You might be exploring how to streamline your organization’s communication channels or enhance collaboration among teams that are working remotely. Especially when the majority, 83%, of workers favor hybrid work arrangements.
Unified Communication (UC) and Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) Technologies have redefined our communication systems, offering unified, integrated solutions that keep you in touch, no matter where you are.
From voice calls to video conferencing and instant messaging, this guide explores how these technologies are differentiated and can be used to transform the way we communicate within our organization.
Understanding What is VoIP
VoIP, or Voice over Internet Protocol, is a telecommunication technology that transforms how we communicate by turning our standard internet connections into a medium for making phone calls (just like our other calling devices).
Here is how VoIP works when you’re speaking into your phone or computer; VoIP converts your spoken words into a digital signal that travels over the Internet.
If in case you are calling a traditional phone service, this digital signal is reconverted into a standard telephone signal just before it reaches the person you are contacting.
This conversion process enables you to use a regular phone, a computer, or a VoIP phone for the call.
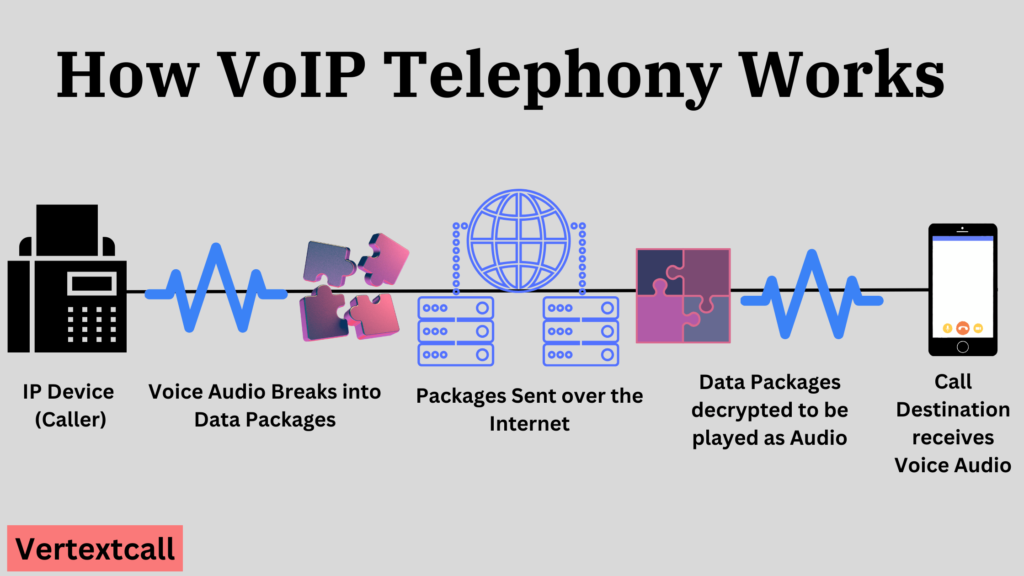
Additionally, VoIP services often come with features that are either unavailable on traditional lines or come at an extra cost, such as caller ID, call waiting, call forwarding, voicemail, and the ability to have conference calls.
What is the meaning of Unified communication?
In simple words, Unified Communications (UC) can be described as an advanced communication system that integrates various communication methods within your business.
This includes not just telephone calls, but also video conferencing, instant messaging, email, and file sharing, all operating together in a single interface or platform.
By combining these different modes of communication into one comprehensive solution, you can improve your operational efficiency, enhance team collaboration, and deliver a superior customer experience within your business.
The main difference between VoIP and unified communication
The following table highlights the fundamental distinctions between VoIP and Unified Communications in terms of their focus, components, functionality, and impact on business operations.
Aspects of Differentiation | Voice over Internet Protocol | Unified Communications (UC) |
Core Functionality | Primarily focuses on transmitting voice over the internet. | Integrates multiple communication forms, including voice, video, messaging, and file sharing. |
Primary Use | Replaces traditional telephony with internet-based calls. | Enhances overall communication across multiple channels and tools. |
Communication Methods | Primarily focused on voice calls. | Supports voice, video, instant messaging, and file sharing. |
Collaboration Capabilities | Supports basic collaboration via voice communication. | Offers extensive collaboration features across different mediums. |
Scalability | Easily scales for voice communication needs. | Provides a comprehensive solution that scales with business growth. |
Flexibility | Primarily offers flexibility in making and receiving calls. | Offers flexibility in communication, collaboration, and integration. |
Cost | Generally more cost-effective for voice communication. | May require a larger initial investment but offers broader capabilities. |
Target Users | Ideal for businesses focused on voice communication. | Suited for enterprises needing a reliable communication ecosystem. |
Advantages of using VoIP
VoIP technology includes several key advantages for businesses aiming to improve their communication systems. Here are some of the key benefits of using it:
1/ Running cost advantage:
Using VoIP services for your organizational communication infrastructure offers a significant reduction in telecommunication costs by up to 50%. Since you’re transitioning from traditional telephony to VoIP, you’re essentially moving from a system that relies on physical phone lines to one that operates over the Internet. This shift not only reduces the cost of making domestic and international calls but also reduces or entirely removes the need for physical hardware and maintenance fees.
2/ Global Connectivity:
VoIP also enables your business to achieve global reach with ease. By integrating voice communication over the Internet, you can connect with colleagues, clients, and partners worldwide without the significant costs traditionally associated with international calling.
3/ Improved Call Quality Explored:
When you switch to VoIP, the improvement in call quality is immediately noticeable. This technology utilizes your existing internet bandwidth, leading to clearer, more reliable voice transmissions than traditional phone lines. This means you will experience fewer dropped calls and a significant reduction in instances of poor connectivity or interference.
4/ Customizability and Control:
With VoIP, you get better control over how your business communications are handled. This technology can be customized to meet the unique requirements and preferences of your phone system. Whether it’s configuring call forwarding options, setting up voicemail to email, or customizing hold music.
5/ Enhanced Security:
Traditional phone lines are open to various kinds of tapping and interception. VoIP, on the other hand, uses advanced encryption protocols to secure your calls. This means that every conversation you have is protected from unauthorized access, ensuring that your business communications remain confidential.
Disadvantages of VoIP calling
1/ Power Outages Impact:
Unlike traditional phone lines that operate during power outages, VoIP requires power for the phones and the internet router to function. In case of a power failure, you lose your ability to communicate, unless you have a backup power solution in place.
2/ Emergency Calls Limitation:
VoIP services can have limitations when it comes to making emergency calls. Especially if you are using a Non-fixed VoIP number since it is not connected to a physical location, it can be difficult for emergency services to pinpoint your exact location during an urgent call.
3/ Issue of Latency and Jitter:
In the context of VoIP calling, Latency, and Jitter are critical concepts to understand for ensuring optimal call quality. Latency in simpler terms, is the delay experienced from the moment a word is spoken while talking on the phone to when the recipient hears it. Jitter, on the other hand, is the variability in packet arrival times. It is a type of disruption in the normal sequence of sending voice packets, which can result in poor audio quality or calls.
4/ Bandwidth Utilization:
VoIP calls consume your internet bandwidth. If your bandwidth is limited, heavy VoIP usage can affect the performance of other online activities, such as email and web browsing.
To know more check out our detailed guide on: Advantages and disadvantages of VoIP phone system
Examples of VoIP applications
Below are examples of popular applications that utilize VoIP to enhance connectivity and streamline communication processes:

Each of these applications offers solutions that range from individual use to enterprise-level functionalities.
Related Reading: Types of VoIP systems
Why use unified communication
Unified Communication (UC) offers many benefits that can enhance the way you connect, collaborate, and operate within your organization. Here’s why you should consider using Unified Communication:
1/ Improved Collaboration:
With UC, your team can utilize shared workspaces, real-time document editing, and project management tools, creating a collaborative environment. This capability ensures that you can work closely with partners, customers, and team members, across different locations, enhancing teamwork and project outcomes.
2/ Increased Flexibility:
Unified Communication solutions are often cloud-based, offering you and your team the ability to communicate and collaborate from any location, and by utilizing any device.
3/ Cost Savings:
By adopting UC, you can significantly reduce the costs associated with maintaining multiple communication platforms and traditional phone systems. Furthermore, the use of VoIP within UC can lower your telephony expenses, particularly for long-distance and international calls.
4/ Improved Customer Experience:
UC enables you to offer more responsive and personalized communication with your customers. Features such as instant messaging and video calls can enhance your customer service, providing timely and effective solutions to their needs.
According to a report, Organizations 97% to be exact, state that remote work has made them more interested in UCaaS & CCaaS.
The 3 main components of unified communication
Unified Communication (UC) integrates multiple communication methods within a business. The main components of Unified Communication include:
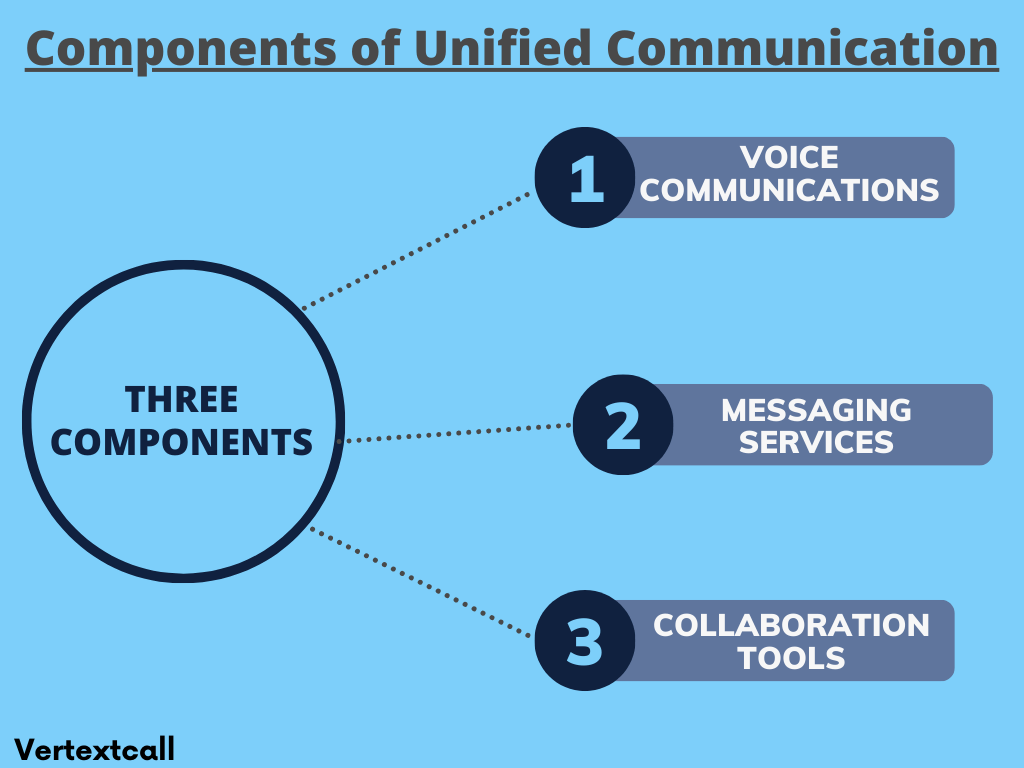
1/ Voice Communications:
This foundational element includes your traditional voice calls, VoIP calls, and video calling. By integrating voice communications into a unified system, you can easily switch between different modes of voice interactions, enhancing your flexibility and efficiency.
2/ Messaging Services:
Messaging services include email, instant messaging (IM), and SMS. This component makes it quick and easy for you to communicate text-based messages across various platforms, ensuring that you and your team members can stay connected and share information rapidly.
3/ Collaboration Tools:
Collaboration tools consist of a range of software and applications designed to support your cooperative work. These tools enable you and your team to work in shared digital spaces, edit documents simultaneously in real time, exchange files, and manage projects efficiently. Combining these tools into a unified communication strategy allows you to develop a more integrated and productive working environment.
What are the channels for unified communication?
Unified Communication (UC) combines various communication channels into a single communication strategy. The primary channels for Unified Communication include:
- Voice Calls: Allowing you to conduct traditional and VoIP voice communications without disruption across devices.
- Video Conferencing: This tool allows participants to engage in real-time, face-to-face conversations, promoting more personal and engaging meetings.
- Email: A fundamental channel for formal and documented communication, ensuring that messages are conveyed clearly and can be easily archived.
- Instant Messaging (IM): Offers real-time text-based communication, ideal for quick queries and discussions.
- Social Media: Many platforms like LinkedIn, Twitter, and Facebook can be synchronized into UC strategies for expanded communication reach.
- File Sharing: Essential for collaboration, allowing you to share documents and other media easily with your team.
- Voicemail: Integrated into your UC system, voicemail ensures you never miss important information, even when you’re unavailable to take a call.
- SMS and MMS: Text and multimedia messaging services are key for concise, direct communication with team members and customers.
- Web Chat: Integrating web chat into your website or customer service platform offers an immediate way for customers to engage with your team.
What is unified communication VoIP?
Unified Communication VoIP is a key component in the current approach to organizational communication, combining traditional telephony and digital technology. This integration is fundamental in a Unified Communication system because it connects the gap between conventional phone systems and the digital communication needs of your business.
As discussed above with Unified Communication VoIP, you have the flexibility to make and receive calls from laptops, smartphones, and tablets, as well as through traditional desk phones that are equipped to connect to the internet.
This adaptability means you can stay connected with your team and clients without being linked to a physical location. For instance, if you’re working from home, you can use your mobile device to answer calls made to your office number, ensuring you remain accessible.
Use Cases
When to Choose VoIP
VoIP is recommended for businesses looking for an entry point into cloud telephony, such as:
- Small to Medium Businesses (SMBs) with basic voice communication needs.
- Businesses Focusing on Cost-Efficient Telephony without the need for expansive UC capabilities.
- Companies with Limited IT Resources looking for a low-barrier, high-impact technology upgrade.
When to Choose Unified Communications
Consider UC for your business needs when diversity in communication methods is a priority:
- Requires a Comprehensive Communication System that aligns with enterprise-wide strategies.
- Has Remote or Globally Distributed Teams, benefiting from a centralized communication platform.
- Aims for Streamlined Collaboration and Productivity to improve competitive advantage.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1) What is the difference between VoIP and UCaaS?
Ans: The main difference between VoIP and UCaaS is the scope of services they offer. VoIP serves as a foundational technology that enables voice-based communication over the internet, effectively transforming the Internet into a platform for phone calls. UCaaS (Unified Communications as a Service), on the other hand, refers to a cloud-delivered service model that integrates various communication methods, including instant messaging, video conferencing, email, and file sharing, into a single, unified platform.
Q2) What is the difference between VoIP and normal calls?
Ans: The main difference between VoIP and normal calls is the technology used to transmit voice data. VoIP converts your voice into a digital signal, allowing it to be sent over the internet, whereas traditional calls utilize the public switched telephone network (PSTN) to transmit analog voice signals.
Q3) Is Zoom unified communication?
Ans: Yes, Zoom can be considered a part of the unified communications system. It is primarily known as a video conferencing service but offers a range of unified communication functionalities. Zoom’s platform integrates video conferencing, messaging, webinars, and even phone services (Zoom Phone), providing a set of tools that support various forms of digital communication.
Q4) What is another name for unified communication?
Ans: Unified Communication (UC) is also commonly referred to as “collaboration software,” or “integrated communications.” These terms highlight the core objective of UC, which is to streamline and integrate various communication tools and channels into a unified system.
Q5) How much does unified communication cost?
Ans: UC solutions are offered through a subscription-based model, with prices ranging from as low as $10 to $20 per user per month for basic packages, to $50 or more per user per month for premium offerings that include advanced features and integrations.

