Two significant technologies that have revolutionized communication are Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) and Voice over WiFi (VoWiFi). Although both provide the convenience of voice communication over digital networks, they operate differently and cater to distinct user needs.
In this blog, we explore the details of VoIP and VoWiFi, examining their functionalities, advantages, and differences to assist you in making informed decisions regarding the most suitable option for your communication requirements.
What is VoIP
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP), is an innovative technology that facilitates voice communication and multimedia sessions over Internet Protocol (IP) networks, including the Internet. By using this advanced technology, you can make calls and engage in real-time audio and video conversations using an internet connection instead of relying on traditional phone lines.
This modern approach to communication offers greater flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and scalability. With VoIP, you can use enhanced features such as call forwarding, voicemail-to-email transcription, and the ability to seamlessly integrate communication services with other digital tools and applications.
The technical aspect of VoIP
The foundational protocol in VoIP technology is the Internet Protocol (IP), which determines how your data travels through networks.
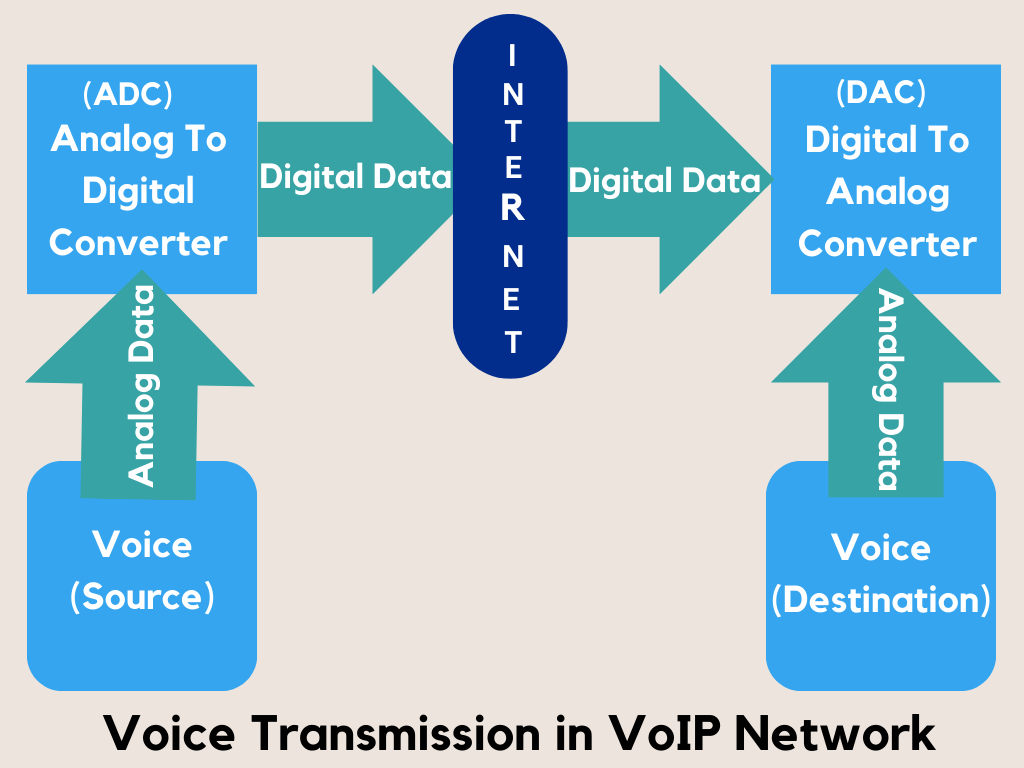
When a voice is spoken, it is captured as an analog signal and transformed into a digital format using an Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC). After conversion, the data is packaged into packets, compressed for transmission, and delivered over the network using the Real-Time Transport Protocol (RTP).
To establish, maintain, and end calls, the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) is utilized for call setup and management, enabling devices to communicate with each other. Upon reaching its destination, the voice data is decompressed and converted back into an analog format using a Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC), allowing the recipient to perceive the message as intended.
Additionally, Voice over IP incorporates dynamic technologies such as jitter buffers, echo cancellation, and Quality of Service (QoS) enhancements to ensure call clarity and stability.
Related Reading: Difference between VoIP and SIP Explained
Advantages of VoIP
Voice over Internet Protocol offers numerous advantages compared to VoWiFi. Some of the key advantages of VoIP include:
- Cost-Effectiveness: VoIP significantly reduces call costs, especially for long-distance and international calls, as it utilizes the internet as the primary channel for communication. This avoids the traditional phone network and its associated tariffs and taxes, resulting in substantial savings. According to an analysis, switching to VoIP can result in a reduction of over 50% in monthly telecom expenses for companies.
- Scalability: Whether for a growing startup or an established corporation, VoIP systems can easily scale to accommodate additional users or be downsized without the need for extensive infrastructure changes. This ensures your business can quickly and efficiently adapt to its communication needs, regardless of size.
- Flexibility: With VoIP, employees are not tied to their office desks. Calls can be made and received using various devices like smartphones, laptops, and tablets, enabling a mobile and flexible workforce.
- Integrations: VoIP effortlessly integrates with various business applications, including project management tools, email platforms, and instant messaging services. This promotes a synergetic and efficient working environment, allowing different tools to work together seamlessly.
- Easy Setup and Maintenance: VoIP systems are relatively easy to set up, maintain, and troubleshoot compared to traditional telephony. With minimal hardware requirements, your business can quickly establish its communication system and keep it running smoothly by understanding VoIP infrastructure requirements.
- Enhanced Features: VoIP offers a range of advanced features that enhance the user experience. These include call recording, voicemail to email transcription, automated call routing, and video conferencing, providing a comprehensive toolset to meet your modern communication needs.
Related Reading: What is the difference between VoIP and video conferencing
Disadvantages of VoIP
- Reliance on Internet Connection: The performance of VoIP is dependent on the quality and speed of the Internet connection. A poor or unstable internet connection can lead to dropped calls or reduced call quality, which can impact your communication.
- Power Dependence: Unlike conventional phone lines, which operate independently during power outages, VoIP depends on a power source for its devices. This reliance on power can be a critical point of failure during emergencies.
- Latency and Jitter: VoIP calls travel over the internet, which means they can experience delays or disruptions known as latency and jitter. These issues can affect the smoothness of speech during a conversation.
- Security Vulnerabilities: VoIP solutions, similar to many online technologies, can be open to VoIP threats and cyber risks, including unauthorized access, interception of communications, and disruption of service via DoS attacks. Proper security measures must be in place to protect against these risks.
Related Reading: Advantages and disadvantages of VoIP for business
What is VoWiFi
Voice over WiFi (VoWiFi) operates by utilizing wireless network connections for voice call transmission and reception, eliminating the need for reliance on a cellular network. This innovative technology uses the power of WiFi networks to seamlessly handle voice calls, offering a reliable and cost-effective alternative to traditional cellular services.
With VoWiFi, you can experience clear voice quality and uninterrupted communication even in areas with weak cellular coverage. This transition between WiFi and cellular services enhances the overall user experience, providing greater flexibility and convenience in staying connected.
Editor’s Comments
Based on the data presented by Mordor Intelligence, the VoWiFi Market is expected to reach a valuation of approximately USD 8.12 billion in 2024. It is projected to experience substantial growth, reaching around USD 18.63 billion by 2029, with a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) surpassing 18.06% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2029.
Advantages of VoWiFi
- Enhanced Coverage: Wi-Fi calling is particularly useful in areas with poor cellular reception, ensuring that you stay connected even when the signal is weak or nonexistent. This can be especially beneficial in remote locations or buildings with thick walls and limited cellular coverage, where traditional voice calls may struggle to connect.
- Cost-Effective: VoWiFi can significantly reduce costs related to international calling and roaming charges, as calls can be made over available WiFi networks. This can be advantageous for frequent travelers or individuals who frequently communicate with international contacts, as it eliminates the need for expensive international calling plans or incurring high roaming charges.
- No Additional Hardware: Unlike some VoIP configurations, VoWiFi does not require additional hardware investment since it can be supported by existing WiFi infrastructure and your mobile device. This means that you can take advantage of WiFi calling without the need to purchase additional equipment or devices, making it a cost-effective and convenient solution.
- Seamless Transition: Calls can transition between LTE and WiFi without dropping, providing a smooth calling experience. Whether you are on a cellular network or connected to a WiFi network, the transition between the two is smooth and seamless. This ensures uninterrupted conversations and eliminates the inconvenience of dropped calls when moving between different network types.
- Battery Efficiency: WiFi networks often use less battery power on mobile devices compared to cellular networks, leading to extended device usage. By utilizing WiFi calling, you can conserve your device’s battery life, allowing for longer usage without the need for frequent charging. This can be particularly beneficial in situations where access to charging outlets may be limited or when you need your device to last for an extended period.
The downside of VoWiFi
- Reliance on WiFi Quality: VoWiFi heavily depends on the stability and strength of the WiFi connection. If the WiFi connection is poor, with frequent interruptions or low signal strength, it can result in call drops and compromised voice quality. This can be especially frustrating when you are in the middle of an important conversation or a business call.
- Limited Availability: While WiFi networks are becoming increasingly common, they are still not as extensive as cellular networks. This means that access to open and secure WiFi can be inconsistent, especially in certain areas or when traveling. This limitation can make it challenging to rely solely on VoWiFi for making calls.
- Security Concerns: Public WiFi networks, such as those found in coffee shops, airports, or hotels, tend to be less secure compared to cellular networks. This can expose your calls to potential vulnerabilities, such as eavesdropping or unauthorized access. It is important to exercise caution and ensure that you are connected to a secure WiFi network when using VoWiFi.
- Compatibility Challenges: While VoWiFi is becoming more popular, it is not universally supported by all mobile devices. This can limit its adoption among users who have older or less common devices. Before relying on VoWiFi, it is important to ensure that your device supports this feature.
- Emergency Services: One of the challenges of using VoWiFi is providing precise location information to emergency services. Unlike traditional cellular calls, which can be easily traced to a specific location, VoWiFi calls can be more challenging to track accurately. This can potentially delay emergency services from reaching you quickly in case of an emergency. It is important to be aware of this limitation and consider alternative means of communication during such situations.
Key Differences Between VoIP and VoWiFi
Although VoIP and VoWiFi both use the internet for communication, they have notable differences that can influence your decision between them. Here are the main distinctions:
Network Infrastructure Requirements
VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) services can be used over any broadband connection, allowing you to make calls using different VoIP phones or dedicated apps on your devices. By utilizing internet connectivity for voice data transmission, this technology offers a cost-effective and flexible communication solution.
On the other hand, VoWiFi (Voice over WiFi) relies on a strong and stable WiFi connection to enable voice calls. It is commonly used through smartphones, allowing you to make calls using your WiFi instead of cellular networks. This can be particularly useful in areas with limited cellular coverage or to avoid using up cellular data allowances.
Quality of Service
VoIP quality can be effectively regulated by the service provider through the implementation of traffic prioritization techniques. By giving priority to voice traffic, service providers can ensure clear call quality and minimize latency issues.
VoWiFi, on the other hand, may experience variable quality due to its reliance on the quality of the WiFi signal. The stability and strength of the WiFi connection play a crucial role in determining the overall quality of the voice calls made over VoWiFi. Factors such as signal strength, network congestion, and interference can impact the clarity and reliability of the calls, highlighting the importance of having a stable WiFi network for optimal VoWiFi performance.
Mobility and Accessibility
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) allows for enhanced mobility, enabling communication over an Internet connection. However, it relies on access to a broadband connection for optimal functionality and call quality.
Voice over WiFi (VoWiFi) provides complete mobility within areas covered by WiFi networks. This means that as long as you are within reach of a WiFi connection, you can make and receive calls seamlessly. However, when you move outside WiFi areas, VoWiFi transitions to cellular services for continued connectivity. This ensures that you stay connected and reachable regardless of your location.
Security Considerations
Voice-over-Internet Protocol (VoIP) systems are designed with multiple layers of security measures. These systems often incorporate secure authentication methods and access control to prevent unauthorized use.
On the other hand, voice-over WiFi (VoWiFi) may require additional security measures due to potential vulnerabilities that can arise when using public WiFi networks. These measures can include authentication mechanisms and encryption techniques to reduce the risk of data breaches and unauthorized interception. By implementing such security measures, you can confidently utilize VoWiFi services while maintaining the privacy and integrity of your communications.
Key Components of VoWiFi
Voice over WiFi (VoWiFi) is built on several crucial components that ensure its efficiency and reliability. First and foremost, there’s the WiFi network, typically a broadband connection, which provides the necessary bandwidth for voice data transmission.
Additionally, there are protocols like the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) that establish, manage, and terminate voice communication sessions.
The IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) core serves as the architectural framework to deliver multimedia and voice services over an IP network. Moreover, handover technology allows for smooth transitioning of calls between LTE and WiFi without dropping the connection, ensuring conversation continuity.
To support VoWiFi calling features, your’ device software needs to be compatible and updated. This includes appropriate settings for connecting to the right wireless network and seamlessly switching to a cellular network when WiFi is unavailable.
Lastly, strong security features, such as end-to-end encryption, are implemented to protect the integrity and privacy of transmitted voice data over public or private networks.
What does WIFI calling require
To make the most of Wi-Fi calling, specific requirements need to be met. These include both technical and hardware requirements to ensure the service functions at its best.
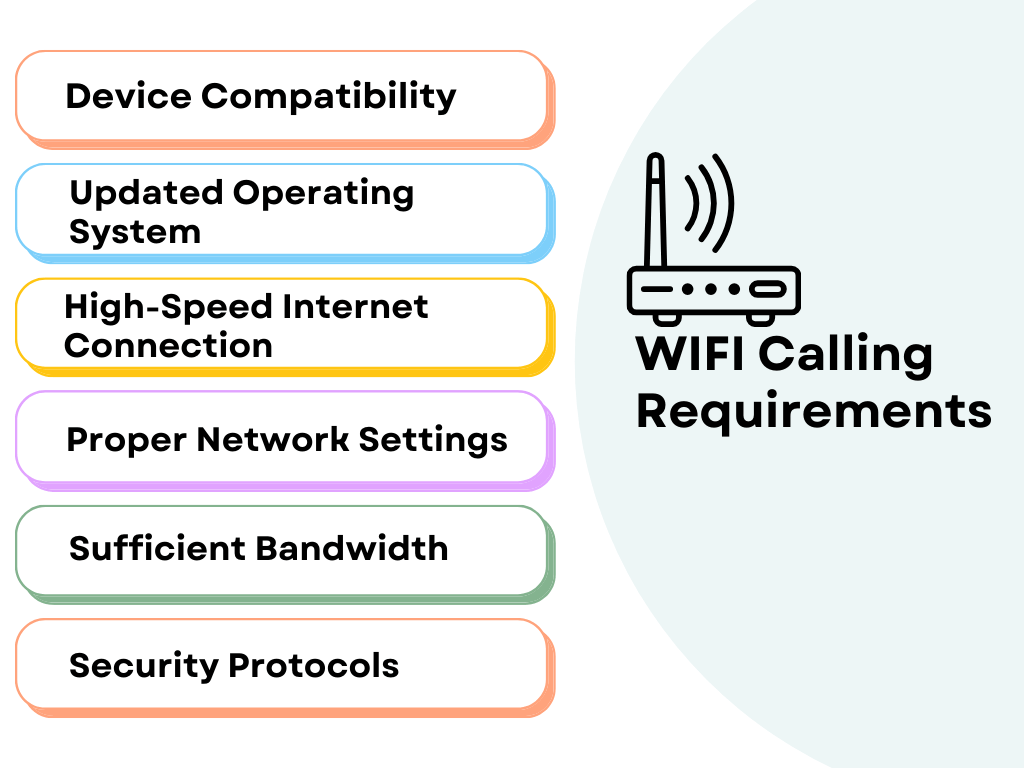
1/ Device Compatibility: To utilize Wi-Fi calling, you must have a smartphone or tablet that supports this feature. It’s important to check if your device is compatible with this service as not all devices come equipped with it.
2/ Updated Operating System: Ensure that your device is running on a recent operating system that supports Wi-Fi calling functionality.
3/ High-Speed Internet Connection: A stable Wi-Fi network is essential for optimal Wi-Fi calling quality. The speed and stability of your broadband connection greatly impact the quality of Wi-Fi calls.
4/ Proper Network Settings: Correct network settings on your device are vital for successful Wi-Fi calling. This may involve setting up the right access point names (APNs) and ensuring that your device is configured to prioritize Wi-Fi calls when available.
5/ Sufficient Bandwidth: The Wi-Fi network should provide enough bandwidth to handle voice data. Simultaneous internet activities can affect call quality, so it’s recommended to have a minimum bandwidth of 1 Mbps for a smooth experience.
6/ Security Protocols: Enable security measures, such as strong encryption on your Wi-Fi network, to safeguard the privacy and integrity of your calls. As discussed above secure Wi-Fi connections prevent eavesdropping and data theft, ensuring the confidentiality of your communications.
Use Cases and Applications
Both Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) and Voice over Wi-Fi (VoWiFi) have found significant applications in modern communication systems. Here are some common use cases and applications for each:
Business Communication: From small startups to large enterprises, organizations are increasingly adopting Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) to expand their communication capabilities. By utilizing VoIP, businesses can easily scale their communication capacities to meet the growing demands of their operations. Additionally, VoWiFi (Voice over Wi-Fi) is particularly advantageous for businesses with remote workers who may need to connect from various locations. With VoWiFi, these workers can communicate over Wi-Fi networks, ensuring uninterrupted and reliable communication regardless of their physical location.
Mobile Communication: VoWiFi offers significant benefits to users who frequently travel, whether domestically or internationally. By leveraging VoWiFi, users can bypass expensive roaming charges and instead make calls over Wi-Fi networks. This not only helps to reduce costs but also ensures uncompromised call quality, even when abroad. Whether for business or personal use, VoWiFi provides a convenient and cost-effective solution for mobile communication needs.
Internet of Things (IoT) Integration: As the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to grow, the integration of VoIP and VoWiFi into smart devices is becoming increasingly common. This integration allows for unified communications that span across varied technology ecosystems. With VoIP and VoWiFi capabilities, IoT devices can communicate with each other, enabling enhanced functionality and efficiency. This integration opens up new avenues for connected devices to interact and collaborate, ultimately leading to a more interconnected and intelligent IoT ecosystem.
What is the difference between VoIP and wireless
VoIP and wireless communication systems are both vital technologies in modern telecommunications. However, they operate on distinct frameworks and serve different applications. Following are the differences between the two:
1/ Base Infrastructure: VoIP relies heavily on a stable internet connection as it utilizes an IP-based network for transmission. In contrast, wireless technology includes various protocols, including cellular networks (such as 4G LTE), which do not necessarily depend on internet connectivity.
2/ Mobility and Range: Wireless systems provide mobility and can operate over larger geographic areas, particularly with cellular networks. On the other hand, VoIP is generally limited by the range of internet access. However, it can still be used on mobile devices connected to wireless networks.
3/ Equipment and Deployment: Deploying VoIP typically requires specific equipment such as IP phones or ATA adapters for older devices, along with a properly configured network infrastructure. In contrast, wireless systems may require a more diverse range of components, ranging from transmitters and receivers to satellites, depending on the specific application.
4/ Quality of Service (QoS): The quality and reliability of VoIP are influenced by bandwidth and internet speed, and can be managed with QoS technologies to prioritize voice traffic on a network. Wireless communication quality, while also affected by bandwidth, can be affected by factors such as signal strength, distance from cell towers, and interference.
5/ Operational Costs: The cost structure for VoIP and wireless systems differs significantly. VoIP can potentially offer more cost-effective solutions, especially for international calls, as it utilizes the internet to bypass traditional telephone networks. On the other hand, wireless communication costs are often tied to service plans, data usage, and roaming charges for mobile devices.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1) Do you need VoIP for Wifi calling?
Ans: No, you do not need a separate VoIP service for Wi-Fi calling. Wi-Fi calling is a feature typically included with your mobile phone service that allows you to make and receive calls over a Wi-Fi network. It’s designed to integrate with your phone’s built-in dialer, without the need for an additional VoIP app.
Q2) Does VoWifi cost money?
Ans: The costs associated with VoWiFi depend largely on the policies of the user’s mobile service provider. Generally, calls made over WiFi do not incur additional charges and are treated the same as traditional cellular calls, deducting from the user’s existing voice plan.
Q3) What is the difference between wifi calling and voice calling?
Ans: Wi-Fi calling and voice calling are two different technologies used for telecommunications. WiFi calling utilizes a wireless internet connection to transmit your call over the internet rather than the traditional cellular networks. This allows for making calls in areas with weak or no cell signal, provided you have access to a stable WiFi network. On the other hand, voice calling generally refers to the conventional method of using a mobile network’s voice service to make phone calls, relying on the signal strength of the mobile network’s cell towers.
Q4) Is VoIP and VoWifi the same?
Ans: The main difference between VoIP and VoWifi is that VoIP is a broad term including any form of voice communication over the internet, enabling voice transmission as data packets through the internet protocol. This technology is not limited to Wi-Fi networks and can function over any internet connection, including wired networks and cellular data services.
On the other hand, VoWiFi refers specifically to voice communication over Wi-Fi networks. It falls under the domain of VoIP technology, providing a similar service but with a primary emphasis on Wi-Fi networks.
Q5) Is Wifi calling the same as Voice over LTE?
Ans: No, Wifi calling and Voice over LTE (VoLTE) are two different technologies for making phone calls. Wifi calling uses a wireless internet connection to place calls, making it a great option in areas with poor cellular reception. In contrast, VoLTE transmits calls over a carrier’s 4G LTE network, providing higher quality voice calls with improved connectivity and the ability to use voice and data simultaneously without relying on a Wifi network.
Related Reading: VoIP Vs VoLTE

