughly designed to ensure consistent connectivity. With a network of multiple strategically placed cell towers, these networks minimize the occurrence of dropped calls and service interruptions, providing you with flawless communication experiences.
3/ Independent Power Source: Cell phones are not dependent on external power sources to function, due to their built-in batteries. This means that even during power outages, when VoIP devices may fail, cell phones will continue to operate, making them even more vital in emergencies.
4/ Simplicity: The simplicity of cellular phones makes them accessible to users of all backgrounds, enabling effortless communication without the need for additional equipment or technical knowledge. With just a few taps on the screen, individuals can connect with family, and colleagues, instantly closing distances and developing meaningful connections.
Disadvantages of cellular phone
1/ Call Costs: Cellular calls can be quite costly, especially when it comes to international calls, and the rates can vary significantly depending on the plan and provider. This variability in rates can have a significant impact on the cost-effectiveness of using cellular phones, which is especially important if your business is looking to optimize its communication expenses.
2/ Battery Life: Cell phones require regular charging, and battery life can be a significant limitation if you rely on your phone throughout the day or do not have ready access to a charging source.
3/ Feature Limitations: When it comes to advanced features, cellular phones often fall short compared to VoIP services. VoIP technology integrates a wide range of functionalities that are specifically designed for businesses. These include advanced call management, integration with customer relationship management (CRM) systems, and comprehensive call analytics.
4/ Quality of Service: The quality of cellular calls can be inconsistent, often affected by various factors such as the user’s proximity to cell towers, the level of network traffic, and even environmental conditions. On the other hand, VoIP technology typically provides higher-quality audio due to its ability to allocate sufficient bandwidth and capitalize on advanced audio codecs.
What type of Phone is needed for VoIP
To utilize Voice over Internet Protocol, specific types of phones are required. They are specially designed with hardware and software that allow them to send and receive voice data over the web.
These can be dedicated IP desk phones that resemble traditional telephones but connect to the network via Ethernet or Wi-Fi.

Softphones are another option, which are essentially software applications that can be installed on smartphones, tablets, or computers, enabling these devices to function as VoIP phones using their built-in microphones and speakers.
Additionally, there are Analog Telephone Adapters (ATAs) that enable the connection of a standard telephone to the Internet for VoIP use. For businesses, VoIP PBX systems can also be employed to serve multiple handset users at once, simulating the functions of traditional PBX with the added features and flexibility of VoIP technology.
Each of these devices facilitates internet-based telephony, allowing for flexible and advanced communication solutions.
Related Reading: PBX vs VoIP differences
How to turn an old phone into VoIP
To turn an old phone into a device capable of making VoIP calls, you’ll need to use an Analog Telephone Adapter (ATA). The process is as follows:
- Evaluate Compatibility: Confirm that the old phone is compatible with an Analog Telephone Adapter (ATA), as not all phones may work with these devices.
- Choose an ATA: Purchase an ATA device that can bridge the gap between the analog signals of your old phone and the digital signals needed for VoIP communication.
- Connect to Your Network: Plug the ATA into your router or network switch using an Ethernet cable. This connects your old phone to your internet network.
- Connect Your Phone: Attach your old phone to the ATA using a standard phone cable.
- Configure the ATA: This may involve accessing a web interface via a computer on the same network to enter the VoIP service credentials provided by your VoIP service provider.
- Activate the Service: Once configured, your VoIP service provider will activate the device on their end, allowing your old phone to make and receive calls over the internet.
By following these steps, you can effectively repurpose an old phone, employing the advanced capabilities of VoIP to stay connected in a cost-effective manner.
VoIP vs Landline
Feature | VoIP | Landline |
Infrastructure | Relies on internet connectivity | Uses copper wires or fiber-optic cables |
Quality | Can vary based on internet connection quality and bandwidth availability | Generally consistent, not affected by internet issues |
Reliability | Subject to internet outages or network congestion | Typically more reliable, less affected by external factors |
Mobility | Can be used from any internet-enabled device, offering mobility | Restricted to the physical location of the landline phone |
Additional Features | Often includes additional features like video calling, instant messaging, and integration with other applications | Typically limited to basic calling features |
Installation | Typically simpler to install and configure, often only needing an internet connection and a compatible device. | Requires physical installation of phone lines and may involve technician assistance |
Use Cases | Suitable for established businesses with specific regulatory or compliance requirements | Ideal for businesses with remote workforce, scalable communication needs, and integration with CRM and other business applications |
Must Read: Check out the differences between VoIP and landline systems
Factors to consider when choosing between VoIP and Cellular Phone
Deciding between VoIP and cellular phones comes down to your specific needs and circumstances.
Factors to consider
When making your decision, it’s important to consider the following factors:
- Usage: Take into account how and where you most frequently make calls. Are you mainly making local calls, long-distance calls, or international calls? Understanding your calling patterns will help you choose a service that aligns with your needs.
- Budget: It’s crucial to evaluate what you can afford and the costs associated with making a switch. Consider any upfront fees, monthly charges, and potential long-term contracts. By understanding your budget, you can make an informed decision that fits your financial situation.
- Features: Determine whether you require advanced telephony features for either personal or business use. Does your organization need calling features like call forwarding, voicemail, or conference calling? Identifying your specific feature requirements will ensure that you select a service that meets your needs.
- Infrastructure: Assess your current internet and cellular network capabilities. Consider the reliability and speed of your internet connection as well as the strength of your cellular network coverage. This evaluation will help you choose a service that is compatible with your existing infrastructure.
Taking these factors into account will enable you to make a well-informed decision that best suits your calling needs and preferences.
Use cases and scenarios for each technology
VoIP and cellular phones address different use cases:
- Business Environments: VoIP is often the preferred choice for business due to its features and scalability.
- On the Go: Cellular remains the go-to for professionals and individuals requiring constant access and mobility.
- Remote Work: When it comes to remote work, VoIP excels as a cost-effective, full-featured solution.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1) Is a VoIP phone better than a cell phone?
Ans: While VoIP phones and cell phones each have their specific uses and benefits, whether one is better than the other largely depends on your needs. VoIP phones are advantageous for businesses and individuals who seek cost efficiency, flexibility, and a range of features not typically available on cell phones, such as advanced call handling, virtual numbers, and integration with other business systems.
Conversely, cell phones offer the essential benefit of mobility, allowing you to make and receive calls without the need for a stable internet connection. Additionally, cell phone plans often include a variety of services like text messaging, data for mobile internet, and roaming options which can be pivotal for those on the go.
Q2) Can a cell phone be a VoIP?
Ans: Yes, A cell phone can serve as a VoIP phone. This functionality is made possible through the utilization of softphone applications that utilize the data connection of the smartphone, such as Wi-Fi or mobile data, to facilitate VoIP calls. By utilizing these applications, a cell phone gains access to a variety of VoIP services and features, providing users with a flexible communication experience.
Q3) Can a VoIP phone be used as a regular phone?
Ans: Yes, a VoIP phone can be used as a regular phone. VoIP phones are designed to replicate the function and user experience of traditional phones while using an internet connection for communication. They have a familiar interface with a handset, dial pad, and ringing capabilities.
Where they differ is in the core technology; VoIP phones convert analog voice signals into digital data packets for transmission over the internet. With proper setup, which includes a connection to a VoIP service provider, you can make and receive calls just as you would with a standard telephone.
Q4) Is VoIP a burner phone?
Ans: No, VoIP is not a burner phone. A “burner phone” is commonly used to describe a disposable mobile device that serves temporary purposes and can be effortlessly disposed of. These phones are frequently linked to anonymity and can be purchased with prepaid minutes, without the need for a contract.
Q5) Which is better VoIP or Wifi calling?
Ans: VoIP is an ideal telephony solution for businesses and individuals seeking a comprehensive communication system with a wide range of features like call forwarding, transfer, hold, and integration with other business systems.
On the other hand, Wi-Fi calling is a service provided by mobile phone carriers that enables users to make and receive calls using a Wi-Fi network instead of relying solely on the cellular network. It is particularly useful in areas with poor cellular reception but strong Wi-Fi signals.
VoIP offers greater capability to meet diverse communication needs, while Wi-Fi calling serves as an excellent supplementary option to ensure connectivity in situations where conventional cellular services may fail.
The choice between VoIP and Wi-Fi calling should be based on a thorough assessment of specific communication requirements, the availability of stable internet services, and the desired range of telephony features.

