As businesses increasingly shift from traditional PSTN systems to advanced VoIP technologies, understanding VoIP termination becomes essential.
This blog explores the core elements of VoIP termination, including its types, operational functions, security considerations, regulatory compliance, and the various tiers of providers.
Read further to understand how VoIP termination can enhance your business communication infrastructure and select the best provider to meet your unique needs.
What is VoIP termination?
VoIP termination, also known as call termination, is the process by which a voice call that you initiate through a VoIP system is connected to the recipient’s traditional telephone network. This crucial aspect of VoIP technology ensures that calls you make over the internet can reach landlines or mobile phones perfectly.
Essentially, VoIP termination allows a call originating from a digital format to translate and connect through the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN). This service is provided by VoIP termination providers, who have agreements with carriers to route these calls.
Understanding VoIP termination is essential for you to ensure efficient, reliable, and cost-effective communication both internally and with your clients.
What is VoIP call origination?
While VoIP termination deals with outbound calls, VoIP origination focuses on inbound voice services. With VoIP origination, you get local and toll-free phone numbers, making it easier for you to manage incoming calls.
This service is crucial if your organization requires multiple phone numbers to handle customer queries, support requests, and other communications.
Table of differences between VoIP origination and termination?
Differentiating Aspect | VoIP Origination | VoIP Termination |
Focus | Inbound calls | Outbound calls |
Service Type | Local and toll-free number provisioning | Call routing to final destinations |
Users | Businesses managing incoming communications | Businesses handling high volumes of outbound calls |
Example Applications | Customer support, inbound sales | Telemarketing, call center operations |
Service Types | Local and toll-free number provision | Call routing to landlines and mobile phones |
Target Users | Businesses needing multiple numbers | Businesses needing reliable call delivery |
Components of VoIP termination
VoIP termination involves several components that work together to support the routing and completion of VoIP calls. Here are the key components:
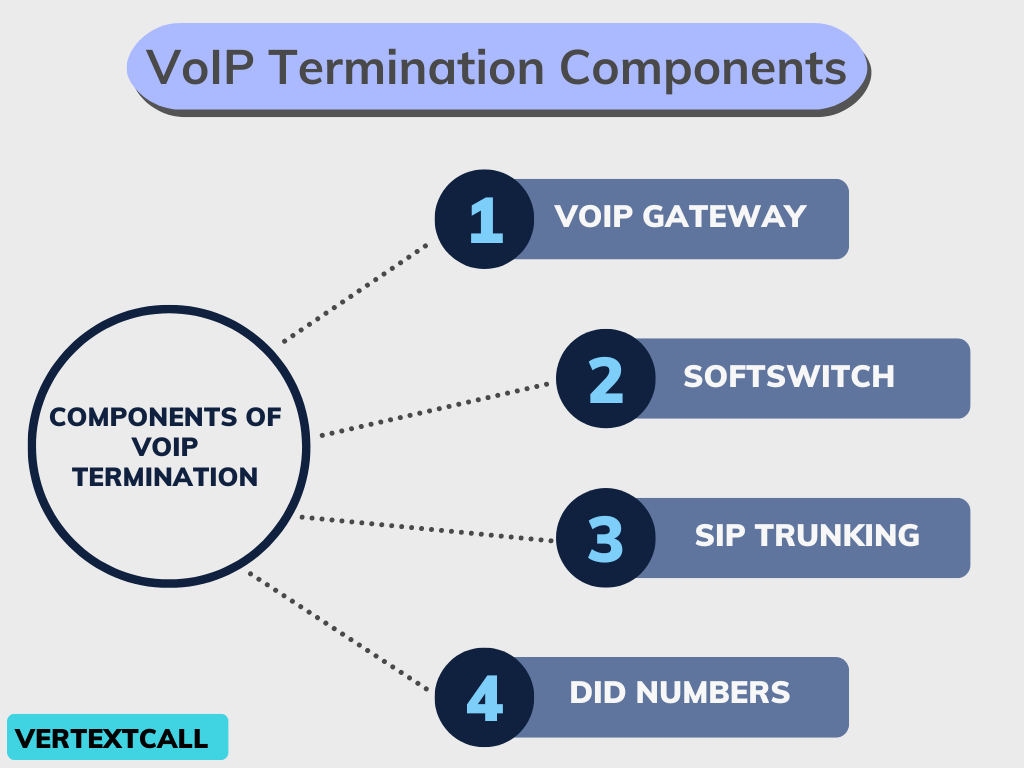
1/ VoIP Gateway:
A VoIP gateway is a critical component in the VoIP termination process. It functions as the link between your VoIP system and the traditional telephone networks.
By converting voice signals from digital packets used in internet communications back into analog signals processed by the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN), the VoIP gateway ensures your voice communications are transmitted clearly and efficiently.
2/ Softswitch:
A softswitch is an integral part of the VoIP termination infrastructure that plays a crucial role in managing and directing voice traffic efficiently.
You can think of a softswitch as the control center of the VoIP network, responsible for routing calls to the appropriate destinations.
Unlike traditional hardware switches, a softswitch uses software to perform switching operations, offering greater flexibility and scalability.
This component ensures that calls are accurately routed through various networks, thereby supporting unbroken connectivity between different communication protocols and systems.
3/ SIP Trunking:
The SIP trunking component enables voice communication over the internet, offering a cost-efficient and scalable substitute for conventional phone lines.
By using the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP), it links your private branch exchange (PBX) to the internet, enabling efficient voice call routing. This means you can route multiple voice calls simultaneously through a single data connection, significantly reducing costs.
Related Reading: SIP and VoIP difference
4/ DID Numbers:
Direct Inward Dialing (DID) numbers are another crucial component you should be aware of in the VoIP termination process.
DID numbers allow your business to allocate individual phone numbers to specific extensions within your private branch exchange (PBX) system.
This means that instead of having just one main phone number for your company, you can provide direct numbers to each department or employee.
Related Reading: PBX phone system vs VoIP
How does VoIP termination work
Here’s a step-by-step explanation of how VoIP termination works:
- Initiating a Call from a VoIP Endpoint: The process begins when a call is initiated from a VoIP-enabled device, such as a VoIP phone or softphone.
- Routing the Call through the VoIP Network: The call is then routed through the VoIP network using a series of softswitches and gateways.
- Handing Off the Call to the PSTN or Another VoIP Network: If the call needs to reach a traditional phone line, it is handed off to the PSTN. Alternatively, it may be routed to another VoIP network for termination.
- Completion of the Call to the Destination Phone Number: The call is finally delivered to the recipient’s phone, completing the VoIP termination process.
Types of VoIP termination
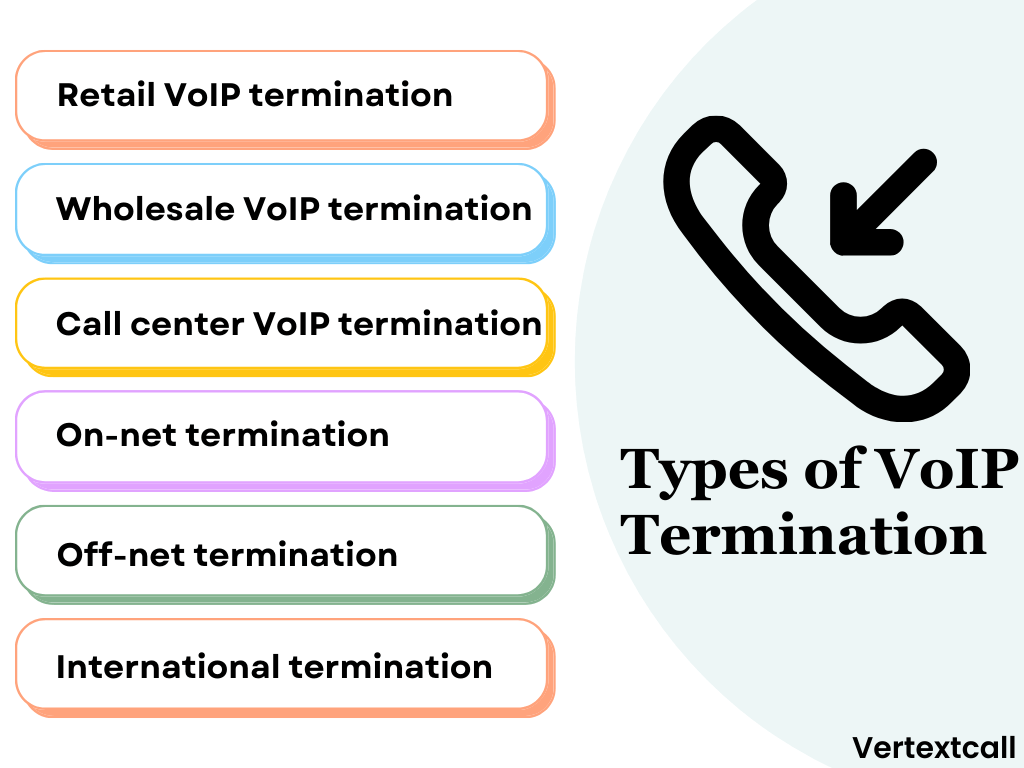
1/ Retail VoIP termination:
Retail VoIP Termination is designed with end customers in mind. Users receive VoIP services directly from a provider, including features such as call forwarding, voicemail, and caller ID, similar to traditional phone services.
Moreover, this service allows for international calls at reduced rates, enhancing both personal and business communications.
2/ Wholesale VoIP termination:
Wholesale VoIP Termination focuses on the needs of other VoIP service providers by delivering large-scale voice communication capabilities, instead of targeting individual end-users.
This type of termination is typically utilized by businesses requiring high call routing and management volumes. Wholesale VoIP providers supply the necessary infrastructure and bandwidth to support extensive voice traffic, enabling connectivity between various VoIP networks and the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN).
These providers usually operate with multiple Points of Presence (PoPs) worldwide, ensuring backup and reliable call quality.
3/ Call center VoIP termination:
Call Center VoIP Termination is specifically customized for call centers that manage a high volume of inbound and outbound calls.
This type of termination provides scalable solutions to handle extensive call traffic while maintaining high call quality and reliability.
Call centers benefit from features like automatic call recording, predictive dialing, and virtual agent support, which optimize workflow and enhance customer service efficiency.
Related Reading: Call center VoIP solutions
4/ On-net termination:
On-net Termination refers to the process of maintaining VoIP calls within the same network from start to finish, without passing through the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN). This type of termination is typically used when the caller and recipient use the same VoIP service provider.
By keeping the communication entirely within a single network, on-net termination can offer several advantages, including reduced latency, higher call quality, and lower overall costs. Additionally, this method ensures more secure calls as the data does not cross multiple networks.
5/ Off-net termination:
Off-net Termination occurs when VoIP calls are routed through external networks, such as the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN), at any point during their transmission.
In other words, off-net termination happens when the call transitions from the originating VoIP network to another network to complete the call to the recipient.
This type of termination is often necessary when the caller and recipient are on different service providers or when the recipient is using a traditional telephone line rather than a VoIP service.
6/ International termination:
International Termination involves routing VoIP calls from one country to another, ensuring that communication can occur across international borders.
This type of termination is essential if your business frequently communicates with foreign parties. By utilizing advanced VoIP infrastructure and partnerships with international carriers, service providers can deliver high-quality, reliable voice connections globally.
Benefits of VoIP termination
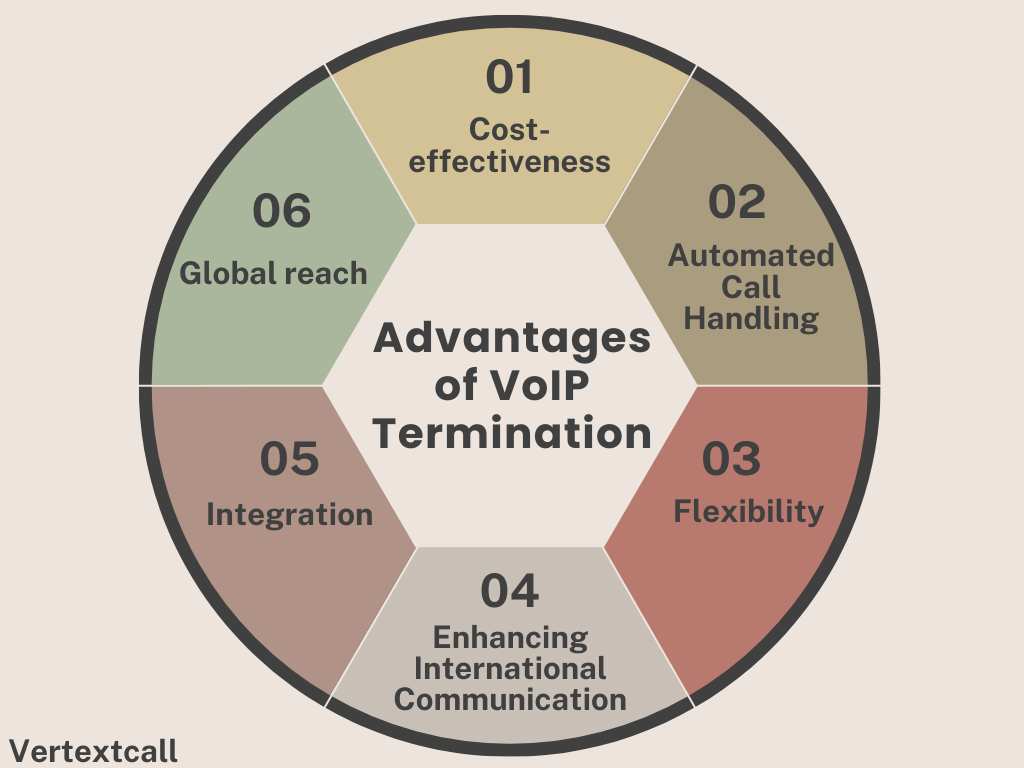
1/ Cost-effectiveness:
One of the principal benefits of VoIP Termination is its ability to significantly reduce your communication costs. By making use of the internet to route calls, you can avoid traditional telephone charges, which are often higher.
This is particularly advantageous for international calls, where VoIP termination can dramatically lower your expenses by utilizing least-cost routing techniques to find the most economical path for each call.
2/ Automated Call Handling:
Automating your call-handling processes within VoIP termination optimizes efficiency and reduces manual intervention. With advanced algorithms and AI-based systems, you can streamline call routing, improve response times, and enhance overall productivity.
Automated workflows can manage tasks such as call set-up, real-time monitoring, and analytics, ensuring an uninterrupted communication experience.
3/ Flexibility:
Flexibility is another significant benefit of VoIP Termination, offering you adaptable communication solutions to meet various business needs.
VoIP Termination allows you to easily manage and modify your communication settings, whether you require additional features, need to adjust call routing, or want to implement specific call handling rules.
Additionally, it supports various features like call routing, call forwarding, and conference calling, providing greater operational flexibility.
4/ Global reach:
By using this technology, your business can effectively broaden its market reach and establish a presence in different countries.
VoIP Termination also allows you to provide local phone numbers for various regions, which can make your business appear more accessible and credible to international customers.
5/ Integration:
By incorporating VoIP Termination into your existing IT infrastructure, you can streamline various communication processes and tools.
This technology supports the integration of multiple communication platforms such as emails, instant messaging, CRM systems, and customer support tools, enabling you to manage all your communications from a single interface.
6/ Enhancing International Communication:
VoIP termination ensures that calls made internationally maintain a high level of audio quality, outperforming traditional phone systems that often suffer from connectivity issues and loss in sound clarity.
This is particularly beneficial for multinational businesses that rely on clear audio to support effective communication between teams, clients, and stakeholders located in different regions.
Through advanced codec technologies and reliable network infrastructure, VoIP termination minimizes latency, jitter, and packet loss, thereby delivering an unaffected communication experience.
Challenges and Considerations
Here are some of the key challenges and considerations of VoIP termination:
1/ Quality of Service (QoS):
Quality of Service (QoS) is a critical consideration when implementing VoIP Termination, as it directly impacts the reliability and clarity of your voice communications.
QoS refers to the performance level of your VoIP service, including various metrics such as latency, jitter, and packet loss.
Ensuring high QoS means your voice data packets are prioritized over other types of data on your network, which helps minimize delays and interruptions during calls.
Challenges related to QoS can arise from insufficient bandwidth, network congestion, or inadequate equipment.
2/ Security:
Security is another essential aspect to consider when deploying VoIP Termination, as it ensures the protection of your voice communications against various threats, including VoIP security issues.
Implementing strong security measures helps secure your VoIP system from potential attacks such as unauthorized access, call interception, and service disruption.
Key strategies to enhance VoIP security include using encryption protocols to protect the data transmitted over the network, implementing firewall and intrusion detection systems to monitor and block suspicious activities, and regularly updating your systems to fix any vulnerabilities.
3/ Regulatory Compliance:
To ensure that your business communication systems comply with legal and industry standards, it is necessary to prioritize regulatory compliance within your VoIP Termination setup.
Adhering to these regulations protects your company from legal consequences and potential fines. VoIP compliance often involves a range of requirements such as data protection, emergency call capabilities, and lawful intercept capabilities.
Make sure that your VoIP provider complies with the relevant regulations in your industry and geography.
4/ Interoperability:
Interoperability ensures that your VoIP systems can integrate and operate with a variety of other communication technologies and platforms.
This capability is vital for maintaining clear communication, both within your organization and in interactions with external partners.
Best VoIP termination providers
VoIP termination providers are typically categorized into three tiers based on their service scope, infrastructure, and pricing models. Understanding these tiers can help your business select the most appropriate provider for their needs.
Tier 1 Providers:
- Characteristics: Tier 1 providers own and operate their extensive networks, offering services directly to other providers and large enterprises.
- Infrastructure: They maintain large-scale, global infrastructure designed to efficiently manage substantial traffic loads.
- Examples: These include major telecom operators such as AT&T, Verizon, and BT, which possess strong global networks.
- Advantages: Provide the highest call quality and reliability due to direct control over their infrastructure.
Tier 2 Providers:
- Characteristics: Tier 2 providers often purchase services from Tier 1 providers and resell them, sometimes adding value through additional features or regional focus.
- Infrastructure: They may own partial infrastructure but largely depend on Tier 1 networks for broader connectivity.
- Examples: Companies like Bandwidth and Twilio often fall into this category.
- Advantages: Offer a balance between cost and quality, typically providing good reliability and customer support.
Tier 3 Providers:
- Characteristics: These providers purchase services from Tier 2 carriers and focus on niche markets or offer highly competitive pricing.
- Infrastructure: They do not own extensive networks and rely heavily on upstream providers for connectivity.
- Examples: Smaller VoIP firms and regional providers.
- Advantages: Offer the most cost-effective solutions, making them ideal for businesses with tight budgets or specific regional needs.
Factors to consider when choosing a VoIP termination provider.
1/ Cost and Value:
When choosing a VoIP termination provider, it’s essential to consider not just the cost per call, but also the value offered for that cost. Consider additional features like call analytics, support services, and the quality of routes used.
2/ Infrastructure and Network:
You must evaluate the provider’s infrastructure and network capabilities. Ensure that the provider has a strong network to guarantee reliable service. Look for geo-redundant infrastructure that can offer backup options in case of network outages or technical issues. Evaluate their network’s quality and coverage to confirm they can deliver clear, uninterrupted calls.
3/ Access and Controls:
The provider should offer a user-friendly interface that allows you to manage and monitor your call activities efficiently. You should be able to configure settings, review call logs, and troubleshoot issues through a centralized control panel. Additionally, check if the provider supports advanced administrative controls, such as role-based access and permissions, so you can delegate responsibilities appropriately within your team.
4/ Availability:
When selecting a VoIP termination provider, you must also consider the availability of their services. You need to ensure that the provider offers high uptime is essential, and this should ideally be backed by a Service Level Agreement (SLA) that guarantees a minimum of 99.99% availability.
This is crucial to avoid disruptions in your communication, which could impact your business continuity and operation Additionally, it is important to check if the provider has a support team available 24/7 to assist with any issues that may arise.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1) What type of termination for voice applications?
Ans: The best type of termination for voice applications is VoIP termination. VoIP termination routes voice traffic over the internet, offering benefits such as reduced expenses, the ability to scale operations, and enhanced call quality. It allows for efficient integration with other digital communication tools, providing businesses with a flexible solution.
Q2) What does it mean if your call is terminated?
Ans: When your call is terminated, it means that the call has been successfully routed to its intended recipient or endpoint. Call termination refers to the process where a voice call, originating from one telephony network, is delivered to its destination network, which could be a different country, a different provider, or a mobile network.
Q3) What does termination mean in VoIP?
Ans: In VoIP, termination refers to the process by which a VoIP call is delivered from its origin to its final destination. This involves routing voice traffic over the internet and integrating with multiple networks, such as Public Switched Telephone Networks (PSTN) or mobile networks, to ensure the call reaches the intended recipient.
Q4) What is VoIP inbound local origination?
Ans: VoIP inbound local origination refers to the process by which incoming voice calls are delivered to a VoIP network from a traditional telephony network, such as PSTN or mobile networks, originating from local phone numbers. This allows businesses to have local phone numbers in various geographic locations, enabling customer accessibility and reducing communication costs.
Q5) How do I trace the origin of a VoIP call?
Ans: To trace a VoIP call, you can start by reviewing the call logs provided by your VoIP service provider, which often include the originating IP address and call timestamps. Additionally, a detailed call detail record (CDR) from your provider may offer further insights into the call path. For a more in-depth trace, network administrators can utilize tools that analyze SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) packets to uncover the source IP address.
Q6) What is A-Z termination in VoIP?
Ans: A-Z termination in VoIP refers to the comprehensive routing of voice traffic to destinations worldwide, covering all possible termination points from A to Z. This term is often used by VoIP service providers to indicate their ability to handle calls to any country or region, offering a complete range of international call termination services. A-Z termination typically ensures high-quality connections, competitive rates, and expansive coverage, making it a valuable solution for businesses with global communication needs.
Q7) What type of VoIP protocol is responsible for terminating a call when one of the partners hangs up?
Ans: The VoIP protocol responsible for terminating a call when one of the partners hangs up is typically the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP). SIP is a signaling protocol used to initiate, manage, and terminate voice and video calls over IP networks. When one of the call participants hangs up, a SIP BYE request is sent from the endpoint of the participant who terminates the call to the other endpoint. Upon receiving the BYE request, the other endpoint acknowledges it with a 200 OK response, thereby closing the session and effectively terminating the call.

